
Streaming current
Encyclopedia
A streaming current and streaming potential are two interrelated electrokinetic phenomena
studied in the areas of surface chemistry and electrochemistry
. They are an electric current
or potential
which originates when an electrolyte
is driven by a pressure gradient through a channel or porous plug with charged walls.
The first observation of the streaming potential is generally attributed to the German physicist Georg Hermann Quincke
in 1859.
of surfaces, which is important in the fields of colloid
and interface science
. In geology, measurements of related spontaneous potential
are used for evaluations of formations. Streaming potential has to be considered in design for flow of poorly conductive fluids (e.g., gasoline lines) because of the danger of buildup of high voltages. They could in principle be used to generate electrical power
, however this process has not been applied so far because of its low efficiency
.
s attracted by the charged surface.
The transport of counterions along with the pressure-driven fluid flow gives rise to a net charge transport: the streaming current. The reverse effect, generating a fluid flow by applying a potential difference, is called electroosmotic flow.
s placed on either side of a fluidic geometry across which a known pressure difference is applied. When both electrodes are held at the same potential, the streaming current is measured directly as the electric current flowing through the electrodes. Alternatively, the electrodes can be left floating, allowing a streaming potential to build up between the two ends of the channel.
A streaming potential is defined as positive when the electric potential is higher on the high pressure end of the flow system that on the low pressure end.
The value of streaming current observed in a capillary
is usually related to the zeta potential
through the relation:
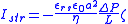 .
.
The conduction current, which is equal in magnitude to the streaming current at steady state, is:
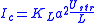
At steady state, the streaming potential built up across the flow system is given by:
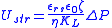
Symbols:
The equation above is usually referred to as the Helmholtz-Smoluchowski equation.
The above equations assume that:
Electrokinetic phenomena
Electrokinetic phenomena are a family of several different effects that occur in heterogeneous fluids or in porous bodies filled with fluid. The term heterogeneous here means a fluid containing particles...
studied in the areas of surface chemistry and electrochemistry
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place in a solution at the interface of an electron conductor and an ionic conductor , and which involve electron transfer between the electrode and the electrolyte or species in solution.If a chemical reaction is...
. They are an electric current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
or potential
Electric potential
In classical electromagnetism, the electric potential at a point within a defined space is equal to the electric potential energy at that location divided by the charge there...
which originates when an electrolyte
Electrolyte
In chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible....
is driven by a pressure gradient through a channel or porous plug with charged walls.
The first observation of the streaming potential is generally attributed to the German physicist Georg Hermann Quincke
Georg Hermann Quincke
Georg Quincke|thumbGeorg Hermann Quincke was a German physicist.Born at Frankfurt , Quincke was the son of prominent physician Geheimer Medicinal-Rath Hermann Quincke and the older brother of physician Heinrich Quincke.Quincke received his Ph. D. in 1858 at Berlin, having previously studied also...
in 1859.
Applications
Streaming currents in well-defined geometries are a sensitive method to characterize the zeta potentialZeta potential
Zeta potential is a scientific term for electrokinetic potential in colloidal systems. In the colloidal chemistry literature, it is usually denoted using the Greek letter zeta, hence ζ-potential...
of surfaces, which is important in the fields of colloid
Colloid
A colloid is a substance microscopically dispersed evenly throughout another substance.A colloidal system consists of two separate phases: a dispersed phase and a continuous phase . A colloidal system may be solid, liquid, or gaseous.Many familiar substances are colloids, as shown in the chart below...
and interface science
Interface (chemistry)
An interface is a surface forming a common boundary among two different phases, such as an insoluble solid and a liquid, two immiscible liquids or a liquid and an insoluble gas. The importance of the interface depends on which type of system is being treated: the bigger the quotient area/volume,...
. In geology, measurements of related spontaneous potential
Spontaneous potential
Spontaneous potential , also called self potential, is a naturally occurring electric potential difference in the Earth, measured by an electrode relative to a fixed reference electrode...
are used for evaluations of formations. Streaming potential has to be considered in design for flow of poorly conductive fluids (e.g., gasoline lines) because of the danger of buildup of high voltages. They could in principle be used to generate electrical power
Electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.-Circuits:Electric power, like mechanical power, is represented by the letter P in electrical equations...
, however this process has not been applied so far because of its low efficiency
Energy conversion efficiency
Energy conversion efficiency is the ratio between the useful output of an energy conversion machine and the input, in energy terms. The useful output may be electric power, mechanical work, or heat.-Overview:...
.
Origin of the streaming current
Adjacent to the channel walls, the charge-neutrality of the liquid is violated due to the presence of the electrical double layer: a thin layer of counterionCounterion
A counterion is the ion that accompanies an ionic species in order to maintain electric neutrality. In table salt the sodium cation is the counterion for the chlorine anion and vice versa.In a charged transition metal complex, a simple A counterion is the ion that accompanies an ionic species in...
s attracted by the charged surface.
The transport of counterions along with the pressure-driven fluid flow gives rise to a net charge transport: the streaming current. The reverse effect, generating a fluid flow by applying a potential difference, is called electroosmotic flow.
Measurement method
A typical setup to measure streaming currents consists of two reversible electrodeElectrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
s placed on either side of a fluidic geometry across which a known pressure difference is applied. When both electrodes are held at the same potential, the streaming current is measured directly as the electric current flowing through the electrodes. Alternatively, the electrodes can be left floating, allowing a streaming potential to build up between the two ends of the channel.
A streaming potential is defined as positive when the electric potential is higher on the high pressure end of the flow system that on the low pressure end.
The value of streaming current observed in a capillary
Capillary
Capillaries are the smallest of a body's blood vessels and are parts of the microcirculation. They are only 1 cell thick. These microvessels, measuring 5-10 μm in diameter, connect arterioles and venules, and enable the exchange of water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and many other nutrient and waste...
is usually related to the zeta potential
Zeta potential
Zeta potential is a scientific term for electrokinetic potential in colloidal systems. In the colloidal chemistry literature, it is usually denoted using the Greek letter zeta, hence ζ-potential...
through the relation:
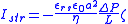 .
.The conduction current, which is equal in magnitude to the streaming current at steady state, is:
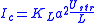
At steady state, the streaming potential built up across the flow system is given by:
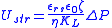
Symbols:
- Istr - streaming current under short-circuit conditions, A
- Ustr - streaming potential at zero net current conditions, V
- Ic - conduction current, A
- εrs - relative permittivity of the liquid, dimensionless
- ε0 - electrical permittivityPermittivityIn electromagnetism, absolute permittivity is the measure of the resistance that is encountered when forming an electric field in a medium. In other words, permittivity is a measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium. The permittivity of a medium describes how...
of vacuum, F·m−1 - η - dynamic viscosityViscosityViscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
of the liquid, kg·m−1·s−1 - ζ - zeta potential, V
- ΔP - pressure difference, Pa
- L - capillary length, m
- a - capillary radius, m
- KL - specific conductivity of the bulk liquid, S·m−1
The equation above is usually referred to as the Helmholtz-Smoluchowski equation.
The above equations assume that:
- the double layer is not too large compared to the pores or capillaries (i.e.,
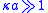 ), where κ is the reciprocal of the Debye lengthDebye lengthIn plasma physics, the Debye length , named after the Dutch physicist and physical chemist Peter Debye, is the scale over which mobile charge carriers screen out electric fields in plasmas and other conductors. In other words, the Debye length is the distance over which significant charge...
), where κ is the reciprocal of the Debye lengthDebye lengthIn plasma physics, the Debye length , named after the Dutch physicist and physical chemist Peter Debye, is the scale over which mobile charge carriers screen out electric fields in plasmas and other conductors. In other words, the Debye length is the distance over which significant charge... - there is no surface conduction (which typically may become important when the zeta potential is large, e.g., |ζ| > 50 mV)
- there is no electrical double layer polarization
- the surface is homogeneous in properties
- there is not axial concentration gradient
- the geometry is that of a capillary/tube.
Literature
- J. Lyklema, Fundamentals of Interface and Colloid Science
- F.H.J. van der Heyden et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 116104 (2005)
- C. Werner et al., J. Colloid Interface Sci. 208, 329 (1998)

