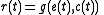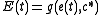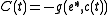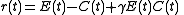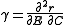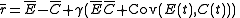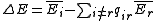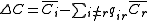Storage effect
Encyclopedia
The storage effect is a coexistence mechanism proposed in the ecological theory of species
coexistence, which tries to explain how such a wide variety of similar species are able to coexist within the same ecological community or guild
. The storage effect was originally proposed in the 1980s to explain coexistence in diverse communities of coral reef fish, however it has since been generalized to cover a variety of ecological communities. The theory proposes one way for multiple species to coexist: in a changing environment, no species can be the best under all conditions. Instead, each species must have a unique response to varying environmental conditions, and a way of buffering against the effects of bad years. The storage effect gets its name because each population “stores” the gains in good years or microhabitats (patches) to help it survive population losses in bad years or patches. One strength of this theory is that, unlike most coexistence mechanisms, the storage effect can be measured and quantified, with units of per-capita growth rate (offspring per adult per generation).
The storage effect can be caused by both temporal and spatial variation. The temporal storage effect (often referred to as simply “the storage effect”) occurs when species benefit from changes in year-to-year environmental patterns, while the spatial storage effect occurs when species benefit from variation in microhabitats across a landscape.
rate of species from year to year (or patch to patch).
For competing species within the same community to coexist, they have to meet one fundamental requirement: the impact of competition from a species on itself must exceed its competitive impact on other species. In other words, intraspecific competition
must exceed interspecific competition
. For example, jackrabbits living in the same area compete for food and nesting grounds. Such competition within the same species is called intraspecific competition
, which limits the growth of the species itself. Members from different species can also compete. For instance, jackrabbits and cottontail rabbits also compete for food and nesting grounds. Competition between different species is called interspecific competition
, which limits the growth of other species. Stable coexistence occurs when any one species in the community limits its own growth more strongly than the growth of others.
The storage effect mixes three essential ingredients to assemble a community of competing species that fulfill the requirement. They are 1) correlation between the quality of an environment and the amount of competition experienced by a population in that environment (i.e. covariance
between environment and competition), 2) differences in species response to the same environment (i.e. species-specific environmental responses), and 3) the ability of a population to diminish the impact of competition under worsening environment (i.e. buffered population growth). Below we describe each ingredient in detail and explain why the combination of the three leads to species coexistence.
and mutualists. Usually organisms reproduce more in a favorable environment (i.e. either during a good year, or within a good patch), build up their population densities, and lead themselves to a high level of competition
due to this increasing crowding. Such a trend means that higher quality environments usually correlate with a higher strength of competition experienced by the organisms in those environments. In short, a better environment results in stronger competition. In statistics, such correlation
means that there will be a non-zero covariance
between the change of population density in response to the environment and that to the competition. That is why the first ingredient is called “covariance
between environment and competition”.
under their optimal environmental conditions because their populations grow most rapidly in those conditions. In nature, we often find that different species from the same community respond to the same conditions in distinctive manners. For example, plant species have different preferred levels of light and water availability, which affect their germination and physical growth rates. Such differences in their response to the environment, which is called “species-specific environmental response,” means no two species from a community will have the same best environment in a given year or a given patch. As a result, when a species is under its optimal environmental conditions and thus experiencing the strongest intraspecific competition
, other species from the same community only experience the strongest interspecific competition
coming from that species, but not the strongest intraspecific competition
coming from themselves.
) or when adults have a high mortality rate (such as many aquatic insects, or some populations of the Eastern Fence Lizard
), buffered growth does not occur. Under the spatial storage effect, buffered population growth is generally automatic, because the effects of a detrimental microhabitat will only be experienced by individuals in that area, rather than the population as a whole.
between environment and competition, and (2) species-specific response to the environment decouple the strongest intraspecific and interspecific competition experienced by a species. Intraspecific competition
is strongest when a species is favored by the environment, whereas interspecific competition
is strongest when its rivals are favored. After this decoupling, buffered population growth limits the impact of interspecific competition
when a species is not favored by the environment. As a consequence, the impact of intraspecific competition
on the species favored by a particular environment exceeds that of the interspecific competition
on species less favored by that environment. We see that the fundamental requirement for species coexistence is fulfilled and thus storage effect is able to maintain stable coexistence in a community of competing species.
For species to coexist in a community, all species must be able to recover from low density. Not surprisingly, being a coexistence mechanism, the storage effect helps species when they become rare. It does so by making the abundant species’ effect on itself greater than its effect on the rare species. The difference between species’ response to environmental conditions means that a rare species’ optimal environment is not the same as its competitors. Under these conditions, the rare species will experience low levels of interspecific competition
. Because the rare species itself is rare, it will experience little impact from intraspecific competition
as well, even at its highest possible levels of intraspecific competition. Free from the impact of competition, the rare species is able to make gains in these good years or patches. Moreover, thanks to the buffered population growth, the rare species is able to survive the bad years or patches by “storing” the gains from the good years/patches. As a result, the population of any rare species is able to grow due to the storage effect.
One natural outcome from the covariance
between environment and competition is that the species with very low densities will have more fluctuation in its recruitment
rates than species with normal densities. This occurs because in good environments, species with high densities will often experience large amount of crowding by members of the same species, thus limiting the benefits of good years/patches, and making good years/patches more similar to bad years/patches. Low-density species are rarely able to cause crowding, thus allowing significantly increased fitness in good years/patches. Since the fluctuation in recruitment
rate is an indicator of covariance between environment and competition, and since species-specific environmental response and buffered population growth can normally be assumed in nature, finding much stronger fluctuation in recruitment
rates in rare and low-density species provides a strong indication that the storage effect is operating within a community.
The fitness
of an individual, as well as expected growth rate
, can be measured in terms of the average number of offspring it will leave during its lifetime. This parameter, r(t), is a function of both environmental factors, e(t), and how much the organism must compete
with other individuals (both of its own species, and different species), c(t). Thus,
where g is an arbitrary function for growth rate. During this article, we will at times use subscripts to represent functions of a particular species (e.g. r j(t) is the fitness of species j). It is assumed that there must be some values e* and c*, such that g(e*, c*) = 0, representing a zero-population growth equilibrium. These values need not be unique, but for every e*, there is a unique c*. For ease of calculation, we define standard parameters E(t) and C(t), such that
Both E and C represent the effect of deviations in environmental response from equilibrium. E represents the effect that varying environmental conditions (e.g. rainfall patterns, temperature, food availability, etc.) have on fitness, in the absence of abnormal competitive effects. For the storage effect to occur, the environmental response for each species must be unique (i.e. E j(t) ≠ E i(t) when j ≠ i). C(t) represents how much average fitness is lowered as a result of competition
. For example, if there is more rain during a given year, E(t) will likely increase. If more plants begin to bloom, and thus compete for that rain, then C(t) will increase as well. Because e* and c* are not unique, E(t) and C(t) are not unique, and thus one should choose them as conveniently as possible. Under most conditions (see Chesson 1994), r(t) can be approximated as
where
γ represents the nonadditivity of growth rates. If γ = 0 (known as additivity
) it means that the impact of competition on fitness does not change with the environment. If γ > 0 (superadditivity), it means that the adverse effects of competition during a bad year are relatively worse than during a good year. In other words, a population suffers more from competition in bad years than in good years. If γ < 0 (subadditivity, or buffered population growth), it means that the harm done by competition during a bad year is relatively minor when compared to a good year. In other words, the population is able to diminish the impact of competition as the environment worsens. As stated above, for the storage effect to contribute to species coexistence, we must have buffered population growth (i.e. it must be the case that γ < 0).
The long-term average of the above equation is
which, under environments with sufficient variation relative to mean effects, can be approximated as
For any effect to act as a coexistence mechanism, it must boost the average fitness of an individual when they are at below-normal population density. Otherwise, a species at low density (known as an `invader') will continue to dwindle, and this negative feedback will cause its extinction. When a species is at equilibrium (known as a `resident'), its average long-term fitness must be 0. For a species to recover from low density, its average fitness must be greater than 0. For the remainder of the text, we refer to functions of the invader with the subscript i, and to the resident with the subscript r.
A long-term average growth rate of an invader is often written as
where,
and, ΔI, the storage effect,
where
In this equation, qir tells us how much the competition experienced by r affects the competition experienced by i.
We can see the biological meaning of the storage effect expressed in the mathematical form of ΔI. The first term of the expression is covariance
between environment and competition (Cov(E C)), scaled by a factor representing buffered population growth (γ). The difference between the first term and the second term represents the difference in species responses to the environment between the invader and the sum of the residents, scaled by the effect each resident has on the invader (qir).
Second, they found that under positive frequency dependent predation, predators can promote coexistence. Positive frequency dependent predation (also known as “prey switching
”) occurs when predators are more likely to attack a particular prey when they are common. When this occurs, death from predation most often befalls dominant species, and individuals from rare species are much more likely to survive and increase in number. When predators become specialized enough, this can promote coexistence, compensating for or even surpassing the weakening of the storage effect. Additionally, if predators are able to quickly respond to the new prey densities, this can generate a storage effect from predation.
s. They experimentally manipulated density and water availability over a two-year period, and found that fitness
and germination
rates varied greatly from year to year, and over different environmental conditions. This shows that each species has a unique environmental response, and implied that likely there is a covariance
between environment and competition. This, combined with the buffered population growth that is a product of a long-lived seed bank
, showed that a temporal storage effect was probably an important factor in mediating coexistence. This study was also important, because it showed that variation in germination
conditions could be a major factor promoting species coexitstence.
The first attempt made at quantifying the temporal storage effect was by Cáceres in 1997. Using 30 years of water-column data from Oneida Lake
, New York, she studied the effect the storage effect had on two species of plankton
(Daphnia galeata mendotae
and D. pulicaria). These species of plankton lay diapausing
eggs which, much like the seeds of annual plants, lay dormant in the sediment for many years before hatching. Cáceres found that the size of reproductive bouts were fairly uncorrelated between the two species. She also found, in the absence of the storage effect, D. galeata mendotae would have gone extinct. She was unable to measure certain important parameters (such as the rate of egg predation), but found that her results were robust to a wide range of estimates.
The first test of the spatial storage effect was done by Sears and Chesson in the desert area east of Portal, Arizona. Using a common neighbor-removal experiment, they examined whether coexistence between two annual plants, Erodium cicutarium
and Phacelia popeii, was due to the spatial storage effect or resource partitioning. The storage effect was quantified in terms of number of inflorescences (a proxy for fitness) instead of actual population growth rate. They found that E. cicutarium was able to outcompete P. popeii in many situations, and in the absence of the storage effect, would likely competitively exclude P. popeii. However, they found a very strong difference in the covariance
between environment and competition, which showed that some of the most favorable areas for P. popeii (the rare species), were unfavorable to E. cicutarium (the common species). This suggests that P. popeii is able to avoid strong interspecific competition
in some good patches, and that this may be enough to compensate for losses in areas favorable to E. cicutarium.
Colleen Kelly and colleagues examined the population size distribution of 12 species of trees coexisting in a tropical deciduous forest at the Chamela Biological Station in Jalisco
, Mexico. They identified individuals of 12 tree species and grouped them by age (assumed to be a function of size). They found that recruitment
of young trees varies from year to year. They also found that within each genus, the locally rarer species unanimously had a more irregular age distributions than the more common species. This finding strongly suggests that between closely competing tree species the rare ones experience stronger recruitment
fluctuation than the common ones. Such difference in recruitment
fluctuation indicates a difference in covariance
between the environment and competition between rare and common species. Since species-specific environmental response and buffered population growth can be naturally assumed, their finding strongly suggests that the storage effect operates in this tropical deciduous forest so as to maintain the coexistence between different tree species.
Angert and colleagues demonstrated the temporal storage effect occurring in the desert annual plant community on Tumamoc Hill
, Arizona. Previous studies had shown the annual plant
s in that community exhibited a trade-off between growth rate (a proxy for competitive ability) and water use efficiency (a proxy for drought tolerance). As a result, some plants grew better during wet years, while others grew better during dry years. This, combined with variation in germination
rates, produced an overall community average storage effect of 0.103. In other words, the storage effect is expected to help the population of any species at low density to increase, on average, by 10.3% each generation, until it recovers from low density.
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
coexistence, which tries to explain how such a wide variety of similar species are able to coexist within the same ecological community or guild
Guild (ecology)
A guild is any group of species that exploit the same resources, often in related ways. As can be seen from the list of examples below, it does not follow that the species within a guild occupy the same, or even similar, ecological niches...
. The storage effect was originally proposed in the 1980s to explain coexistence in diverse communities of coral reef fish, however it has since been generalized to cover a variety of ecological communities. The theory proposes one way for multiple species to coexist: in a changing environment, no species can be the best under all conditions. Instead, each species must have a unique response to varying environmental conditions, and a way of buffering against the effects of bad years. The storage effect gets its name because each population “stores” the gains in good years or microhabitats (patches) to help it survive population losses in bad years or patches. One strength of this theory is that, unlike most coexistence mechanisms, the storage effect can be measured and quantified, with units of per-capita growth rate (offspring per adult per generation).
The storage effect can be caused by both temporal and spatial variation. The temporal storage effect (often referred to as simply “the storage effect”) occurs when species benefit from changes in year-to-year environmental patterns, while the spatial storage effect occurs when species benefit from variation in microhabitats across a landscape.
The concept
For the storage effect to operate, it requires variation (i.e. fluctuations) in the environment and thus can be termed a “fluctuation-dependent mechanism”. This variation can come from a large degree of factors, including resource availability, temperature, and predation levels. However, for the storage effect to function, this variation must change the birth, survival, or recruitmentRecruitment (biology)
In biology, recruitment occurs when juvenile organisms survive to be added to a population. The term is generally used to refer to a stage whereby the organisms are settled and able to be detected by an observer....
rate of species from year to year (or patch to patch).
For competing species within the same community to coexist, they have to meet one fundamental requirement: the impact of competition from a species on itself must exceed its competitive impact on other species. In other words, intraspecific competition
Intraspecific competition
Intraspecific competition is a particular form of competition in which members of the same species vie for the same resource in an ecosystem...
must exceed interspecific competition
Interspecific competition
Interspecific competition, in ecology, is a form of competition in which individuals of different species compete for the same resource in an ecosystem...
. For example, jackrabbits living in the same area compete for food and nesting grounds. Such competition within the same species is called intraspecific competition
Intraspecific competition
Intraspecific competition is a particular form of competition in which members of the same species vie for the same resource in an ecosystem...
, which limits the growth of the species itself. Members from different species can also compete. For instance, jackrabbits and cottontail rabbits also compete for food and nesting grounds. Competition between different species is called interspecific competition
Interspecific competition
Interspecific competition, in ecology, is a form of competition in which individuals of different species compete for the same resource in an ecosystem...
, which limits the growth of other species. Stable coexistence occurs when any one species in the community limits its own growth more strongly than the growth of others.
The storage effect mixes three essential ingredients to assemble a community of competing species that fulfill the requirement. They are 1) correlation between the quality of an environment and the amount of competition experienced by a population in that environment (i.e. covariance
Covariance
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of how much two variables change together. Variance is a special case of the covariance when the two variables are identical.- Definition :...
between environment and competition), 2) differences in species response to the same environment (i.e. species-specific environmental responses), and 3) the ability of a population to diminish the impact of competition under worsening environment (i.e. buffered population growth). Below we describe each ingredient in detail and explain why the combination of the three leads to species coexistence.
Covariance between environment and competition
The growth of a population can be strongly influenced by the environment it experiences. An environment consists of not only physical elements such as resource abundance, temperature, and level of physical disturbance, but also biological elements such as the abundance of natural enemiesPredation
In ecology, predation describes a biological interaction where a predator feeds on its prey . Predators may or may not kill their prey prior to feeding on them, but the act of predation always results in the death of its prey and the eventual absorption of the prey's tissue through consumption...
and mutualists. Usually organisms reproduce more in a favorable environment (i.e. either during a good year, or within a good patch), build up their population densities, and lead themselves to a high level of competition
Competition (biology)
Competition is an interaction between organisms or species, in which the fitness of one is lowered by the presence of another. Limited supply of at least one resource used by both is required. Competition both within and between species is an important topic in ecology, especially community ecology...
due to this increasing crowding. Such a trend means that higher quality environments usually correlate with a higher strength of competition experienced by the organisms in those environments. In short, a better environment results in stronger competition. In statistics, such correlation
Correlation
In statistics, dependence refers to any statistical relationship between two random variables or two sets of data. Correlation refers to any of a broad class of statistical relationships involving dependence....
means that there will be a non-zero covariance
Covariance
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of how much two variables change together. Variance is a special case of the covariance when the two variables are identical.- Definition :...
between the change of population density in response to the environment and that to the competition. That is why the first ingredient is called “covariance
Covariance
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of how much two variables change together. Variance is a special case of the covariance when the two variables are identical.- Definition :...
between environment and competition”.
Species-specific environmental responses
Covariance between environment and competition suggests that organisms experience the strongest competitionCompetition (biology)
Competition is an interaction between organisms or species, in which the fitness of one is lowered by the presence of another. Limited supply of at least one resource used by both is required. Competition both within and between species is an important topic in ecology, especially community ecology...
under their optimal environmental conditions because their populations grow most rapidly in those conditions. In nature, we often find that different species from the same community respond to the same conditions in distinctive manners. For example, plant species have different preferred levels of light and water availability, which affect their germination and physical growth rates. Such differences in their response to the environment, which is called “species-specific environmental response,” means no two species from a community will have the same best environment in a given year or a given patch. As a result, when a species is under its optimal environmental conditions and thus experiencing the strongest intraspecific competition
Intraspecific competition
Intraspecific competition is a particular form of competition in which members of the same species vie for the same resource in an ecosystem...
, other species from the same community only experience the strongest interspecific competition
Interspecific competition
Interspecific competition, in ecology, is a form of competition in which individuals of different species compete for the same resource in an ecosystem...
coming from that species, but not the strongest intraspecific competition
Intraspecific competition
Intraspecific competition is a particular form of competition in which members of the same species vie for the same resource in an ecosystem...
coming from themselves.
Buffered population growth
A population can decline when environmental conditions worsen and when competition intensifies. If a species cannot limit the impact of competition in a hostile environment, its population will crash, and it will become locally extinct. Marvelously, in nature organisms are often able to slow down the rate of population decline in a hostile environment by alleviating the impact of competition. In so doing, they are able to set up a lower limit on the rate of their population decline. This phenomenon is called “buffered population growth”, which occurs under a variety of situations. Under the temporal storage effect, it can be accomplished by the adults of a species having long life spans, which are relatively unaffected by environmental stressors. For example, an adult tree is unlikely to be killed by a few weeks of drought or a single night of freezing temperatures, whereas a seedling may not survive these conditions. Even if all seedlings are killed by bad environmental conditions, the long-lived adults are able to keep the overall population from crashing. Moreover, the adults usually adopt strategies such as dormancy or hibernation under a hostile environment, which make them less sensitive to competition, and allows them to buffer against the double blades of the hostile environment and competition from their rivals. For a different example, buffered population growth is attained by annual plants with a persistent seed bank. Thanks to these long-lived seeds, the entire population cannot be destroyed by a single bad year. Moreover, the seeds stay dormant under unfavorable environmental conditions, avoiding direct competition with rivals who are favored by the same environment, and thus diminish the impact of competition in bad years. There are some temporal situations in which buffered population growth is not expected to occur. Namely, when multiple generations do not overlap (such as Labord’s chameleonFurcifer labordi
Labord's chameleon is a species of chameleon endemic to Madagascar. Like other Furcifer species , it has obligate year-long lifecycle...
) or when adults have a high mortality rate (such as many aquatic insects, or some populations of the Eastern Fence Lizard
Eastern fence lizard
The eastern fence lizard is a medium-sized species of lizard found along forest edges, rock piles, and rotting logs or stumps in the eastern United States...
), buffered growth does not occur. Under the spatial storage effect, buffered population growth is generally automatic, because the effects of a detrimental microhabitat will only be experienced by individuals in that area, rather than the population as a whole.
Outcome
The combined effect of (1) covarianceCovariance
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of how much two variables change together. Variance is a special case of the covariance when the two variables are identical.- Definition :...
between environment and competition, and (2) species-specific response to the environment decouple the strongest intraspecific and interspecific competition experienced by a species. Intraspecific competition
Intraspecific competition
Intraspecific competition is a particular form of competition in which members of the same species vie for the same resource in an ecosystem...
is strongest when a species is favored by the environment, whereas interspecific competition
Interspecific competition
Interspecific competition, in ecology, is a form of competition in which individuals of different species compete for the same resource in an ecosystem...
is strongest when its rivals are favored. After this decoupling, buffered population growth limits the impact of interspecific competition
Interspecific competition
Interspecific competition, in ecology, is a form of competition in which individuals of different species compete for the same resource in an ecosystem...
when a species is not favored by the environment. As a consequence, the impact of intraspecific competition
Intraspecific competition
Intraspecific competition is a particular form of competition in which members of the same species vie for the same resource in an ecosystem...
on the species favored by a particular environment exceeds that of the interspecific competition
Interspecific competition
Interspecific competition, in ecology, is a form of competition in which individuals of different species compete for the same resource in an ecosystem...
on species less favored by that environment. We see that the fundamental requirement for species coexistence is fulfilled and thus storage effect is able to maintain stable coexistence in a community of competing species.
For species to coexist in a community, all species must be able to recover from low density. Not surprisingly, being a coexistence mechanism, the storage effect helps species when they become rare. It does so by making the abundant species’ effect on itself greater than its effect on the rare species. The difference between species’ response to environmental conditions means that a rare species’ optimal environment is not the same as its competitors. Under these conditions, the rare species will experience low levels of interspecific competition
Interspecific competition
Interspecific competition, in ecology, is a form of competition in which individuals of different species compete for the same resource in an ecosystem...
. Because the rare species itself is rare, it will experience little impact from intraspecific competition
Intraspecific competition
Intraspecific competition is a particular form of competition in which members of the same species vie for the same resource in an ecosystem...
as well, even at its highest possible levels of intraspecific competition. Free from the impact of competition, the rare species is able to make gains in these good years or patches. Moreover, thanks to the buffered population growth, the rare species is able to survive the bad years or patches by “storing” the gains from the good years/patches. As a result, the population of any rare species is able to grow due to the storage effect.
One natural outcome from the covariance
Covariance
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of how much two variables change together. Variance is a special case of the covariance when the two variables are identical.- Definition :...
between environment and competition is that the species with very low densities will have more fluctuation in its recruitment
Recruitment (biology)
In biology, recruitment occurs when juvenile organisms survive to be added to a population. The term is generally used to refer to a stage whereby the organisms are settled and able to be detected by an observer....
rates than species with normal densities. This occurs because in good environments, species with high densities will often experience large amount of crowding by members of the same species, thus limiting the benefits of good years/patches, and making good years/patches more similar to bad years/patches. Low-density species are rarely able to cause crowding, thus allowing significantly increased fitness in good years/patches. Since the fluctuation in recruitment
Recruitment (biology)
In biology, recruitment occurs when juvenile organisms survive to be added to a population. The term is generally used to refer to a stage whereby the organisms are settled and able to be detected by an observer....
rate is an indicator of covariance between environment and competition, and since species-specific environmental response and buffered population growth can normally be assumed in nature, finding much stronger fluctuation in recruitment
Recruitment (biology)
In biology, recruitment occurs when juvenile organisms survive to be added to a population. The term is generally used to refer to a stage whereby the organisms are settled and able to be detected by an observer....
rates in rare and low-density species provides a strong indication that the storage effect is operating within a community.
Mathematical formulation
It is important to note that the storage effect is not a model for population growth (such as the Lotka–Volterra equation) itself, but is an effect that appears in non-additive models of population growth. Thus, the equations shown below will work for any arbitrary model of population growth, but will only be as accurate as the original model. The derivation below is taken from Chesson 1994. It is a derivation of the temporal storage effect, but is very similar to the spatial storage effect.The fitness
Fitness (biology)
Fitness is a central idea in evolutionary theory. It can be defined either with respect to a genotype or to a phenotype in a given environment...
of an individual, as well as expected growth rate
Population growth
Population growth is the change in a population over time, and can be quantified as the change in the number of individuals of any species in a population using "per unit time" for measurement....
, can be measured in terms of the average number of offspring it will leave during its lifetime. This parameter, r(t), is a function of both environmental factors, e(t), and how much the organism must compete
Competition (biology)
Competition is an interaction between organisms or species, in which the fitness of one is lowered by the presence of another. Limited supply of at least one resource used by both is required. Competition both within and between species is an important topic in ecology, especially community ecology...
with other individuals (both of its own species, and different species), c(t). Thus,
where g is an arbitrary function for growth rate. During this article, we will at times use subscripts to represent functions of a particular species (e.g. r j(t) is the fitness of species j). It is assumed that there must be some values e* and c*, such that g(e*, c*) = 0, representing a zero-population growth equilibrium. These values need not be unique, but for every e*, there is a unique c*. For ease of calculation, we define standard parameters E(t) and C(t), such that
Both E and C represent the effect of deviations in environmental response from equilibrium. E represents the effect that varying environmental conditions (e.g. rainfall patterns, temperature, food availability, etc.) have on fitness, in the absence of abnormal competitive effects. For the storage effect to occur, the environmental response for each species must be unique (i.e. E j(t) ≠ E i(t) when j ≠ i). C(t) represents how much average fitness is lowered as a result of competition
Competition (biology)
Competition is an interaction between organisms or species, in which the fitness of one is lowered by the presence of another. Limited supply of at least one resource used by both is required. Competition both within and between species is an important topic in ecology, especially community ecology...
. For example, if there is more rain during a given year, E(t) will likely increase. If more plants begin to bloom, and thus compete for that rain, then C(t) will increase as well. Because e* and c* are not unique, E(t) and C(t) are not unique, and thus one should choose them as conveniently as possible. Under most conditions (see Chesson 1994), r(t) can be approximated as
where
γ represents the nonadditivity of growth rates. If γ = 0 (known as additivity
Additive function
In mathematics the term additive function has two different definitions, depending on the specific field of application.In algebra an additive function is a function that preserves the addition operation:for any two elements x and y in the domain. For example, any linear map is additive...
) it means that the impact of competition on fitness does not change with the environment. If γ > 0 (superadditivity), it means that the adverse effects of competition during a bad year are relatively worse than during a good year. In other words, a population suffers more from competition in bad years than in good years. If γ < 0 (subadditivity, or buffered population growth), it means that the harm done by competition during a bad year is relatively minor when compared to a good year. In other words, the population is able to diminish the impact of competition as the environment worsens. As stated above, for the storage effect to contribute to species coexistence, we must have buffered population growth (i.e. it must be the case that γ < 0).
The long-term average of the above equation is
which, under environments with sufficient variation relative to mean effects, can be approximated as
For any effect to act as a coexistence mechanism, it must boost the average fitness of an individual when they are at below-normal population density. Otherwise, a species at low density (known as an `invader') will continue to dwindle, and this negative feedback will cause its extinction. When a species is at equilibrium (known as a `resident'), its average long-term fitness must be 0. For a species to recover from low density, its average fitness must be greater than 0. For the remainder of the text, we refer to functions of the invader with the subscript i, and to the resident with the subscript r.
A long-term average growth rate of an invader is often written as
where,
and, ΔI, the storage effect,
where
In this equation, qir tells us how much the competition experienced by r affects the competition experienced by i.
We can see the biological meaning of the storage effect expressed in the mathematical form of ΔI. The first term of the expression is covariance
Covariance
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of how much two variables change together. Variance is a special case of the covariance when the two variables are identical.- Definition :...
between environment and competition (Cov(E C)), scaled by a factor representing buffered population growth (γ). The difference between the first term and the second term represents the difference in species responses to the environment between the invader and the sum of the residents, scaled by the effect each resident has on the invader (qir).
The storage effect and predation
The effect of predation on the storage effect was recently considered in a series of papers by Peter Chesson and Jessica Kuang. Their work focused on a model for annual plants with seed predators, from which they reached two conclusions. First, they showed that predation can undermine the benefits of the storage effect. This occurs because generalist predators depress population levels by eating individuals. When this happens, there are fewer plants competing for resources. This lowers the strength of intraspecific competition relative to interspecific competition. As a result, the strength of the storage effect is weakened. In other words, when population levels are held in check by predation, rather than competition, the beneficial effects of intraspecific competition will be undermined.Second, they found that under positive frequency dependent predation, predators can promote coexistence. Positive frequency dependent predation (also known as “prey switching
Prey switching
Prey switching is frequency-dependent predation, where the predator preferentially consumes the most common type of prey. The phenomenon has also been described as apostatic selection, however the two terms are generally used to describe different parts of the same phenomenon. Apostatic selection...
”) occurs when predators are more likely to attack a particular prey when they are common. When this occurs, death from predation most often befalls dominant species, and individuals from rare species are much more likely to survive and increase in number. When predators become specialized enough, this can promote coexistence, compensating for or even surpassing the weakening of the storage effect. Additionally, if predators are able to quickly respond to the new prey densities, this can generate a storage effect from predation.
Empirical studies
The first empirical study that tested the requirements of the storage effect was done by Pake and Venable, who looked at three desert annual plantAnnual plant
An annual plant is a plant that usually germinates, flowers, and dies in a year or season. True annuals will only live longer than a year if they are prevented from setting seed...
s. They experimentally manipulated density and water availability over a two-year period, and found that fitness
Fitness (biology)
Fitness is a central idea in evolutionary theory. It can be defined either with respect to a genotype or to a phenotype in a given environment...
and germination
Germination
Germination is the process in which a plant or fungus emerges from a seed or spore, respectively, and begins growth. The most common example of germination is the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm. However the growth of a sporeling from a spore, for example the...
rates varied greatly from year to year, and over different environmental conditions. This shows that each species has a unique environmental response, and implied that likely there is a covariance
Covariance
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of how much two variables change together. Variance is a special case of the covariance when the two variables are identical.- Definition :...
between environment and competition. This, combined with the buffered population growth that is a product of a long-lived seed bank
Soil Seed Bank
The soil seed bank refers to the natural storage of seeds, often dormant, within the soil of most ecosystems. The study of soil seed banks started in 1859 when Charles Darwin observed the emergence of seedlings using soil samples from the bottom of a lake. The first scientific paper on the subject...
, showed that a temporal storage effect was probably an important factor in mediating coexistence. This study was also important, because it showed that variation in germination
Germination
Germination is the process in which a plant or fungus emerges from a seed or spore, respectively, and begins growth. The most common example of germination is the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm. However the growth of a sporeling from a spore, for example the...
conditions could be a major factor promoting species coexitstence.
The first attempt made at quantifying the temporal storage effect was by Cáceres in 1997. Using 30 years of water-column data from Oneida Lake
Oneida Lake
Oneida Lake is the largest lake entirely within New York State . The lake is located northeast of Syracuse and near the Great Lakes. It serves as one of the links in the Erie Canal. It empties into the Oneida River which flows into the Oswego River which in turn flows into Lake Ontario...
, New York, she studied the effect the storage effect had on two species of plankton
Daphnia
Daphnia are small, planktonic crustaceans, between 0.2 and 5 mm in length. Daphnia are members of the order Cladocera, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because of their saltatory swimming style...
(Daphnia galeata mendotae
Daphnia galeata mendotae
Daphnia galeata is a small species of planktonic crustacean. It lives in freshwater environments across a large area of the Northern Hemisphere, mostly in lakes....
and D. pulicaria). These species of plankton lay diapausing
Diapause
Diapause is the delay in development in response to regularly and recurring periods of adverse environmental conditions. It is considered to be a physiological state of dormancy with very specific initiating and inhibiting conditions...
eggs which, much like the seeds of annual plants, lay dormant in the sediment for many years before hatching. Cáceres found that the size of reproductive bouts were fairly uncorrelated between the two species. She also found, in the absence of the storage effect, D. galeata mendotae would have gone extinct. She was unable to measure certain important parameters (such as the rate of egg predation), but found that her results were robust to a wide range of estimates.
The first test of the spatial storage effect was done by Sears and Chesson in the desert area east of Portal, Arizona. Using a common neighbor-removal experiment, they examined whether coexistence between two annual plants, Erodium cicutarium
Erodium cicutarium
Erodium cicutarium, also known as Redstem filaree, Common Stork's-bill, is an herbaceous annual, and in warm climates a biennial member of the Geranium Family of flowering plants...
and Phacelia popeii, was due to the spatial storage effect or resource partitioning. The storage effect was quantified in terms of number of inflorescences (a proxy for fitness) instead of actual population growth rate. They found that E. cicutarium was able to outcompete P. popeii in many situations, and in the absence of the storage effect, would likely competitively exclude P. popeii. However, they found a very strong difference in the covariance
Covariance
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of how much two variables change together. Variance is a special case of the covariance when the two variables are identical.- Definition :...
between environment and competition, which showed that some of the most favorable areas for P. popeii (the rare species), were unfavorable to E. cicutarium (the common species). This suggests that P. popeii is able to avoid strong interspecific competition
Interspecific competition
Interspecific competition, in ecology, is a form of competition in which individuals of different species compete for the same resource in an ecosystem...
in some good patches, and that this may be enough to compensate for losses in areas favorable to E. cicutarium.
Colleen Kelly and colleagues examined the population size distribution of 12 species of trees coexisting in a tropical deciduous forest at the Chamela Biological Station in Jalisco
Jalisco
Jalisco officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Jalisco is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is located in Western Mexico and divided in 125 municipalities and its capital city is Guadalajara.It is one of the more important states...
, Mexico. They identified individuals of 12 tree species and grouped them by age (assumed to be a function of size). They found that recruitment
Recruitment (biology)
In biology, recruitment occurs when juvenile organisms survive to be added to a population. The term is generally used to refer to a stage whereby the organisms are settled and able to be detected by an observer....
of young trees varies from year to year. They also found that within each genus, the locally rarer species unanimously had a more irregular age distributions than the more common species. This finding strongly suggests that between closely competing tree species the rare ones experience stronger recruitment
Recruitment (biology)
In biology, recruitment occurs when juvenile organisms survive to be added to a population. The term is generally used to refer to a stage whereby the organisms are settled and able to be detected by an observer....
fluctuation than the common ones. Such difference in recruitment
Recruitment (biology)
In biology, recruitment occurs when juvenile organisms survive to be added to a population. The term is generally used to refer to a stage whereby the organisms are settled and able to be detected by an observer....
fluctuation indicates a difference in covariance
Covariance
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of how much two variables change together. Variance is a special case of the covariance when the two variables are identical.- Definition :...
between the environment and competition between rare and common species. Since species-specific environmental response and buffered population growth can be naturally assumed, their finding strongly suggests that the storage effect operates in this tropical deciduous forest so as to maintain the coexistence between different tree species.
Angert and colleagues demonstrated the temporal storage effect occurring in the desert annual plant community on Tumamoc Hill
Tumamoc Hill
Tumamoc Hill is located west of downtown Tucson, Arizona and is home to many radio, television, and public safety transmitters. The University of Arizona owns a preserve and leases another as a research and education facility with a small astronomical observatory with a telescope on the hill...
, Arizona. Previous studies had shown the annual plant
Annual plant
An annual plant is a plant that usually germinates, flowers, and dies in a year or season. True annuals will only live longer than a year if they are prevented from setting seed...
s in that community exhibited a trade-off between growth rate (a proxy for competitive ability) and water use efficiency (a proxy for drought tolerance). As a result, some plants grew better during wet years, while others grew better during dry years. This, combined with variation in germination
Germination
Germination is the process in which a plant or fungus emerges from a seed or spore, respectively, and begins growth. The most common example of germination is the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm. However the growth of a sporeling from a spore, for example the...
rates, produced an overall community average storage effect of 0.103. In other words, the storage effect is expected to help the population of any species at low density to increase, on average, by 10.3% each generation, until it recovers from low density.