Stencil jumping
Encyclopedia
Stencil jumping, at times called stencil walking, is an algorithm
to locate the grid element enclosing a given point for any structured mesh. In simple words, given a point and a structured mesh
, this algorithm will help locate the grid element that will enclose the given point.
This algorithm finds extensive use in Computational Fluid Dynamics
(CFD) in terms of holecutting and interpolation when two meshes lie one inside the other. The other variations of the problem would be something like this: Given a place, at which latitude and longitude does it lie? The brute force algorithm would find the distance of the point from every mesh point and see which is smallest. Another approach would be to use a binary search algorithm
which would yield a result comparable in speed to the stencil jumping algorithm. A combination of both the binary search and the stencil jumping algorithm will yield an optimum result in the minimum possible time.
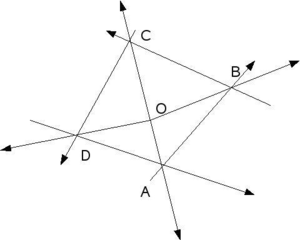 Consider one grid element of a 2 dimensional mesh as shown, for simplicity and consider a point O inside.
Consider one grid element of a 2 dimensional mesh as shown, for simplicity and consider a point O inside.
The vertices of the grid element are denoted by A, B, C and D and the vectors AB, BC, CD, DA, OA, OB, OC and OD are represented.
The cross product
of OA and AB will yield a vector perpendicular to the plane coming out of the screen. We say that the magnitude of the cross product is positive. It will be observed that the cross products of OB and BC, OC and CD; and OD and DA are all positive.
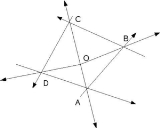
 This is not the case when the point is outside.
This is not the case when the point is outside.
Here we see that not all the cross products are positive. This is the major testing criterion in the algorithm.
Each of these cross products are checked one by one (in the order shown) on which becomes negative first. If OA × AB becomes negative first, the next guess should be one step ahead along DA. If OB × BC is negative first, move along AB by one step to find the next guess and so on.
The algorithm will converge at the exact grid element where all the cross products are positive.
Stencil jumping, at times called stencil walking, is an algorithm
to locate the grid element enclosing a given point for any structured mesh. In simple words, given a point and a structured mesh
, this algorithm will help locate the grid element that will enclose the given point.
This algorithm finds extensive use in Computational Fluid Dynamics
(CFD) in terms of holecutting and interpolation when two meshes lie one inside the other. The other variations of the problem would be something like this: Given a place, at which latitude and longitude does it lie? The brute force algorithm would find the distance of the point from every mesh point and see which is smallest. Another approach would be to use a binary search algorithm
which would yield a result comparable in speed to the stencil jumping algorithm. A combination of both the binary search and the stencil jumping algorithm will yield an optimum result in the minimum possible time.
 Consider one grid element of a 2 dimensional mesh as shown, for simplicity and consider a point O inside.
Consider one grid element of a 2 dimensional mesh as shown, for simplicity and consider a point O inside.
The vertices of the grid element are denoted by A, B, C and D and the vectors AB, BC, CD, DA, OA, OB, OC and OD are represented.
The cross product
of OA and AB will yield a vector perpendicular to the plane coming out of the screen. We say that the magnitude of the cross product is positive. It will be observed that the cross products of OB and BC, OC and CD; and OD and DA are all positive.
 This is not the case when the point is outside.
This is not the case when the point is outside.
Here we see that not all the cross products are positive. This is the major testing criterion in the algorithm.
Each of these cross products are checked one by one (in the order shown) on which becomes negative first. If OA × AB becomes negative first, the next guess should be one step ahead along DA. If OB × BC is negative first, move along AB by one step to find the next guess and so on.
The algorithm will converge at the exact grid element where all the cross products are positive.
Stencil jumping, at times called stencil walking, is an algorithm
to locate the grid element enclosing a given point for any structured mesh. In simple words, given a point and a structured mesh
, this algorithm will help locate the grid element that will enclose the given point.
This algorithm finds extensive use in Computational Fluid Dynamics
(CFD) in terms of holecutting and interpolation when two meshes lie one inside the other. The other variations of the problem would be something like this: Given a place, at which latitude and longitude does it lie? The brute force algorithm would find the distance of the point from every mesh point and see which is smallest. Another approach would be to use a binary search algorithm
which would yield a result comparable in speed to the stencil jumping algorithm. A combination of both the binary search and the stencil jumping algorithm will yield an optimum result in the minimum possible time.
 Consider one grid element of a 2 dimensional mesh as shown, for simplicity and consider a point O inside.
Consider one grid element of a 2 dimensional mesh as shown, for simplicity and consider a point O inside.
The vertices of the grid element are denoted by A, B, C and D and the vectors AB, BC, CD, DA, OA, OB, OC and OD are represented.
The cross product
of OA and AB will yield a vector perpendicular to the plane coming out of the screen. We say that the magnitude of the cross product is positive. It will be observed that the cross products of OB and BC, OC and CD; and OD and DA are all positive.
 This is not the case when the point is outside.
This is not the case when the point is outside.
Here we see that not all the cross products are positive. This is the major testing criterion in the algorithm.
Each of these cross products are checked one by one (in the order shown) on which becomes negative first. If OA × AB becomes negative first, the next guess should be one step ahead along DA. If OB × BC is negative first, move along AB by one step to find the next guess and so on.
The algorithm will converge at the exact grid element where all the cross products are positive.
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
to locate the grid element enclosing a given point for any structured mesh. In simple words, given a point and a structured mesh
Unstructured grid
An unstructured grid is a tessellation of a part of the Euclidean plane or Euclidean space by simple shapes, such as triangles or tetrahedra, in an irregular pattern...
, this algorithm will help locate the grid element that will enclose the given point.
This algorithm finds extensive use in Computational Fluid Dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics, usually abbreviated as CFD, is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical methods and algorithms to solve and analyze problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the interaction of liquids and gases with...
(CFD) in terms of holecutting and interpolation when two meshes lie one inside the other. The other variations of the problem would be something like this: Given a place, at which latitude and longitude does it lie? The brute force algorithm would find the distance of the point from every mesh point and see which is smallest. Another approach would be to use a binary search algorithm
Binary search algorithm
In computer science, a binary search or half-interval search algorithm finds the position of a specified value within a sorted array. At each stage, the algorithm compares the input key value with the key value of the middle element of the array. If the keys match, then a matching element has been...
which would yield a result comparable in speed to the stencil jumping algorithm. A combination of both the binary search and the stencil jumping algorithm will yield an optimum result in the minimum possible time.
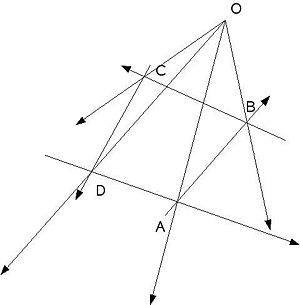
The principle

The vertices of the grid element are denoted by A, B, C and D and the vectors AB, BC, CD, DA, OA, OB, OC and OD are represented.
The cross product
Cross product
In mathematics, the cross product, vector product, or Gibbs vector product is a binary operation on two vectors in three-dimensional space. It results in a vector which is perpendicular to both of the vectors being multiplied and normal to the plane containing them...
of OA and AB will yield a vector perpendicular to the plane coming out of the screen. We say that the magnitude of the cross product is positive. It will be observed that the cross products of OB and BC, OC and CD; and OD and DA are all positive.

Here we see that not all the cross products are positive. This is the major testing criterion in the algorithm.
How does it move forward?
The algorithm needs a guess grid element to start off. The grid element can be found by the location of one point say A. The other points can be automatically located by getting the subsequent points. The required cross products are then found in the order- OA × AB
- OB × BC
- OC × CD
- OD × DA
Each of these cross products are checked one by one (in the order shown) on which becomes negative first. If OA × AB becomes negative first, the next guess should be one step ahead along DA. If OB × BC is negative first, move along AB by one step to find the next guess and so on.
The algorithm will converge at the exact grid element where all the cross products are positive.
See also
- Five-point stencilFive-point stencilIn numerical analysis, given a square grid in one or two dimensions, the five-point stencil of a point in the grid is made up of the point itself together with its four "neighbors"...
Stencil jumping, at times called stencil walking, is an algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
to locate the grid element enclosing a given point for any structured mesh. In simple words, given a point and a structured mesh
Unstructured grid
An unstructured grid is a tessellation of a part of the Euclidean plane or Euclidean space by simple shapes, such as triangles or tetrahedra, in an irregular pattern...
, this algorithm will help locate the grid element that will enclose the given point.
This algorithm finds extensive use in Computational Fluid Dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics, usually abbreviated as CFD, is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical methods and algorithms to solve and analyze problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the interaction of liquids and gases with...
(CFD) in terms of holecutting and interpolation when two meshes lie one inside the other. The other variations of the problem would be something like this: Given a place, at which latitude and longitude does it lie? The brute force algorithm would find the distance of the point from every mesh point and see which is smallest. Another approach would be to use a binary search algorithm
Binary search algorithm
In computer science, a binary search or half-interval search algorithm finds the position of a specified value within a sorted array. At each stage, the algorithm compares the input key value with the key value of the middle element of the array. If the keys match, then a matching element has been...
which would yield a result comparable in speed to the stencil jumping algorithm. A combination of both the binary search and the stencil jumping algorithm will yield an optimum result in the minimum possible time.
The principle

The vertices of the grid element are denoted by A, B, C and D and the vectors AB, BC, CD, DA, OA, OB, OC and OD are represented.
The cross product
Cross product
In mathematics, the cross product, vector product, or Gibbs vector product is a binary operation on two vectors in three-dimensional space. It results in a vector which is perpendicular to both of the vectors being multiplied and normal to the plane containing them...
of OA and AB will yield a vector perpendicular to the plane coming out of the screen. We say that the magnitude of the cross product is positive. It will be observed that the cross products of OB and BC, OC and CD; and OD and DA are all positive.

Here we see that not all the cross products are positive. This is the major testing criterion in the algorithm.
How does it move forward?
The algorithm needs a guess grid element to start off. The grid element can be found by the location of one point say A. The other points can be automatically located by getting the subsequent points. The required cross products are then found in the order- OA × AB
- OB × BC
- OC × CD
- OD × DA
Each of these cross products are checked one by one (in the order shown) on which becomes negative first. If OA × AB becomes negative first, the next guess should be one step ahead along DA. If OB × BC is negative first, move along AB by one step to find the next guess and so on.
The algorithm will converge at the exact grid element where all the cross products are positive.
See also
- Five-point stencilFive-point stencilIn numerical analysis, given a square grid in one or two dimensions, the five-point stencil of a point in the grid is made up of the point itself together with its four "neighbors"...
Stencil jumping, at times called stencil walking, is an algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
to locate the grid element enclosing a given point for any structured mesh. In simple words, given a point and a structured mesh
Unstructured grid
An unstructured grid is a tessellation of a part of the Euclidean plane or Euclidean space by simple shapes, such as triangles or tetrahedra, in an irregular pattern...
, this algorithm will help locate the grid element that will enclose the given point.
This algorithm finds extensive use in Computational Fluid Dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics, usually abbreviated as CFD, is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical methods and algorithms to solve and analyze problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the interaction of liquids and gases with...
(CFD) in terms of holecutting and interpolation when two meshes lie one inside the other. The other variations of the problem would be something like this: Given a place, at which latitude and longitude does it lie? The brute force algorithm would find the distance of the point from every mesh point and see which is smallest. Another approach would be to use a binary search algorithm
Binary search algorithm
In computer science, a binary search or half-interval search algorithm finds the position of a specified value within a sorted array. At each stage, the algorithm compares the input key value with the key value of the middle element of the array. If the keys match, then a matching element has been...
which would yield a result comparable in speed to the stencil jumping algorithm. A combination of both the binary search and the stencil jumping algorithm will yield an optimum result in the minimum possible time.
The principle

The vertices of the grid element are denoted by A, B, C and D and the vectors AB, BC, CD, DA, OA, OB, OC and OD are represented.
The cross product
Cross product
In mathematics, the cross product, vector product, or Gibbs vector product is a binary operation on two vectors in three-dimensional space. It results in a vector which is perpendicular to both of the vectors being multiplied and normal to the plane containing them...
of OA and AB will yield a vector perpendicular to the plane coming out of the screen. We say that the magnitude of the cross product is positive. It will be observed that the cross products of OB and BC, OC and CD; and OD and DA are all positive.

Here we see that not all the cross products are positive. This is the major testing criterion in the algorithm.
How does it move forward?
The algorithm needs a guess grid element to start off. The grid element can be found by the location of one point say A. The other points can be automatically located by getting the subsequent points. The required cross products are then found in the order- OA × AB
- OB × BC
- OC × CD
- OD × DA
Each of these cross products are checked one by one (in the order shown) on which becomes negative first. If OA × AB becomes negative first, the next guess should be one step ahead along DA. If OB × BC is negative first, move along AB by one step to find the next guess and so on.
The algorithm will converge at the exact grid element where all the cross products are positive.

