
Statistical coupling analysis
Encyclopedia
Statistical coupling analysis or SCA is a technique used in bioinformatics
to measure covariation between pairs of amino acids in a protein multiple sequence alignment
(MSA). More specifically, it quantifies how much the amino acid distribution at some position i changes upon a perturbation of the amino acid distribution at another position j. The resulting statistical coupling energy indicates the degree of evolutionary dependence between the residues, with higher coupling energy corresponding to increased dependence.
and the remaining 40% of sequences have a leucine
, at position j the distribution is 40% isoleucine
, 40% histidine
and 20% methionine
, k has an average distribution (the 20 amino acids are present at roughly the same frequencies seen in all proteins), and l has 80% histidine, 20% valine. Since positions i, j and l have an amino acid distribution different from the mean distribution observed in all proteins, they are said to have some degree of conservation.
In statistical coupling analysis, the conservation (ΔGstat) at each site (i) is defined as: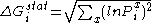 .
.
Here, Pix describes the probability of finding amino acid x at position i, and is defined by a function in binomial form as follows:
where N is 100, nx is the percentage of sequences with residue x (e.g. methionine) at position i, and px corresponds to the approximate distribution of amino acid x in all positions among all sequenced proteins. The summation runs over all 20 amino acids. After ΔGistat is computed, the conservation for position i in a subalignment produced after a perturbation of amino acid distribution at j (ΔGi | δjstat) is taken. Statistical coupling energy, denoted ΔΔGi, jstat, is simply the difference between these two values. That is:
Statistical coupling energy is often systematically calculated between a fixed, perturbated position, and all other positions in an MSA. Continuing with the example MSA from the beginning of the section, consider a perturbation at position j where the amino distribution changes from 40% I, 40% H, 20% M to 100% I. If, in a subsequent subalignment, this changes the distribution at i from 60% V, 40% L to 90% V , 10% L, but does not change the distribution at position l, then there would be some amount of statistical coupling energy between i and j but none between l and j.
family, they were able to identify a small network of residues that were energetically coupled to a binding site residue. The network consisted of both residues spatially close to the binding site in the tertiary fold, called contact pairs, and more distant residues that participate in longer-range energetic interactions. Later applications of SCA by the Ranganathan group on the GPCR, serine protease
and hemoglobin
families also showed energetic coupling in sparse networks of residues that cooperate in allosteric communication.
Statistical coupling analysis has also been used as a basis for computational protein design. In 2005, Russ et al. used an SCA for the WW domain
to create artificial proteins with similar thermodynamic stability and structure
to natural WW domains. The fact that 12 out of the 43 designed proteins with the same SCA profile as natural WW domains properly folded provided strong evidence that little information—only coupling information—was required for specifying the protein fold. This support for the SCA hypothesis was made more compelling considering that a) the successfully folded proteins had only 36% average sequence identity
to natural WW folds, and b) none of the artificial proteins designed without coupling information folded properly. An accompanying study showed that the artificial WW domains were functionally similar to natural WW domains in ligand binding affinity and specificity.
In de novo protein structure prediction, it has been shown that, when combined with a simple residue-residue distance metric, SCA-based scoring can fairly accurately distinguish native from non-native protein folds.
Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics is the application of computer science and information technology to the field of biology and medicine. Bioinformatics deals with algorithms, databases and information systems, web technologies, artificial intelligence and soft computing, information and computation theory, software...
to measure covariation between pairs of amino acids in a protein multiple sequence alignment
Multiple sequence alignment
A multiple sequence alignment is a sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences, generally protein, DNA, or RNA. In many cases, the input set of query sequences are assumed to have an evolutionary relationship by which they share a lineage and are descended from a common ancestor...
(MSA). More specifically, it quantifies how much the amino acid distribution at some position i changes upon a perturbation of the amino acid distribution at another position j. The resulting statistical coupling energy indicates the degree of evolutionary dependence between the residues, with higher coupling energy corresponding to increased dependence.
Definition of statistical coupling energy
Statistical coupling energy measures how a perturbation of amino acid distribution at one site in an MSA effects the amino acid distribution at another site. For example, consider a multiple sequence alignment with sites (or columns) a through z, where each site has some distribution of amino acids. At position i, 60% of the sequences have a valineValine
Valine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2. L-Valine is one of 20 proteinogenic amino acids. Its codons are GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG. This essential amino acid is classified as nonpolar...
and the remaining 40% of sequences have a leucine
Leucine
Leucine is a branched-chain α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2. Leucine is classified as a hydrophobic amino acid due to its aliphatic isobutyl side chain. It is encoded by six codons and is a major component of the subunits in ferritin, astacin and other 'buffer' proteins...
, at position j the distribution is 40% isoleucine
Isoleucine
Isoleucine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCHCH2CH3. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested. Its codons are AUU, AUC and AUA....
, 40% histidine
Histidine
Histidine Histidine, an essential amino acid, has a positively charged imidazole functional group. It is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids. Its codons are CAU and CAC. Histidine was first isolated by German physician Albrecht Kossel in 1896. Histidine is an essential amino acid in humans...
and 20% methionine
Methionine
Methionine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2SCH3. This essential amino acid is classified as nonpolar. This amino-acid is coded by the codon AUG, also known as the initiation codon, since it indicates mRNA's coding region where translation into protein...
, k has an average distribution (the 20 amino acids are present at roughly the same frequencies seen in all proteins), and l has 80% histidine, 20% valine. Since positions i, j and l have an amino acid distribution different from the mean distribution observed in all proteins, they are said to have some degree of conservation.
In statistical coupling analysis, the conservation (ΔGstat) at each site (i) is defined as:
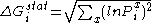 .
.Here, Pix describes the probability of finding amino acid x at position i, and is defined by a function in binomial form as follows:
where N is 100, nx is the percentage of sequences with residue x (e.g. methionine) at position i, and px corresponds to the approximate distribution of amino acid x in all positions among all sequenced proteins. The summation runs over all 20 amino acids. After ΔGistat is computed, the conservation for position i in a subalignment produced after a perturbation of amino acid distribution at j (ΔGi | δjstat) is taken. Statistical coupling energy, denoted ΔΔGi, jstat, is simply the difference between these two values. That is:
Statistical coupling energy is often systematically calculated between a fixed, perturbated position, and all other positions in an MSA. Continuing with the example MSA from the beginning of the section, consider a perturbation at position j where the amino distribution changes from 40% I, 40% H, 20% M to 100% I. If, in a subsequent subalignment, this changes the distribution at i from 60% V, 40% L to 90% V , 10% L, but does not change the distribution at position l, then there would be some amount of statistical coupling energy between i and j but none between l and j.
Applications
Ranganathan and Lockless originally developed SCA to examine thermodynamic (energetic) coupling of residue pairs in proteins. Using the PDZ domainPDZ domain
The PDZ domain is a common structural domain of 80-90 amino-acids found in the signaling proteins of bacteria, yeast, plants, viruses and animals...
family, they were able to identify a small network of residues that were energetically coupled to a binding site residue. The network consisted of both residues spatially close to the binding site in the tertiary fold, called contact pairs, and more distant residues that participate in longer-range energetic interactions. Later applications of SCA by the Ranganathan group on the GPCR, serine protease
Serine protease
Serine proteases are enzymes that cleave peptide bonds in proteins, in which serine serves as the nucleophilic amino acid at the active site.They are found ubiquitously in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes...
and hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells of all vertebrates, with the exception of the fish family Channichthyidae, as well as the tissues of some invertebrates...
families also showed energetic coupling in sparse networks of residues that cooperate in allosteric communication.
Statistical coupling analysis has also been used as a basis for computational protein design. In 2005, Russ et al. used an SCA for the WW domain
WW domain
The WW domain is a protein domain with two highly conserved tryptophans that binds proline-rich peptide motifs...
to create artificial proteins with similar thermodynamic stability and structure
Protein structure
Proteins are an important class of biological macromolecules present in all organisms. Proteins are polymers of amino acids. Classified by their physical size, proteins are nanoparticles . Each protein polymer – also known as a polypeptide – consists of a sequence formed from 20 possible L-α-amino...
to natural WW domains. The fact that 12 out of the 43 designed proteins with the same SCA profile as natural WW domains properly folded provided strong evidence that little information—only coupling information—was required for specifying the protein fold. This support for the SCA hypothesis was made more compelling considering that a) the successfully folded proteins had only 36% average sequence identity
Sequence alignment
In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are...
to natural WW folds, and b) none of the artificial proteins designed without coupling information folded properly. An accompanying study showed that the artificial WW domains were functionally similar to natural WW domains in ligand binding affinity and specificity.
In de novo protein structure prediction, it has been shown that, when combined with a simple residue-residue distance metric, SCA-based scoring can fairly accurately distinguish native from non-native protein folds.
External links
- What is a WW domain?
- Ranganathan lecture on statistical coupling analysis (audio included)
- Protein folding — a step closer? - A summary of the Ranganathan lab's SCA-based design of artificial yet functional WW domains.

