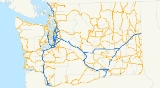
State highways in Washington
Encyclopedia
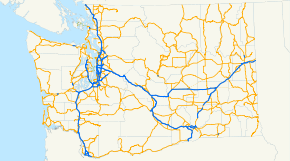
U.S. state
A U.S. state is any one of the 50 federated states of the United States of America that share sovereignty with the federal government. Because of this shared sovereignty, an American is a citizen both of the federal entity and of his or her state of domicile. Four states use the official title of...
of Washington, the Washington State Department of Transportation
Washington State Department of Transportation
The Washington State Department of Transportation , was established in 1905. The agency, led by a Secretary and overseen by the Governor, is a Washington governmental agency that constructs, maintains, and regulates the use of the state's transportation infrastructure...
(WSDOT) maintains a network of over 7000 miles (11000 km) of state highway
State highway
State highway, state road or state route can refer to one of three related concepts, two of them related to a state or provincial government in a country that is divided into states or provinces :#A...
s, including all Interstate and U.S. Highways that pass through the state. The system comprises 8.5% of the state's public road mileage, but carries over half of the traffic. All other public roads in the state are either inside incorporated places (cities or towns) or are maintained by the county.
__FORCETOC__
System description
All state highways are designated by the Washington State LegislatureWashington State Legislature
The Washington State Legislature is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Washington. It is a bipartisan, bicameral body, composed of the lower Washington House of Representatives, composed of 98 Representatives, and the upper Washington State Senate, with 49 Senators.The State Legislature...
and codified in the Revised Code of Washington
Revised Code of Washington
The Revised Code of Washington is the compilation of all permanent laws currently in force in the U.S. state of Washington. Temporary laws such as appropriations acts are excluded....
(RCW). These routes are defined generally by termini and points along the route; WSDOT may otherwise choose the details, and may bypass the designated points as long as the road serves the general vicinity. WSDOT's duties include "locating, designing, constructing, improving, repairing, operating, and maintaining" these state highways, including bridge
Bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span physical obstacles such as a body of water, valley, or road, for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle...
s and other related structures. Within cities and towns, the local governments are responsible for certain aspects of the streets maintained as parts of a state highway, including their grade and the portion not used for highway purposes. All routes, even Interstate and U.S. Highways, are defined as "state route number" plus the number; for instance, Interstate 5 is "state route number 5" and U.S. Route 395 is "state route number 395". Also included in the RCW are "state route number 20 north" (signed as State Route 20 Spur) and "state route number 97-alternate" (signed as U.S. Route 97 Alternate). Some other spurs, such as State Route 503 Spur, are defined as part of the main routes, as is U.S. Route 101 Alternate. WSDOT has also defined some spurs that mainly serve to provide full access between intersecting routes.
Although most state highways as defined by law are open to traffic, State Route 109 dead-ends at Taholah, State Route 501 has a gap in the middle, and State Routes 35, 168, 230
Washington State Route 230
State Route 230 is a legislated, but unconstructed, state highway to be located in Adams and Whitman counties in the U.S. state of Washington. The highway would begin at a junction with concurrent highways Interstate 90 and U.S. Route 395 in Ritzville and travel east to an intersection with...
, 276, and most of SR 171
Washington State Route 171
State Route 171 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Washington, running from SR 17 north of Moses Lake to Interstate 90 south of Moses Lake. The state law designating SR 171 dictates that it will be extended to State Route 28 west of Odessa-History:...
, 213
Washington State Route 213
State Route 213 is the shortest state highway in the U.S. state of Washington. The long unsigned highway serves Malott, a community in Okanogan County. Extending from over the Okanogan River via a bridge to First Avenue in Malott, the roadway is semi-complete, as state law designates that...
, and 704, have not been constructed. Notable sections of state highways include the six crossings of the Cascade Range
Cascade Range
The Cascade Range is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as the North Cascades, and the notable volcanoes known as the High Cascades...
- the Columbia River Gorge
Columbia River Gorge
The Columbia River Gorge is a canyon of the Columbia River in the Pacific Northwest of the United States. Up to deep, the canyon stretches for over as the river winds westward through the Cascade Range forming the boundary between the State of Washington to the north and Oregon to the south...
(SR 14), White Pass
White Pass (Washington)
White Pass is a mountain pass in the Cascade Range south of Mount Rainier and north of Goat Rocks in Washington, USA. U.S. Highway 12 passes over White Pass, connecting Yakima County with Lewis County....
(US 12), Chinook Pass
Chinook Pass
Chinook Pass is a pass through the Cascade Range in the state of Washington.The pass provides the east entrance to Mount Rainier National Park, and carries State Route 410 between the towns of Enumclaw and Naches. Because of the high elevation, Chinook Pass is usually closed in November due to...
(SR 410), Snoqualmie Pass
Snoqualmie Pass
Snoqualmie Pass is a mountain pass that carries Interstate 90 through the Cascade Range in the U.S. State of Washington. The elevation of the pass summit is , and is on the county line between Kittitas County and King County...
(I-90), Stevens Pass
Stevens Pass
Stevens Pass is a mountain pass through the Cascade Mountains located at the border of King County and Chelan County in Washington, United States....
(US 2), and the North Cascades Highway (SR 20). Of the 13 public road crossings of the Canadian border in Washington, nine are on state highways. Major bridges include the Tacoma Narrows Bridge
Tacoma Narrows Bridge
The Tacoma Narrows Bridge is a pair of twin suspension bridges in the U.S. state of Washington, which carry State Route 16 across the Tacoma Narrows strait of Puget Sound between Tacoma and the Kitsap Peninsula...
and three floating bridge
Pontoon bridge
A pontoon bridge or floating bridge is a bridge that floats on water and in which barge- or boat-like pontoons support the bridge deck and its dynamic loads. While pontoon bridges are usually temporary structures, some are used for long periods of time...
s: the Evergreen Point Bridge, Hood Canal Bridge
Hood Canal Bridge
The Hood Canal Bridge is a floating bridge located in the U.S. state of Washington that carries Washington State Route 104 across Hood Canal and connects the Olympic and Kitsap Peninsulas. At long, The Hood Canal Bridge (officially William A. Bugge Bridge) is a floating bridge located in the U.S....
, and Lake Washington Bridge. The Washington State Ferries
Washington State Ferries
Washington State Ferries is a passenger and automobile ferry service owned and operated by the Washington State Department of Transportation that serves communities on Puget Sound and in the San Juan Islands. It is the most used ferry system in the world and the largest passenger and automobile...
, except the route to Sidney, British Columbia
Sidney, British Columbia
Sidney is a town located at the northern end of the Saanich Peninsula, on Vancouver Island in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It is one of the 13 Greater Victoria municipalities. It has a population of approximately 11,300. Sidney is located just east of Victoria International Airport,...
, were legally included in the state highway system in 1994; a new State Route 339 was created at that time for the passenger-only Seattle-Vashon Ferry. According to the Washington State Department of Licensing, ocean beach
Beach
A beach is a geological landform along the shoreline of an ocean, sea, lake or river. It usually consists of loose particles which are often composed of rock, such as sand, gravel, shingle, pebbles or cobblestones...
es are legally state highways with a general speed limit
Speed limit
Road speed limits are used in most countries to regulate the speed of road vehicles. Speed limits may define maximum , minimum or no speed limit and are normally indicated using a traffic sign...
of 25 mph (40 km/h), many only open to vehicles between the day after Labor Day
Labor Day
Labor Day is a United States federal holiday observed on the first Monday in September that celebrates the economic and social contributions of workers.-History:...
and April 14, but state law places the beaches under the control of the Washington State Parks and Recreation Commission and only designates them as "public highways".
Most state routes are numbered in a grid, with even-numbered routes running east–west and odd-numbered routes running north–south. Even two-digit routes increase from south to north in three "strips", with SR 4, SR 6, and SR 8 in the western part of the state, SR 14, SR 16, SR 18, and SR 20 in central Washington, and SR 22, SR 24, SR 26, SR 28, and former SR 30 in the east. Odd numbers similarly increase from west to east, with SR 3, SR 7, SR 9, SR 11, SR 17, SR 21, SR 23, SR 25, SR 27, and SR 31 following this general progression. (SR 19 was added in 1991, and lies west of SR 3; SR 41 is an extension of Idaho State Highway 41
Idaho State Highway 41
State Highway 41, abbreviated SH-41, is a state highway mostly in the U.S. state of Idaho. It runs from Interstate 90 in Post Falls to U.S. Route 2 on the Washington state line. The northernmost of SH-41 run along State Street along the state line, with the southbound lane in the town of...
.) Three-digit routes (and SR 92 and SR 96) are usually numbered by taking the first one or two digits of a route it connects to and adding another digit or two. In some cases, instead of using the two-digit route's actual number, a number that would fit the grid is used instead. Three-digit routes have been numbered as follows:
| Main | Branches | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| SR 9 | 92, 96 | |
| US 101 | 100-119 | |
| SR 11 | 110 | Only existed from 1967 to 1975; SR 110 has since been re-applied to a spur of US 101 |
| US 12 | 121-131 | |
| US 830, SR 12, US 410 | 120-129 | Only existed from 1964 to 1967, when US 830 and SR 12 became SR 14 and US 410 became US 12 |
| US 97 | 131 | Fits in the grid as SR 13; only existed from 1964 to 1975, when US 97 replaced SR 131; SR 131 has since been re-applied to a spur of US 12 |
| SR 14 | 140-143 | |
| SR 14 | 141-143 | Only existed from 1964 to 1967, when SR 14 became US 12 |
| US 97 | 150-155 | Fits in the grid as SR 15 |
| SR 16, SR 410 | 160-169 | |
| SR 17 | 170-174 | |
| SR 18 | 181 | |
| US 195 | 193-194 | |
| US 2 | 202-209 | |
| SR 20 | 211-215, 237 | SR 237 replaced SR 537 in 1975 after SR 20 replaced part of SR 536. SR 237 was then decommissioned in 1991. |
| SR 22 | 220-225 | |
| SR 23 | 230-232 | |
| SR 24 | 240-243 | |
| SR 25 | 251 | |
| SR 26 | 260-263 | |
| SR 27 | 270-278 | |
| SR 28 | 281-285 | |
| US 395 | 290-294 | Fits in the grid as SR 29 |
| SR 3 | 300-310, 339 | |
| SR 31 | 311 | SR 311 became SR 211 in 1975 after SR 20 replaced part of SR 31 |
| US 395 | 397 | |
| SR 4 | 401-409, 411, 431-433 | 431-433 replaced 831-833 in 1967 when SR 4 replaced US 830 |
| I-5 | 500-548, 599 | |
| SR 6 | 603 | |
| SR 7 | 702-706 | |
| SR 8 | 801 | Only existed from 1964 to 1967, when SR 8 became part of US 12 and SR 801 became SR 121 |
| I-82 | 821-823 | |
| US 830 | 831-833 | Only existed from 1964 to 1967, when US 830 became SR 4 and 831-833 became 431-433 |
| I-90 | 900-908, 920 | |
| US 97 | 970-971 |
History
Washington State Legislature
The Washington State Legislature is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Washington. It is a bipartisan, bicameral body, composed of the lower Washington House of Representatives, composed of 98 Representatives, and the upper Washington State Senate, with 49 Senators.The State Legislature...
created the State Highway Board in 1905 and appropriated funds to construct - but not maintain - twelve numbered "state roads" in sparsely settled areas of the state. (Main highways in more populated areas would continue to be entirely under county control, though sometimes built with 50% state aid.) Six of these highways were east–west crossings of the Cascades; others included a portion of Chuckanut Drive and a road around the west side of the Olympic Peninsula
Olympic Peninsula
The Olympic Peninsula is the large arm of land in western Washington state of the USA, that lies across Puget Sound from Seattle. It is bounded on the west by the Pacific Ocean, the north by the Strait of Juan de Fuca, and the east by Puget Sound. Cape Alava, the westernmost point in the contiguous...
. Under a 1909 law, the State Highway Board surveyed a connected network of proposed state roads, The legislature added most of these routes to the state highway system in 1913, when they formed a two-tiered system of primary and secondary roads. Primary roads were completely controlled by the state, including maintenance, and received only names, while secondary roads kept their numbers and county maintenance. Unlike the earlier state roads, these primary roads mostly followed existing passable county roads.
A 1923 restructuring of the system re-assigned numbers to almost all the primary state highways, which were soon marked on signs. In 1937, the old primary/secondary split was abolished, and a new system of primary and secondary state highways was created, all to be maintained by the state in the same manner. The old state roads all kept their numbers as new primary state highways, and secondary state highways were created as alphanumeric branches of those primary highways (for instance SSH 8D was a branch of PSH 8). The final renumbering was authorized by law in 1963 and posted in January 1964, when new "sign route" numbers were assigned that matched the inter-state systems and otherwise formed the present grid. Until 1970, these numbers coexisted with the older primary and secondary state highways, when the legislature adopted the sign route numbers as "state routes", finally eliminating all vestiges of the 1905 numbering.

