
Stanton number
Encyclopedia
The Stanton number, St or CH, is a dimensionless number that measures the ratio of heat transferred into a fluid to the thermal capacity of fluid. It is used to characterize heat transfer
in forced convection
flows.
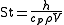
where
It can also be represented in terms of the fluid's Nusselt
, Reynolds, and Prandtl numbers:
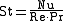
where
The Stanton number arises in the consideration of the geometric similarity of the momentum boundary layer
and the thermal boundary layer, where it can be used to express a relationship between the shear force at the wall (due to viscous drag
) and the total heat transfer at the wall (due to thermal diffusivity
).
The Stanton number is named after Thomas Edward Stanton (1865-1931).
Heat transfer
Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the exchange of thermal energy from one physical system to another. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as heat conduction, convection, thermal radiation, and phase-change transfer...
in forced convection
Convection
Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids and rheids. It cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids....
flows.
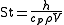
where
- h = convectionConvectionConvection is the movement of molecules within fluids and rheids. It cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids....
heat transfer coefficient 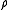 = densityDensityThe mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
= densityDensityThe mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
of the fluid- cp = specific heat of the fluid
- V = velocityVelocityIn physics, velocity is speed in a given direction. Speed describes only how fast an object is moving, whereas velocity gives both the speed and direction of the object's motion. To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed and motion in a constant direction. Constant ...
of the fluid
It can also be represented in terms of the fluid's Nusselt
Nusselt number
In heat transfer at a boundary within a fluid, the Nusselt number is the ratio of convective to conductive heat transfer across the boundary. Named after Wilhelm Nusselt, it is a dimensionless number...
, Reynolds, and Prandtl numbers:
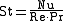
where
- Nu is the Nusselt numberNusselt numberIn heat transfer at a boundary within a fluid, the Nusselt number is the ratio of convective to conductive heat transfer across the boundary. Named after Wilhelm Nusselt, it is a dimensionless number...
- Re is the Reynolds number
- Pr is the Prandtl number
The Stanton number arises in the consideration of the geometric similarity of the momentum boundary layer
Boundary layer
In physics and fluid mechanics, a boundary layer is that layer of fluid in the immediate vicinity of a bounding surface where effects of viscosity of the fluid are considered in detail. In the Earth's atmosphere, the planetary boundary layer is the air layer near the ground affected by diurnal...
and the thermal boundary layer, where it can be used to express a relationship between the shear force at the wall (due to viscous drag
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
) and the total heat transfer at the wall (due to thermal diffusivity
Thermal diffusivity
In heat transfer analysis, thermal diffusivity is the thermal conductivity divided by density and specific heat capacity at constant pressure. It has the SI unit of m²/s...
).
The Stanton number is named after Thomas Edward Stanton (1865-1931).

