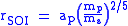Sphere of influence (astrodynamics)
Encyclopedia
A sphere of influence in astrodynamics
and astronomy
is the spherical
region (actually is an oblate sphere) around a celestial body
where the primary gravitational influence on an orbit
ing object is that body. This is usually used to describe the areas in our solar system
where planets dominate the orbits of surrounding objects (such as moon
s), despite the presence of the much more massive (but distant) Sun
. In a more general sense, the patched conic approximation is only valid within the SOI.
The general equation describing the radius
of the sphere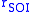 of a planet:
of a planet:
where
In the patched conic approximation, once an object leaves the planet's SOI, the primary/only gravitational influence is the Sun (until the object enters another body's SOI). Since the definition of rSOI relies on the presence of the Sun and a planet, the term is only applicable in a three body
or greater system. It requires the mass of the primary body to be much greater than the mass of the secondary body. This changes the three-body problem into a restricted two-body problem.
Astrodynamics
Orbital mechanics or astrodynamics is the application of ballistics and celestial mechanics to the practical problems concerning the motion of rockets and other spacecraft. The motion of these objects is usually calculated from Newton's laws of motion and Newton's law of universal gravitation. It...
and astronomy
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
is the spherical
Sphere
A sphere is a perfectly round geometrical object in three-dimensional space, such as the shape of a round ball. Like a circle in two dimensions, a perfect sphere is completely symmetrical around its center, with all points on the surface lying the same distance r from the center point...
region (actually is an oblate sphere) around a celestial body
Celestial Body
Celestial Body is a Croatian film directed by Lukas Nola. It was released in 2000....
where the primary gravitational influence on an orbit
Orbit
In physics, an orbit is the gravitationally curved path of an object around a point in space, for example the orbit of a planet around the center of a star system, such as the Solar System...
ing object is that body. This is usually used to describe the areas in our solar system
Solar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
where planets dominate the orbits of surrounding objects (such as moon
Natural satellite
A natural satellite or moon is a celestial body that orbits a planet or smaller body, which is called its primary. The two terms are used synonymously for non-artificial satellites of planets, of dwarf planets, and of minor planets....
s), despite the presence of the much more massive (but distant) Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
. In a more general sense, the patched conic approximation is only valid within the SOI.
The general equation describing the radius
Radius
In classical geometry, a radius of a circle or sphere is any line segment from its center to its perimeter. By extension, the radius of a circle or sphere is the length of any such segment, which is half the diameter. If the object does not have an obvious center, the term may refer to its...
of the sphere
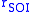 of a planet:
of a planet:
where
-
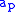 is the semimajor axis of the planet's orbit relative to the largest body in the system, usually the Sun
is the semimajor axis of the planet's orbit relative to the largest body in the system, usually the Sun -
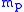 and
and 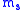 are the massMassMass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
are the massMassMass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
es of the planet and Sun, respectively.
In the patched conic approximation, once an object leaves the planet's SOI, the primary/only gravitational influence is the Sun (until the object enters another body's SOI). Since the definition of rSOI relies on the presence of the Sun and a planet, the term is only applicable in a three body
N-body problem
The n-body problem is the problem of predicting the motion of a group of celestial objects that interact with each other gravitationally. Solving this problem has been motivated by the need to understand the motion of the Sun, planets and the visible stars...
or greater system. It requires the mass of the primary body to be much greater than the mass of the secondary body. This changes the three-body problem into a restricted two-body problem.
Table of planetary SOI radii
| Body | SOI Radius | SOI Radius |
| - | (km Kilometre The kilometre is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one thousand metres and is therefore exactly equal to the distance travelled by light in free space in of a second... ) |
(body radii) |
| Mercury Mercury (planet) Mercury is the innermost and smallest planet in the Solar System, orbiting the Sun once every 87.969 Earth days. The orbit of Mercury has the highest eccentricity of all the Solar System planets, and it has the smallest axial tilt. It completes three rotations about its axis for every two orbits... |
 |
45 |
| Venus Venus Venus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting it every 224.7 Earth days. The planet is named after Venus, the Roman goddess of love and beauty. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky, reaching an apparent magnitude of −4.6, bright enough to cast shadows... |
 |
100 |
| Earth Earth Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets... |
 |
145 |
| Moon Moon The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more... |
 |
38 |
| Mars Mars Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance... |
 |
170 |
| Jupiter Jupiter Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn,... |
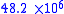 |
677 |
| Saturn Saturn Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest planet in the Solar System, after Jupiter. Saturn is named after the Roman god Saturn, equated to the Greek Cronus , the Babylonian Ninurta and the Hindu Shani. Saturn's astronomical symbol represents the Roman god's sickle.Saturn,... |
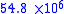 |
901 |
| Uranus Uranus Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It has the third-largest planetary radius and fourth-largest planetary mass in the Solar System. It is named after the ancient Greek deity of the sky Uranus , the father of Cronus and grandfather of Zeus... |
 |
2025 |
| Neptune Neptune Neptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun in the Solar System. Named for the Roman god of the sea, it is the fourth-largest planet by diameter and the third largest by mass. Neptune is 17 times the mass of Earth and is slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus, which is 15 times... |
 |
3866 |