Sodium-cooled fast reactor
Encyclopedia
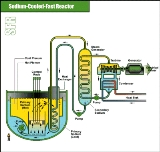
The sodium-cooled fast reactor or SFR is a Generation IV reactor
project to design an advanced fast neutron reactor
.
It builds on two closely related existing projects, the LMFBR and the Integral Fast Reactor
, with the objective of producing a fast-spectrum, sodium
-cooled
reactor.
The reactors are intended for use in nuclear power plant
s to produce nuclear power
from nuclear fuel
.
recycle with two major options: One is an intermediate-size (150–600 MWe) sodium-cooled reactor with uranium
-plutonium
-minor-actinide-zirconium
metal alloy fuel, supported by a fuel cycle based on pyrometallurgical reprocessing in facilities integrated with the reactor. The second is a medium to large (500–1,500 MWe) sodium-cooled reactor with mixed uranium-plutonium oxide fuel, supported by a fuel cycle based upon advanced aqueous processing at a central location serving a number of reactors. The outlet temperature is approximately 510–550 degrees Celsius for both.
which provides thermal inertia against overheating. Water
is difficult to use as a coolant
for a fast reactor because water acts as a neutron
moderator that slows the fast neutrons into thermal neutrons. While it may be possible to use supercritical water as a coolant in a fast reactor, this would require a very high pressure. In contrast, sodium
atoms are much heavier than both the oxygen
and hydrogen
atoms found in water, and therefore the neutrons lose less energy in collision
s with sodium atoms. Sodium also need not be pressurized since its boiling point
is much higher than the reactor's operating temperature
, and sodium does not corrode steel reactor parts. A disadvantage of sodium is its chemical reactivity, which requires special precautions to prevent and suppress fires. If sodium comes into contact with water it explodes, and it burns when in contact with air. In addition, neutrons cause it to become radioactive; however, activated
sodium has a half-life of only 15 hours.
(a fission product
) inter-diffuse with the iron of the cladding. The alloy that forms has a low eutectic melting temperature. FCCI causes the cladding to reduce in strength and could eventually rupture. The amount of transuranic transmutation is limited by the production of plutonium from uranium. A design work-around has been proposed to have an inert matrix. Magnesium
oxide has been proposed as the inert matrix. Magnesium oxide has an entire order of magnitude smaller probability of interacting with neutrons (thermal and fast) than elements like iron.
The SFR is designed for management of high-level wastes and, in particular, management of plutonium and other actinides. Important safety features of the system include a long thermal response time, a large margin to coolant boiling, a primary system that operates near atmospheric pressure, and intermediate sodium system between the radioactive sodium in the primary system and the water and steam in the power plant. With innovations to reduce capital cost, such as making a modular design, removing a primary loop, integrating the pump and intermediate heat exchanger, or simply find better materials for construction, the SFR can be a viable technology for electricity generation.
The SFR's fast spectrum also makes it possible to use available fissile and fertile materials (including depleted uranium
) considerably more efficiently than thermal spectrum reactors with once-through fuel cycles.
Related:
Generation IV reactor
Generation IV reactors are a set of theoretical nuclear reactor designs currently being researched. Most of these designs are generally not expected to be available for commercial construction before 2030...
project to design an advanced fast neutron reactor
Fast neutron reactor
A fast neutron reactor or simply a fast reactor is a category of nuclear reactor in which the fission chain reaction is sustained by fast neutrons...
.
It builds on two closely related existing projects, the LMFBR and the Integral Fast Reactor
Integral Fast Reactor
The Integral Fast Reactor is a design for a nuclear reactor using fast neutrons and no neutron moderator . IFR is distinguished by a nuclear fuel cycle that uses reprocessing via electrorefining at the reactor site.The U.S...
, with the objective of producing a fast-spectrum, sodium
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride...
-cooled
Nuclear reactor coolant
A nuclear reactor coolant is a coolant in a nuclear reactor used to remove heat from the nuclear reactor core and transfer it to electrical generators and the environment....
reactor.
The reactors are intended for use in nuclear power plant
Nuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant is a thermal power station in which the heat source is one or more nuclear reactors. As in a conventional thermal power station the heat is used to generate steam which drives a steam turbine connected to a generator which produces electricity.Nuclear power plants are usually...
s to produce nuclear power
Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
from nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel is a material that can be 'consumed' by fission or fusion to derive nuclear energy. Nuclear fuels are the most dense sources of energy available...
.
Fuel cycle
The fuel cycle employs a full actinideActinide
The actinide or actinoid series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium.The actinide series derives its name from the group 3 element actinium...
recycle with two major options: One is an intermediate-size (150–600 MWe) sodium-cooled reactor with uranium
Uranium
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons...
-plutonium
Plutonium
Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation...
-minor-actinide-zirconium
Zirconium
Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name of zirconium is taken from the mineral zircon. Its atomic mass is 91.224. It is a lustrous, grey-white, strong transition metal that resembles titanium...
metal alloy fuel, supported by a fuel cycle based on pyrometallurgical reprocessing in facilities integrated with the reactor. The second is a medium to large (500–1,500 MWe) sodium-cooled reactor with mixed uranium-plutonium oxide fuel, supported by a fuel cycle based upon advanced aqueous processing at a central location serving a number of reactors. The outlet temperature is approximately 510–550 degrees Celsius for both.
Sodium as a coolant
An advantage of liquid metal coolants is high heat capacityHeat capacity
Heat capacity , or thermal capacity, is the measurable physical quantity that characterizes the amount of heat required to change a substance's temperature by a given amount...
which provides thermal inertia against overheating. Water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
is difficult to use as a coolant
Coolant
A coolant is a fluid which flows through a device to prevent its overheating, transferring the heat produced by the device to other devices that use or dissipate it. An ideal coolant has high thermal capacity, low viscosity, is low-cost, non-toxic, and chemically inert, neither causing nor...
for a fast reactor because water acts as a neutron
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
moderator that slows the fast neutrons into thermal neutrons. While it may be possible to use supercritical water as a coolant in a fast reactor, this would require a very high pressure. In contrast, sodium
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride...
atoms are much heavier than both the oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
and hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
atoms found in water, and therefore the neutrons lose less energy in collision
Collision
A collision is an isolated event which two or more moving bodies exert forces on each other for a relatively short time.Although the most common colloquial use of the word "collision" refers to accidents in which two or more objects collide, the scientific use of the word "collision" implies...
s with sodium atoms. Sodium also need not be pressurized since its boiling point
Boiling point
The boiling point of an element or a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid....
is much higher than the reactor's operating temperature
Operating temperature
An operating temperature is the temperature at which an electrical or mechanical device operates. The device will operate effectively within a specified temperature range which varies based on the device function and application context, and ranges from the minimum operating temperature to the...
, and sodium does not corrode steel reactor parts. A disadvantage of sodium is its chemical reactivity, which requires special precautions to prevent and suppress fires. If sodium comes into contact with water it explodes, and it burns when in contact with air. In addition, neutrons cause it to become radioactive; however, activated
Neutron activation
Neutron activation is the process in which neutron radiation induces radioactivity in materials, and occurs when atomic nuclei capture free neutrons, becoming heavier and entering excited states. The excited nucleus often decays immediately by emitting particles such as neutrons, protons, or alpha...
sodium has a half-life of only 15 hours.
Design goals
The operating temperature should not exceed the melting temperature of the fuel. Fuel-to-cladding chemical interaction (FCCI) has to be designed against. FCCI is eutectic melting between the fuel and the cladding; uranium, plutonium, and lanthanumLanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57.Lanthanum is a silvery white metallic element that belongs to group 3 of the periodic table and is the first element of the lanthanide series. It is found in some rare-earth minerals, usually in combination with cerium and...
(a fission product
Fission product
Nuclear fission products are the atomic fragments left after a large atomic nucleus fissions. Typically, a large nucleus like that of uranium fissions by splitting into two smaller nuclei, along with a few neutrons and a large release of energy in the form of heat , gamma rays and neutrinos. The...
) inter-diffuse with the iron of the cladding. The alloy that forms has a low eutectic melting temperature. FCCI causes the cladding to reduce in strength and could eventually rupture. The amount of transuranic transmutation is limited by the production of plutonium from uranium. A design work-around has been proposed to have an inert matrix. Magnesium
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole...
oxide has been proposed as the inert matrix. Magnesium oxide has an entire order of magnitude smaller probability of interacting with neutrons (thermal and fast) than elements like iron.
The SFR is designed for management of high-level wastes and, in particular, management of plutonium and other actinides. Important safety features of the system include a long thermal response time, a large margin to coolant boiling, a primary system that operates near atmospheric pressure, and intermediate sodium system between the radioactive sodium in the primary system and the water and steam in the power plant. With innovations to reduce capital cost, such as making a modular design, removing a primary loop, integrating the pump and intermediate heat exchanger, or simply find better materials for construction, the SFR can be a viable technology for electricity generation.
The SFR's fast spectrum also makes it possible to use available fissile and fertile materials (including depleted uranium
Depleted uranium
Depleted uranium is uranium with a lower content of the fissile isotope U-235 than natural uranium . Uses of DU take advantage of its very high density of 19.1 g/cm3...
) considerably more efficiently than thermal spectrum reactors with once-through fuel cycles.
Reactors
Sodium-cooled reactors include:- BN-350 reactorBN-350 reactorThe BN-350 was a sodium-cooled fast reactor nuclear power plant located at Aktau , Kazakhstan, situated on the shore of the Caspian Sea. Construction of the BN-350 Fast breeder reactor began in 1964, and the plant first produced electricity in 1973...
, Russia - BN-600 reactorBN-600 reactorThe BN-600 reactor is a sodium-cooled fast breeder reactor, built at the Beloyarsk Nuclear Power Station, in Zarechny, Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia. Designed to generate electrical power of 600 MW in total, the plant dispatches 560 MW to the Middle Urals power grid...
, Russia - Clinch River Breeder Reactor ProjectClinch River Breeder Reactor ProjectThe Clinch River Breeder Reactor Project was a joint effort of the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission and the U.S. electric power industry to design and construct a sodium-cooled fast-neutron nuclear reactor...
, United States - Dounreay Prototype Fast Reactor, United Kingdom
- Fermi 1, United States
- Experimental Breeder Reactor IExperimental Breeder Reactor IExperimental Breeder Reactor I is a decommissioned research reactor and U.S. National Historic Landmark located in the desert about southeast of Arco, Idaho. At 1:50 pm on December 20, 1951 it became the world's first electricity-generating nuclear power plant when it produced sufficient...
, United States - Experimental Breeder Reactor IIExperimental Breeder Reactor IIExperimental Breeder Reactor-II is a reactor at the Materials and Fuels Complex of the Idaho National Laboratory, formerly the West Campus of Argonne National Laboratory in Idaho....
, United States - Fast Breeder Test ReactorFBTRThe Fast Breeder Test Reactor is a breeder reactor located at Kalpakkam, India. The Indira Gandhi Center for Atomic Research and Bhabha Atomic Research Center jointly designed, constructed, and operate the reactor.-History:...
, India - JōyōJoyo (nuclear reactor)is a test sodium-cooled fast reactor located in Ōarai, Ibaraki, Japan, operated by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The name comes from the previous country name of the area around Ibaraki....
, Japan - Monju Nuclear Power Plant, Japan
- PhénixPhénixPhénix was a small-scale prototype fast breeder reactor, located at the Marcoule nuclear site, near Orange, France. It was a pool-type liquid-metal fast breeder reactor cooled with liquid sodium...
, France - Prototype Fast Breeder ReactorPrototype fast breeder reactorThe Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor is a 500MWe fast breeder nuclear reactor presently being constructed in Kalpakkam, India. The Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research is responsible for the design of this reactor....
, India - S1GS1G reactorThe S1G reactor is a naval reactor used by the United States Navy to provide electricity generation and propulsion on warships. The S1G designation stands for:* S = Submarine platform* 1 = First generation core designed by the contractor...
and S2GS2G reactorThe S2G reactor was a naval reactor used by the United States Navy to provide electricity generation and propulsion on warships, and the only liquid metal cooled reactor yet deployed by the US Navy...
, United States Navy - SNR-300SNR-300The Fast Breeder nuclear reactor SNR-300 was built near the town of Kalkar, Germany The Fast Breeder nuclear reactor SNR-300 was built near the town of Kalkar, Germany The Fast Breeder nuclear reactor SNR-300 was built near the town of Kalkar, Germany (located in the federal state of North...
, Germany - Sodium Reactor ExperimentSodium Reactor ExperimentThe Sodium Reactor Experiment was a pioneering nuclear power plant built by Atomics International at the Santa Susana Field Laboratory, nearby Simi Valley, California. The reactor operated from 1957 to 1964...
, United States - SuperphénixSuperphénixSuperphénix or SPX was a nuclear power station on the Rhône River at Creys-Malville in France, close to the border with Switzerland. A fast breeder reactor, it halted electricity production in 1996 and was closed as a commercial plant in 1997....
, France - RapsodieRapsodieRapsodie is an experimental nuclear reactor built in Cadarache in France.It was France's first fast reactor, and first achieved criticality in 1967. Rapsodie was a loop-type reactor with a thermal output of 40MW and no electrical generation facilities, and closed in 1983....
, France
Related:
- Fast Flux Test FacilityFast Flux Test FacilityThe Fast Flux Test Facility is a 400 MW nuclear test reactor owned by the U.S. Department of Energy.It is situated in the 400 Area of the Hanford Site, which is located in the state of Washington.-History:...
, United States, a sodium-cooled fast neutron reactorFast neutron reactorA fast neutron reactor or simply a fast reactor is a category of nuclear reactor in which the fission chain reaction is sustained by fast neutrons...
See also
- Fast breeder reactor
- Fast neutron reactorFast neutron reactorA fast neutron reactor or simply a fast reactor is a category of nuclear reactor in which the fission chain reaction is sustained by fast neutrons...
- Integral Fast ReactorIntegral Fast ReactorThe Integral Fast Reactor is a design for a nuclear reactor using fast neutrons and no neutron moderator . IFR is distinguished by a nuclear fuel cycle that uses reprocessing via electrorefining at the reactor site.The U.S...
- Lead-cooled fast reactorLead cooled fast reactorThe lead-cooled fast reactor is a nuclear power Generation IV reactor that features a fast neutron spectrum, molten lead or lead-bismuth eutectic coolant. Options include a range of plant ratings, including a number of 50 to 150 MWe units featuring long-life, pre-manufactured cores...
- Gas-cooled fast reactorGas-cooled fast reactorThe Gas-Cooled Fast Reactor system is a nuclear reactor design which is currently in development. Classed as a Generation IV reactor, it features a fast-neutron spectrum and closed fuel cycle for efficient conversion of fertile uranium and management of actinides...
- Generation IV reactorGeneration IV reactorGeneration IV reactors are a set of theoretical nuclear reactor designs currently being researched. Most of these designs are generally not expected to be available for commercial construction before 2030...

