
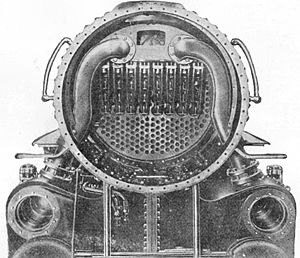
Smokebox
Encyclopedia

Steam locomotive exhaust system
The Steam locomotive exhaust system consists of those parts of a steam locomotive which together discharge exhaust steam from the cylinders in order to increase the draught through the fire...
. Smoke
Smoke
Smoke is a collection of airborne solid and liquid particulates and gases emitted when a material undergoes combustion or pyrolysis, together with the quantity of air that is entrained or otherwise mixed into the mass. It is commonly an unwanted by-product of fires , but may also be used for pest...
and hot gases pass from the firebox through tubes where they pass heat to the surrounding water
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a physical science that studies the effects on material bodies, and on radiation in regions of space, of transfer of heat and of work done on or by the bodies or radiation...
in the boiler
Boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which water or other fluid is heated. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications.-Materials:...
. The smoke then enters the smokebox, and is exhausted to the atmosphere through the chimney
Chimney
A chimney is a structure for venting hot flue gases or smoke from a boiler, stove, furnace or fireplace to the outside atmosphere. Chimneys are typically vertical, or as near as possible to vertical, to ensure that the gases flow smoothly, drawing air into the combustion in what is known as the...
(or funnel
Funnel
A funnel is a pipe with a wide, often conical mouth and a narrow stem. It is used to channel liquid or fine-grained substances into containers with a small opening. Without a funnel, spillage would occur....
).
To assist the passage of the smoke and hot gases, a blower
Blower
Blower may refer to:* USS Blower , a submarine of the United States Navy* a ducted centrifugal fan, especially when used in a heating, ventilating, and air-conditioning system* a supercharger on an internal-combustion engine...
is often used. This is a pipe ending in a ring containing pin-sized holes, which creates a "ring" of steam
Steam
Steam is the technical term for water vapor, the gaseous phase of water, which is formed when water boils. In common language it is often used to refer to the visible mist of water droplets formed as this water vapor condenses in the presence of cooler air...
jets. The steam forces out the smoke and draws further gases through the tubes. This in turn causes air to be drawn through the grate and firehole, making the fire burn brighter.
When the locomotive is in motion, exhaust
Exhaust gas
Exhaust gas or flue gas is emitted as a result of the combustion of fuels such as natural gas, gasoline/petrol, diesel fuel, fuel oil or coal. According to the type of engine, it is discharged into the atmosphere through an exhaust pipe, flue gas stack or propelling nozzle.It often disperses...
steam passes through the blastpipe
Blastpipe
The blastpipe is part of the exhaust system of a steam locomotive that discharges exhaust steam from the cylinders into the smokebox beneath the chimney in order to increase the draught through the fire.- History :...
, which is located within the smokebox. The steam is ejected through the chimney, again drawing the fire. The blastpipe is what produces the characteristic "chuff" sound.
Ashes and soot
Soot
Soot is a general term that refers to impure carbon particles resulting from the incomplete combustion of a hydrocarbon. It is more properly restricted to the product of the gas-phase combustion process but is commonly extended to include the residual pyrolyzed fuel particles such as cenospheres,...
which may be present in the smoke are often deposited in the smokebox. The front of the smokebox has a door which is opened to remove these deposits at the end of each locomotive's working day. The handle(s) must be tightened fully to prevent air leaks. Some smokebox doors have a single handle in the form of a wheel
Wheel
A wheel is a device that allows heavy objects to be moved easily through rotating on an axle through its center, facilitating movement or transportation while supporting a load, or performing labor in machines. Common examples found in transport applications. A wheel, together with an axle,...
; many British-built locomotives have a pair of smokebox door handles resembling the hands of a clock
Clock
A clock is an instrument used to indicate, keep, and co-ordinate time. The word clock is derived ultimately from the Celtic words clagan and clocca meaning "bell". A silent instrument missing such a mechanism has traditionally been known as a timepiece...
; other designs also exist.
The classic layout of a steam locomotive has the smokebox and chimney at the front of the locomotive, referred to as travelling "smokebox-first". Some designs reversed the layout to avoid problems (asphyxiation and poor visibility) caused by having the exhaust blowing back onto the crew, these were called cab forward
Cab forward
The term cab forward refers to various rail and road vehicle designs which place the driver's compartment substantially farther towards the front than is common practice.- Rail locomotives :...
locomotives.
On many steamroller
Steamroller
A steamroller is a form of road roller – a type of heavy construction machinery used for levelling surfaces, such as roads or airfields – that is powered by a steam engine...
s an extension to the body of the smokebox also houses the bearing which supports the front roller. Due to limitations of space, these rollers usually have a drop-down flap instead of a circular smokebox door.
Spark Arrester
A spark arrester is often installed within the smokebox. This may take the form of a cylindrical mesh running from the top of the blast pipe to the bottom of the chimney. The purpose of a spark arrester is to prevent excessively large fragments of hot ash from being exhausted into the environment where they may pose a fire risk. For this reason, spark arresters are generally installed on locomotives running through dry environments. The presence of a spark arrester may have a thermodynamic effect, distorting the draw of air over the fire and thereby reducing total power output. Thus their use can be contentious.Superheating
Locomotives fitted with a superheaterSuperheater
A superheater is a device used to convert saturated steam or wet steam into dry steam used for power generation or processes. There are three types of superheaters namely: radiant, convection, and separately fired...
will usually have a superheater header in the smokebox. Steam enters the header as "wet" (saturated) steam, and then passes through a superheater element. This takes the form of a pipe which runs twice through an enlarged smoke tube in the boiler. The steam enters a separate chamber in the header, this time as superheated or dry steam. The advantage of superheating is that the steam has greater expansive properties when entering the cylinders, so more power can be gained from a smaller amount of water and fuel.

