Single-Photon Avalanche Diode
Encyclopedia
In optoelectronics
the term Single-Photon Avalanche Diode (SPAD)
(also known as a Geiger-mode APD or G-APD) identifies a class of solid-state photodetectors based on a reverse biased p-n junction
in which a photo-generated carrier can trigger an avalanche current due to the impact ionization
mechanism. This device is able to detect low intensity signals (down to the single photon) and to signal the arrival times of the photons with a jitter
of a few tens of picoseconds.
SPADs, like the avalanche photodiode
(APD), exploits the photon-triggered avalanche current of a reverse biased p-n junction to detect an incident radiation. The fundamental difference between SPAD and APD is that SPADs are specifically designed to operate with a reverse bias voltage well above the breakdown voltage
(on the contrary APDs operate at a bias lesser than the breakdown voltage). This kind of operation is also called Geiger mode in literature, for the analogy with the Geiger counter
.
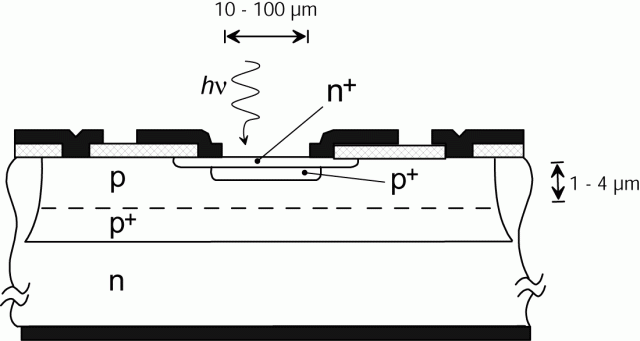
devices based on a p-n junction
reverse-biased at a voltage Va higher than VB (Figure 1). "At this bias, the electric field
is so high [higher than 3×105 V/cm] that a single charge carrier injected into the depletion layer can trigger a self-sustaining avalanche. The current rises swiftly [sub-nanosecond rise-time] to a macroscopic steady level in the milliampere range. If the primary carrier is photo-generated, the leading edge of the avalanche pulse marks [with picosecond time jitter ] the arrival time of the detected photon
." The current continues until the avalanche is quenched by lowering the bias voltage VD down to or below VB: the lower electric field is no longer able to accelerate carriers to impact-ionize with lattice
atoms, therefore current ceases. In order to be able to detect another photon, the bias voltage must be raised again above breakdown.
 "This operation requires a suitable circuit, which has to:
"This operation requires a suitable circuit, which has to:
.
a fast discriminator senses the steep onset of the avalanche current across a 50 Ω resistor and provides a digital (CMOS
, TTL
, ECL
, NIM
) output pulse, synchronous with the photon arrival time. It then quickly reduces the bias voltage to below breakdown, then relatively quickly returns bias to above the breakdown voltage ready to sense the next photon.
of the signal is obtained by measuring the time distribution of the output pulses (photon timing). The latter is obtained by means of a Time Correlated Single Photon Counting (TCSPC) instrument.
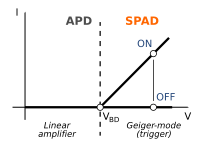 If a SPAD is observed by an analogue curve-tracer, it is possible to observe a bifurcation of the current-voltage characteristics beyond breakdown, during the voltage sweeps applied to the device. When the avalanche is triggered, the SPAD sustains the avalanche current (on-branch), instead when no carrier has been generated (by a photon or a thermal generation), no charge flows through the SPAD (off-branch). If the SPAD is triggered during a sweep above breakdown, a transition from the off-branch to the on-branch can be easily observed (like a "flickering").
If a SPAD is observed by an analogue curve-tracer, it is possible to observe a bifurcation of the current-voltage characteristics beyond breakdown, during the voltage sweeps applied to the device. When the avalanche is triggered, the SPAD sustains the avalanche current (on-branch), instead when no carrier has been generated (by a photon or a thermal generation), no charge flows through the SPAD (off-branch). If the SPAD is triggered during a sweep above breakdown, a transition from the off-branch to the on-branch can be easily observed (like a "flickering").
s and SPADs are reverse biased semiconductor p-n junctions. However, APDs are biased close to, but below the breakdown voltage of the semiconductor. This high electric field provides an internal multiplication gain only on the order of few hundreds, since the avalanche process is not diverging as in SPADs. The resulting avalanche current intensity is linearly related to the optical signal intensity. A SPAD however operates with a bias voltage above the breakdown voltage. Because the device is operating in this unstable above-breakdown regime, a single photon (or a single dark current electron) can set off a significant avalanche of electrons.
Practically, this means that in an APD a single photon produces only tens or few hundreds of electrons, but in a SPAD a single photon triggers a current in the mA region (billions of billions of electrons per second) that can be easily "counted".
Therefore, while the APD is a linear amplifier for the input optical signal with limited gain, the SPAD is a trigger device so the gain concept is meaningless.
Optoelectronics
Optoelectronics is the study and application of electronic devices that source, detect and control light, usually considered a sub-field of photonics. In this context, light often includes invisible forms of radiation such as gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet and infrared, in addition to visible light...
the term Single-Photon Avalanche Diode (SPAD)
(also known as a Geiger-mode APD or G-APD) identifies a class of solid-state photodetectors based on a reverse biased p-n junction
P-n junction
A p–n junction is formed at the boundary between a P-type and N-type semiconductor created in a single crystal of semiconductor by doping, for example by ion implantation, diffusion of dopants, or by epitaxy .If two separate pieces of material were used, this would...
in which a photo-generated carrier can trigger an avalanche current due to the impact ionization
Impact ionization
Impact ionization is the process in a material by which one energetic charge carrier can lose energy by the creation of other charge carriers...
mechanism. This device is able to detect low intensity signals (down to the single photon) and to signal the arrival times of the photons with a jitter
Jitter
Jitter is the undesired deviation from true periodicity of an assumed periodic signal in electronics and telecommunications, often in relation to a reference clock source. Jitter may be observed in characteristics such as the frequency of successive pulses, the signal amplitude, or phase of...
of a few tens of picoseconds.
SPADs, like the avalanche photodiode
Avalanche photodiode
An avalanche photodiode is a highly sensitive semiconductor electronic device that exploits the photoelectric effect to convert light to electricity. APDs can be thought of as photodetectors that provide a built-in first stage of gain through avalanche multiplication. From a functional standpoint,...
(APD), exploits the photon-triggered avalanche current of a reverse biased p-n junction to detect an incident radiation. The fundamental difference between SPAD and APD is that SPADs are specifically designed to operate with a reverse bias voltage well above the breakdown voltage
Breakdown voltage
The breakdown voltage of an insulator is the minimum voltage that causes a portion of an insulator to become electrically conductive.The breakdown voltage of a diode is the minimum reverse voltage to make the diode conduct in reverse...
(on the contrary APDs operate at a bias lesser than the breakdown voltage). This kind of operation is also called Geiger mode in literature, for the analogy with the Geiger counter
Geiger counter
A Geiger counter, also called a Geiger–Müller counter, is a type of particle detector that measures ionizing radiation. They detect the emission of nuclear radiation: alpha particles, beta particles or gamma rays. A Geiger counter detects radiation by ionization produced in a low-pressure gas in a...
.
SPAD operating principle
SPADs are semiconductorSemiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
devices based on a p-n junction
P-n junction
A p–n junction is formed at the boundary between a P-type and N-type semiconductor created in a single crystal of semiconductor by doping, for example by ion implantation, diffusion of dopants, or by epitaxy .If two separate pieces of material were used, this would...
reverse-biased at a voltage Va higher than VB (Figure 1). "At this bias, the electric field
Electric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
is so high [higher than 3×105 V/cm] that a single charge carrier injected into the depletion layer can trigger a self-sustaining avalanche. The current rises swiftly [sub-nanosecond rise-time] to a macroscopic steady level in the milliampere range. If the primary carrier is photo-generated, the leading edge of the avalanche pulse marks [with picosecond time jitter ] the arrival time of the detected photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
." The current continues until the avalanche is quenched by lowering the bias voltage VD down to or below VB: the lower electric field is no longer able to accelerate carriers to impact-ionize with lattice
Crystal structure
In mineralogy and crystallography, crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. A crystal structure is composed of a pattern, a set of atoms arranged in a particular way, and a lattice exhibiting long-range order and symmetry...
atoms, therefore current ceases. In order to be able to detect another photon, the bias voltage must be raised again above breakdown.

- sense the leading edge of the avalanche current;
- generate a standard output pulse synchronous with the avalanche build-up;
- quench the avalanche by lowering the bias down to the breakdown voltage;
- restore the photodiodePhotodiodeA photodiode is a type of photodetector capable of converting light into either current or voltage, depending upon the mode of operation.The common, traditional solar cell used to generateelectric solar power is a large area photodiode....
to the operative level. This circuit is usually referred to as a quenching circuit."
Passive quenching
The simplest quenching circuit is commonly called Passive Quenching Circuit and composed of a single resistor in series to the SPAD. This experimental setup has been employed since the early studies on the avalanche breakdown in junctions. The avalanche current self-quenches simply because it develops a voltage drop across a high-value ballast load RL (about 100 kΩ or more). After the quenching of the avalanche current, the SPAD bias VD slowly recovers to Va, and therefore the detector is ready to be ignited again. A detailed description of the quenching process is reported in.
Active quenching
A more advanced quenching scheme is called active quenching. In this casea fast discriminator senses the steep onset of the avalanche current across a 50 Ω resistor and provides a digital (CMOS
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits...
, TTL
TTL
TTL may refer to:* Taiwan Tobacco and Liquor, a state-owned manufacturer of cigarettes and alcohol in Taiwan* Through-the-lens metering, a feature of cameras capable of measuring light levels in a scene through their lens...
, ECL
ECL
ECL may stand for:*ECL programming language, an extensible programming language developed at Harvard*ECL, data-centric programming language for Big Data, a declarative, data centric programming language used for data intensive supercomputing...
, NIM
NIM
The Nuclear Instrumentation Module standard defines mechanical and electrical specifications for electronics modules used in experimental particle and nuclear physics...
) output pulse, synchronous with the photon arrival time. It then quickly reduces the bias voltage to below breakdown, then relatively quickly returns bias to above the breakdown voltage ready to sense the next photon.
Photon counting and timing
The intensity of the signal is obtained by counting (photon counting) the number of output pulses within a measurement time slot, while the time-dependent waveformWaveform
Waveform means the shape and form of a signal such as a wave moving in a physical medium or an abstract representation.In many cases the medium in which the wave is being propagated does not permit a direct visual image of the form. In these cases, the term 'waveform' refers to the shape of a graph...
of the signal is obtained by measuring the time distribution of the output pulses (photon timing). The latter is obtained by means of a Time Correlated Single Photon Counting (TCSPC) instrument.
Saturation
While the avalanche recovery circuit is quenching the avalanche and restoring bias, the SPAD cannot detect photons. Any photons that reach the detector during this brief period are not counted. As the number of photons increases such that the (statistical) time interval between photons gets within a factor of ten or so of the avalanche recovery time, missing counts become statistically significant and the count rate begins to depart from a linear relationship with detected light level. At this point the SPAD begins to saturate. If the light level were to increase further, ultimately to the point where the SPAD immediately avalanches the moment the avalanche recovery circuit restores bias, the count rate reaches a maximum defined purely by the avalanche recovery time (ten million counts per second or more). This can be harmful to the SPAD as it will be experiencing avalanche current nearly continuously.Internal noise
Besides photon-generated carriers, thermally-generated carriers (through generation-recombination processes within the semiconductor) can also fire the avalanche process. Therefore, it is possible to observe output pulses when the SPAD is in complete darkness. The resulting average number of counts per second is called dark count rate and is the key parameter in defining the detector noise. It is worth noting that the reciprocal of the dark count rate defines the mean time that the SPAD remains biased above breakdown before being triggered by an undesired thermal generation. Therefore, in order to work as a single-photon detector, the SPAD must be able to remain biased above breakdown for a sufficiently long time (e.g., a few milliseconds, corresponding to a count rate well under a thousand counts per second, cps).I-V characteristic

APDs versus SPADs
Both APDAvalanche photodiode
An avalanche photodiode is a highly sensitive semiconductor electronic device that exploits the photoelectric effect to convert light to electricity. APDs can be thought of as photodetectors that provide a built-in first stage of gain through avalanche multiplication. From a functional standpoint,...
s and SPADs are reverse biased semiconductor p-n junctions. However, APDs are biased close to, but below the breakdown voltage of the semiconductor. This high electric field provides an internal multiplication gain only on the order of few hundreds, since the avalanche process is not diverging as in SPADs. The resulting avalanche current intensity is linearly related to the optical signal intensity. A SPAD however operates with a bias voltage above the breakdown voltage. Because the device is operating in this unstable above-breakdown regime, a single photon (or a single dark current electron) can set off a significant avalanche of electrons.
Practically, this means that in an APD a single photon produces only tens or few hundreds of electrons, but in a SPAD a single photon triggers a current in the mA region (billions of billions of electrons per second) that can be easily "counted".
Therefore, while the APD is a linear amplifier for the input optical signal with limited gain, the SPAD is a trigger device so the gain concept is meaningless.

