
Shannon switching game
Encyclopedia
The Shannon switching game is an abstract strategy game for two players, invented by Claude Shannon, and (at least in its common rectangular-grid form) independently invented by David Gale
; it has also been known as Gale, Bridg-It, and Bird Cage.
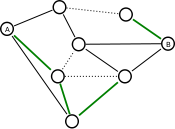 The game is played on a finite graph
The game is played on a finite graph
with two special nodes, A and B. Each edge of the graph can be either colored or removed. The two players are called Short and Cut, and alternate moves. On Cut 's turn, he deletes from the graph a non-colored edge of his choice. On Short 's turn, he colors any edge still in the graph. If Cut manages to turn the graph into one where A and B are no longer connected, he wins. If Short manages to create a colored path from A to B, he wins.
There are also versions of the Shannon switching game played on a directed graph and an oriented matroid
. A solution has been explicitly found for any such game using matroid
theory, unlike a similar game Hex
, which is PSPACE
hard.
The Short and Cut games are a duality; that is, the game can be restated so that both players have the same goal: to secure a certain edge set with distinguished edge e. Short tries to secure the edge set that with e makes up a circuit
, while Cut tries to secure an edge set that with e makes up a cutset, the minimal set of edges that connect two subgraphs.
David Gale
David Gale was a distinguished American mathematician and economist. He was a Professor Emeritus at University of California, Berkeley, affiliated with departments of Mathematics, Economics, and Industrial Engineering and Operations Research...
; it has also been known as Gale, Bridg-It, and Bird Cage.
Rules

Graph theory
In mathematics and computer science, graph theory is the study of graphs, mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects from a certain collection. A "graph" in this context refers to a collection of vertices or 'nodes' and a collection of edges that connect pairs of...
with two special nodes, A and B. Each edge of the graph can be either colored or removed. The two players are called Short and Cut, and alternate moves. On Cut 's turn, he deletes from the graph a non-colored edge of his choice. On Short 's turn, he colors any edge still in the graph. If Cut manages to turn the graph into one where A and B are no longer connected, he wins. If Short manages to create a colored path from A to B, he wins.
There are also versions of the Shannon switching game played on a directed graph and an oriented matroid
Oriented matroid
An oriented matroid is a mathematical structure that abstracts the properties of directed graphs and of arrangements of vectors in a vector space over an ordered field...
. A solution has been explicitly found for any such game using matroid
Matroid
In combinatorics, a branch of mathematics, a matroid or independence structure is a structure that captures the essence of a notion of "independence" that generalizes linear independence in vector spaces....
theory, unlike a similar game Hex
Hex (board game)
Hex is a board game played on a hexagonal grid, theoretically of any size and several possible shapes, but traditionally as an 11x11 rhombus. Other popular dimensions are 13x13 and 19x19 as a result of the game's relationship to the older game of Go...
, which is PSPACE
PSPACE
In computational complexity theory, PSPACE is the set of all decision problems which can be solved by a Turing machine using a polynomial amount of space.- Formal definition :...
hard.
Winning algorithms
The game always terminates after a finite number of moves, and one of the two players has to win. Either Short, Cut, or the player moving first is guaranteed the existence of a winning strategy on any given graph.The Short and Cut games are a duality; that is, the game can be restated so that both players have the same goal: to secure a certain edge set with distinguished edge e. Short tries to secure the edge set that with e makes up a circuit
Cycle (graph theory)
In graph theory, the term cycle may refer to a closed path. If repeated vertices are allowed, it is more often called a closed walk. If the path is a simple path, with no repeated vertices or edges other than the starting and ending vertices, it may also be called a simple cycle, circuit, circle,...
, while Cut tries to secure an edge set that with e makes up a cutset, the minimal set of edges that connect two subgraphs.
External links
- Graph Game, a Java implementation of the Shannon switching game
- Bridj-It, a PHP implementation of GALE

