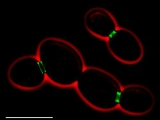
Septins
Encyclopedia
Septins are evolutionary conserved protein
s with essential functions in cytokinesis
, and more subtle roles throughout the cell cycle
. Much of our knowledge about septins originates from studies of budding
yeast
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
, where they form a ring-like protein
scaffold at the mother-bud neck.
and colleagues in a screen for temperature-sensitive mutant
s affecting cell division
(cdc mutant
s). The screen revealed four mutant
s which prevented cytokinesis
at restrictive temperature. The corresponding gene
s represent the four original septins, ScCDC3, ScCDC10, ScCDC11, and ScCDC12. Despite disrupted cytokinesis
, the cells
continued budding
, DNA synthesis
, and nuclear division
, which resulted in large multinucleate
cells with multiple, elongated bud
s. In 1976, analysis of electron micrograph
s revealed ~20 evenly spaced striation
s of 10-nm filament
s around the mother-bud neck in wild-type but not in septin-mutant cells. Immunofluorescence
studies revealed that the septin protein
s colocalize
into a septin ring at the neck. The localization of all four septins is disrupted in conditional Sccdc3 and Sccdc12 mutant
s, indicating interdependence of the septin protein
s. Strong support for this finding was provided by biochemical
studies: The four original septins co-purified on affinity column
s, together with a fifth septin protein
, encoded by ScSEP7 or ScSHS1. Purified septins from budding
yeast
, Drosophila
, Xenopus
, and mammal
ian cells are able to self associate in vitro
to form highly ordered, filamentous structures
. How the septins interact in vitro
to form heteropentamers
that assemble into filaments was studied in detail in S. cerevisiae
. Based on these and former studies, the septins are composed of a variable N-terminus with a basic
phosphoinositide binding
motif
, a conserved core comprising a GTP-binding domain
, a septin-unique element and a C-terminal extension including a predicted coiled coil
.
Micrograph
s of purified filaments
raised the possibility that the septins are organized in parallel to the mother-bud axis. The 10-nm striation
s seen on electron micrograph
s may be the result of lateral interaction between the filament
s. Mutant
strains lacking factors important for septin organization support this view. Instead of continuous rings, the septins form bars oriented along the mother-bud axis in deletion mutant
s of ScGIN4, ScNAP1 and ScCLA4.
s. These protein complexes are involved in cytokinesis
, chitin
deposition, cell
polarity, spore
formation, in the morphogenesis
checkpoint, spindle
alignment checkpoint
and bud site selection.
is driven through two septin dependent, redundant processes: recruitment and contraction of the actomyosin
ring and formation of the septum
by vesicle
fusion with the plasma membrane
. In contrast to septin mutant
s, disruption of one single pathway only leads to a delay in cytokinesis
, not complete failure of cell division
. Hence, the septins are predicted to act at the most upstream level of cytokinesis
.
-isotropic
switch in budding yeast
, cortical
components, supposedly of the exocyst
and polarisome, are delocalized from the apical pole to the entire plasma membrane
of the bud, but not the mother cell. The septin ring at the neck serves as a cortical barrier that prevents membrane diffusion
of these factors between the two compartments. This asymmetric distribution is abolished in septin mutant
s.
Some conditional septin mutant
s do not form bud
s at their normal axial location. Moreover, the typical localization of some bud-site-selection factors in a double ring at the neck is lost or disturbed in these mutant
s. This indicates that the septins may serve as anchoring site for such factors in axially budding
cells.
: The first visible septin structure is a distinct ring which appears ~15 min before bud
emergence. After bud
emergence, the ring broadens to assume the shape of an hourglass
around the mother-bud neck. During cytokinesis
, the septin cortex splits into a double ring which eventually disappears. How can the septin cortex undergo so dramatic changes, although some of its functions may require it to be a stable structure? FRAP
analysis has revealed that the turnover of septins at the neck undergoes multiple changes during the cell cycle
. The predominant, functional conformation is characterized by a low turnover rate (frozen state), during which the septins are phosphorylated
. Structural changes require a destabilization of the septin cortex (fluid state) induced by dephosphorylation
prior to bud
emergence, ring splitting and cell
separation.
The composition of the septin cortex does not only vary throughout the cell cycle
but also along the mother-bud axis. This inherent polarity of septin filament
s allows concentration of some protein
s primarily to the mother side of the neck, some to the center and others to the bud
site.
, septin homologues
have been found throughout the eukaryotic kingdom, with the exception of plant
s. The variety of different shapes that septins can assume within a single cell
is especially apparent in filamentous fungi, where they control aspects of filament
ous morphology
.
of C. albicans
encodes homologues
to all S. cerevisiae
septins (CaCDC3, CaCDC10, CaCDC11, CaCDC12, CaSEP7). They form a diffuse band at the base of emerging hyphae, a bright double ring at septation
sites, an extended diffuse cap at hyphal tips and elongated filament
s stretching around the spherical chlamydospore
s. As an effect of maturation, double rings reflect hyphal polarity by disassembling the tip proximal ring. CaCdc3p and CaCdc12p are essential for proliferation in yeast
or hyphal forms. Cacdc10Δ and Cacdc11Δ deletion mutant
s are viable but show aberrant chitin
localization and cannot properly maintain hyphal growth direction.
(AnAspAp, AnAspBp, AnAspCp, AnAspDp, AnAspEp). AnAspBp forms single rings at septation sites that eventually split into double rings. Additionally, AnAspBp forms a ring at sites of branch emergence which broadens into a band as the branch grows. Like in C. albicans
, double rings reflect polarity of the hypha
, but by disassembling the more basal ring. Bases for the various patterns of septin organization could be different modifications and/or localization of different septin interaction partners. Conditional mutant
s of the essential AnAspBp display diffuse chitin
deposition and a hyper-branching phenotype
.
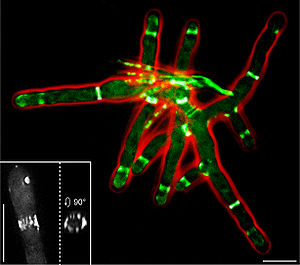 The ascomycete A. gossypii
The ascomycete A. gossypii
possesses homologues
to all S. cerevisiae
septins, with one being duplicated (AgCDC3, AgCDC10, AgCDC11A, AgCDC11B, AgCDC12, AgSEP7). In vivo
studies of AgSep7p-GFP
have revealed that septins assemble into discontinuous hyphal rings close to growing tips and sites of branch formation and into asymmetric
structures at the base of branching points. Rings are made of filament
s which are long and diffuse close to growing tips and short and compact further away from the tip. During septum
formation, the septin ring splits into two to form a double ring. Agcdc3Δ, Agcdc10Δ and Agcdc12Δ deletion mutant
s display aberrant morphology
and are defective for actin
-ring formation, chitin
-ring formation, and sporulation. Due to the lack of septa
, septin deletion mutant
s are highly sensitive, and damage of a single hypha
can result into complete lysis
of a young mycelium
.
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s with essential functions in cytokinesis
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the process in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the late stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a binucleate cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation...
, and more subtle roles throughout the cell cycle
Cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that takes place in a cell leading to its division and duplication . In cells without a nucleus , the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission...
. Much of our knowledge about septins originates from studies of budding
Budding
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction in which a new organism grows on another one. The new organism remains attached as it grows, separating from the parent organism only when it is mature. Since the reproduction is asexual, the newly created organism is a clone and is genetically identical...
yeast
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic micro-organisms classified in the kingdom Fungi, with 1,500 species currently described estimated to be only 1% of all fungal species. Most reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by an asymmetric division process called budding...
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a species of yeast. It is perhaps the most useful yeast, having been instrumental to baking and brewing since ancient times. It is believed that it was originally isolated from the skin of grapes...
, where they form a ring-like protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
scaffold at the mother-bud neck.
Septins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae

History
The septins were discovered in 1970 by Leland H. HartwellLeland H. Hartwell
Leland Harrison Hartwell is former president and director of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, Washington. He shared the 2001 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Paul Nurse and R...
and colleagues in a screen for temperature-sensitive mutant
Mutant
In biology and especially genetics, a mutant is an individual, organism, or new genetic character, arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is a base-pair sequence change within the DNA of a gene or chromosome of an organism resulting in the creation of a new character or trait not...
s affecting cell division
Cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that takes place in a cell leading to its division and duplication . In cells without a nucleus , the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission...
(cdc mutant
Mutant
In biology and especially genetics, a mutant is an individual, organism, or new genetic character, arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is a base-pair sequence change within the DNA of a gene or chromosome of an organism resulting in the creation of a new character or trait not...
s). The screen revealed four mutant
Mutant
In biology and especially genetics, a mutant is an individual, organism, or new genetic character, arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is a base-pair sequence change within the DNA of a gene or chromosome of an organism resulting in the creation of a new character or trait not...
s which prevented cytokinesis
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the process in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the late stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a binucleate cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation...
at restrictive temperature. The corresponding gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
s represent the four original septins, ScCDC3, ScCDC10, ScCDC11, and ScCDC12. Despite disrupted cytokinesis
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the process in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the late stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a binucleate cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation...
, the cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
continued budding
Budding
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction in which a new organism grows on another one. The new organism remains attached as it grows, separating from the parent organism only when it is mature. Since the reproduction is asexual, the newly created organism is a clone and is genetically identical...
, DNA synthesis
DNA replication
DNA replication is a biological process that occurs in all living organisms and copies their DNA; it is the basis for biological inheritance. The process starts with one double-stranded DNA molecule and produces two identical copies of the molecule...
, and nuclear division
Mitosis
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells containing roughly...
, which resulted in large multinucleate
Multinucleate
Multinucleate cells have more than one nucleus per cell, which is the result of nuclear division not being followed by cytokinesis. As a consequence, multiple nuclei share one common cytoplasm. This can be the consequence of a disturbed cell cycle control Multinucleate (also multinucleated,...
cells with multiple, elongated bud
Budding
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction in which a new organism grows on another one. The new organism remains attached as it grows, separating from the parent organism only when it is mature. Since the reproduction is asexual, the newly created organism is a clone and is genetically identical...
s. In 1976, analysis of electron micrograph
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an item.Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy.-Photomicrograph:...
s revealed ~20 evenly spaced striation
Striation
Striations means a series of ridges, furrows or linear marks, and are used in several ways* Glacial striation* Striation , a striation as a result of a geological fault* In medicine, striated muscle...
s of 10-nm filament
Protein filament
In biology, a filament is a "long chain of proteins, such as those found in hair, muscle, or in flagella". They are often bundled together for strength and rigidity. Some cellular examples include:*Actin filaments*Microtubules*Intermediate filaments...
s around the mother-bud neck in wild-type but not in septin-mutant cells. Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence is a technique used for light microscopy with a fluorescence microscope and is used primarily on biological samples. This technique uses the specificity of antibodies to their antigen to target fluorescent dyes to specific biomolecule targets within a cell, and therefore allows...
studies revealed that the septin protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s colocalize
Colocalization
In fluorescence microscopy, colocalization refers to observation of the spatial overlap between two different fluorescent labels, each having a separate emission wavelength, to see if the different "targets" are located in the same area of the cell or very near to one another...
into a septin ring at the neck. The localization of all four septins is disrupted in conditional Sccdc3 and Sccdc12 mutant
Mutant
In biology and especially genetics, a mutant is an individual, organism, or new genetic character, arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is a base-pair sequence change within the DNA of a gene or chromosome of an organism resulting in the creation of a new character or trait not...
s, indicating interdependence of the septin protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s. Strong support for this finding was provided by biochemical
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
studies: The four original septins co-purified on affinity column
Affinity chromatography
Affinity chromatography is a method of separating biochemical mixtures and based on a highly specific interaction such as that between antigen and antibody, enzyme and substrate, or receptor and ligand.-Uses:Affinity chromatography can be used to:...
s, together with a fifth septin protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
, encoded by ScSEP7 or ScSHS1. Purified septins from budding
Budding
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction in which a new organism grows on another one. The new organism remains attached as it grows, separating from the parent organism only when it is mature. Since the reproduction is asexual, the newly created organism is a clone and is genetically identical...
yeast
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic micro-organisms classified in the kingdom Fungi, with 1,500 species currently described estimated to be only 1% of all fungal species. Most reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by an asymmetric division process called budding...
, Drosophila
Drosophila
Drosophila is a genus of small flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "fruit flies" or more appropriately pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many species to linger around overripe or rotting fruit...
, Xenopus
Xenopus
Xenopus is a genus of highly aquatic frogs native to Sub-Saharan Africa. There are 19 species in the Xenopus genus...
, and mammal
Mammal
Mammals are members of a class of air-breathing vertebrate animals characterised by the possession of endothermy, hair, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands functional in mothers with young...
ian cells are able to self associate in vitro
In vitro
In vitro refers to studies in experimental biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological context in order to permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms. Colloquially, these experiments...
to form highly ordered, filamentous structures
Protein filament
In biology, a filament is a "long chain of proteins, such as those found in hair, muscle, or in flagella". They are often bundled together for strength and rigidity. Some cellular examples include:*Actin filaments*Microtubules*Intermediate filaments...
. How the septins interact in vitro
In vitro
In vitro refers to studies in experimental biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological context in order to permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms. Colloquially, these experiments...
to form heteropentamers
Polymer
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
that assemble into filaments was studied in detail in S. cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a species of yeast. It is perhaps the most useful yeast, having been instrumental to baking and brewing since ancient times. It is believed that it was originally isolated from the skin of grapes...
. Based on these and former studies, the septins are composed of a variable N-terminus with a basic
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
phosphoinositide binding
Binding (molecular)
Molecular binding is an attractive interaction between two molecules which results in a stable association in which the molecules are in close proximity to each other...
motif
Sequence motif
In genetics, a sequence motif is a nucleotide or amino-acid sequence pattern that is widespread and has, or is conjectured to have, a biological significance...
, a conserved core comprising a GTP-binding domain
G protein
G proteins are a family of proteins involved in transmitting chemical signals outside the cell, and causing changes inside the cell. They communicate signals from many hormones, neurotransmitters, and other signaling factors. G protein-coupled receptors are transmembrane receptors...
, a septin-unique element and a C-terminal extension including a predicted coiled coil
Coiled coil
A coiled coil is a structural motif in proteins, in which 2-7 alpha-helices are coiled together like the strands of a rope . Many coiled coil type proteins are involved in important biological functions such as the regulation of gene expression e.g. transcription factors...
.
Micrograph
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an item.Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy.-Photomicrograph:...
s of purified filaments
Protein filament
In biology, a filament is a "long chain of proteins, such as those found in hair, muscle, or in flagella". They are often bundled together for strength and rigidity. Some cellular examples include:*Actin filaments*Microtubules*Intermediate filaments...
raised the possibility that the septins are organized in parallel to the mother-bud axis. The 10-nm striation
Striation
Striations means a series of ridges, furrows or linear marks, and are used in several ways* Glacial striation* Striation , a striation as a result of a geological fault* In medicine, striated muscle...
s seen on electron micrograph
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an item.Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy.-Photomicrograph:...
s may be the result of lateral interaction between the filament
Protein filament
In biology, a filament is a "long chain of proteins, such as those found in hair, muscle, or in flagella". They are often bundled together for strength and rigidity. Some cellular examples include:*Actin filaments*Microtubules*Intermediate filaments...
s. Mutant
Mutant
In biology and especially genetics, a mutant is an individual, organism, or new genetic character, arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is a base-pair sequence change within the DNA of a gene or chromosome of an organism resulting in the creation of a new character or trait not...
strains lacking factors important for septin organization support this view. Instead of continuous rings, the septins form bars oriented along the mother-bud axis in deletion mutant
Mutant
In biology and especially genetics, a mutant is an individual, organism, or new genetic character, arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is a base-pair sequence change within the DNA of a gene or chromosome of an organism resulting in the creation of a new character or trait not...
s of ScGIN4, ScNAP1 and ScCLA4.
Scaffold
The septins act as a scaffold, recruiting a plethora of proteinProtein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s. These protein complexes are involved in cytokinesis
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the process in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the late stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a binucleate cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation...
, chitin
Chitin
Chitin n is a long-chain polymer of a N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose, and is found in many places throughout the natural world...
deposition, cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
polarity, spore
Spore
In biology, a spore is a reproductive structure that is adapted for dispersal and surviving for extended periods of time in unfavorable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many bacteria, plants, algae, fungi and some protozoa. According to scientist Dr...
formation, in the morphogenesis
Morphogenesis
Morphogenesis , is the biological process that causes an organism to develop its shape...
checkpoint, spindle
Mitotic spindle
In cell biology, the spindle fibers are the structure that separates the chromosomes into the daughter cells during cell division. It is part of the cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells...
alignment checkpoint
Cell cycle checkpoint
Cell cycle checkpoints are control mechanisms that ensure the fidelity of cell division in eukaryotic cells. These checkpoints verify whether the processes at each phase of the cell cycle have been accurately completed before progression into the next phase...
and bud site selection.
Cytokinesis
Budding yeast cytokinesisCytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the process in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the late stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a binucleate cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation...
is driven through two septin dependent, redundant processes: recruitment and contraction of the actomyosin
Myofibril
A myofibril is a basic unit of a muscle. Muscles are composed of tubular cells called myocytes or myofibers. Myofibers are composed of tubular myofibrils. Myofibrils are composed of long proteins such as actin, myosin, and titin, and other proteins that hold them together...
ring and formation of the septum
Septum
In anatomy, a septum is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones.-In human anatomy:...
by vesicle
Vesicle (biology)
A vesicle is a bubble of liquid within another liquid, a supramolecular assembly made up of many different molecules. More technically, a vesicle is a small membrane-enclosed sack that can store or transport substances. Vesicles can form naturally because of the properties of lipid membranes , or...
fusion with the plasma membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
. In contrast to septin mutant
Mutant
In biology and especially genetics, a mutant is an individual, organism, or new genetic character, arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is a base-pair sequence change within the DNA of a gene or chromosome of an organism resulting in the creation of a new character or trait not...
s, disruption of one single pathway only leads to a delay in cytokinesis
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the process in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the late stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a binucleate cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation...
, not complete failure of cell division
Cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells . Cell division is usually a small segment of a larger cell cycle. This type of cell division in eukaryotes is known as mitosis, and leaves the daughter cell capable of dividing again. The corresponding sort...
. Hence, the septins are predicted to act at the most upstream level of cytokinesis
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the process in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the late stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a binucleate cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation...
.
Cell polarity
After the apicalApical
Apical, from the Latin apex meaning to be at the apex or tip, may refer to:*Apical , an anatomical term of location for features associated with the base of an organism or structure...
-isotropic
Isotropy
Isotropy is uniformity in all orientations; it is derived from the Greek iso and tropos . Precise definitions depend on the subject area. Exceptions, or inequalities, are frequently indicated by the prefix an, hence anisotropy. Anisotropy is also used to describe situations where properties vary...
switch in budding yeast
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a species of yeast. It is perhaps the most useful yeast, having been instrumental to baking and brewing since ancient times. It is believed that it was originally isolated from the skin of grapes...
, cortical
Cortex (anatomy)
In anatomy and zoology the cortex is the outermost layer of an organ. Organs with well-defined cortical layers include kidneys, adrenal glands, ovaries, the thymus, and portions of the brain, including the cerebral cortex, the most well-known of all cortices.The cerebellar cortex is the thin gray...
components, supposedly of the exocyst
Exocyst
The exocyst is an octameric protein complex involved in vesicle trafficking, specifically the tethering and spatial targeting of post-Golgi vesicles to the plasma membrane prior to vesicle fusion. It is implicated in a number of cell processes, including exocytosis and also cell migration and...
and polarisome, are delocalized from the apical pole to the entire plasma membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
of the bud, but not the mother cell. The septin ring at the neck serves as a cortical barrier that prevents membrane diffusion
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
of these factors between the two compartments. This asymmetric distribution is abolished in septin mutant
Mutant
In biology and especially genetics, a mutant is an individual, organism, or new genetic character, arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is a base-pair sequence change within the DNA of a gene or chromosome of an organism resulting in the creation of a new character or trait not...
s.
Some conditional septin mutant
Mutant
In biology and especially genetics, a mutant is an individual, organism, or new genetic character, arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is a base-pair sequence change within the DNA of a gene or chromosome of an organism resulting in the creation of a new character or trait not...
s do not form bud
Budding
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction in which a new organism grows on another one. The new organism remains attached as it grows, separating from the parent organism only when it is mature. Since the reproduction is asexual, the newly created organism is a clone and is genetically identical...
s at their normal axial location. Moreover, the typical localization of some bud-site-selection factors in a double ring at the neck is lost or disturbed in these mutant
Mutant
In biology and especially genetics, a mutant is an individual, organism, or new genetic character, arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is a base-pair sequence change within the DNA of a gene or chromosome of an organism resulting in the creation of a new character or trait not...
s. This indicates that the septins may serve as anchoring site for such factors in axially budding
Budding
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction in which a new organism grows on another one. The new organism remains attached as it grows, separating from the parent organism only when it is mature. Since the reproduction is asexual, the newly created organism is a clone and is genetically identical...
cells.
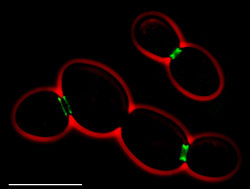
Organization
It seems that one single septin organization should not be sufficient to fulfill such a variety of tasks. Accordingly, the septin cortex undergoes several changes throughout the cell cycleCell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that takes place in a cell leading to its division and duplication . In cells without a nucleus , the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission...
: The first visible septin structure is a distinct ring which appears ~15 min before bud
Budding
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction in which a new organism grows on another one. The new organism remains attached as it grows, separating from the parent organism only when it is mature. Since the reproduction is asexual, the newly created organism is a clone and is genetically identical...
emergence. After bud
Budding
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction in which a new organism grows on another one. The new organism remains attached as it grows, separating from the parent organism only when it is mature. Since the reproduction is asexual, the newly created organism is a clone and is genetically identical...
emergence, the ring broadens to assume the shape of an hourglass
Hourglass
An hourglass measures the passage of a few minutes or an hour of time. It has two connected vertical glass bulbs allowing a regulated trickle of material from the top to the bottom. Once the top bulb is empty, it can be inverted to begin timing again. The name hourglass comes from historically...
around the mother-bud neck. During cytokinesis
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the process in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the late stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a binucleate cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation...
, the septin cortex splits into a double ring which eventually disappears. How can the septin cortex undergo so dramatic changes, although some of its functions may require it to be a stable structure? FRAP
Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching
Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching denotes an optical technique capable of quantifying the two dimensional lateral diffusion of a molecularly thin film containing fluorescently labeled probes, or to examine single cells. This technique is very useful in biological studies of cell membrane...
analysis has revealed that the turnover of septins at the neck undergoes multiple changes during the cell cycle
Cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that takes place in a cell leading to its division and duplication . In cells without a nucleus , the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission...
. The predominant, functional conformation is characterized by a low turnover rate (frozen state), during which the septins are phosphorylated
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation activates or deactivates many protein enzymes....
. Structural changes require a destabilization of the septin cortex (fluid state) induced by dephosphorylation
Dephosphorylation
Dephosphorylation is the essential process of removing phosphate groups from an organic compound by hydrolysis. Its opposite is phosphorylation...
prior to bud
Budding
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction in which a new organism grows on another one. The new organism remains attached as it grows, separating from the parent organism only when it is mature. Since the reproduction is asexual, the newly created organism is a clone and is genetically identical...
emergence, ring splitting and cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
separation.
The composition of the septin cortex does not only vary throughout the cell cycle
Cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that takes place in a cell leading to its division and duplication . In cells without a nucleus , the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission...
but also along the mother-bud axis. This inherent polarity of septin filament
Protein filament
In biology, a filament is a "long chain of proteins, such as those found in hair, muscle, or in flagella". They are often bundled together for strength and rigidity. Some cellular examples include:*Actin filaments*Microtubules*Intermediate filaments...
s allows concentration of some protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s primarily to the mother side of the neck, some to the center and others to the bud
Budding
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction in which a new organism grows on another one. The new organism remains attached as it grows, separating from the parent organism only when it is mature. Since the reproduction is asexual, the newly created organism is a clone and is genetically identical...
site.
Septins in filamentous fungi
Since their discovery in S. cerevisiaeSaccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a species of yeast. It is perhaps the most useful yeast, having been instrumental to baking and brewing since ancient times. It is believed that it was originally isolated from the skin of grapes...
, septin homologues
Homology (biology)
Homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. In 1843, Richard Owen defined homology as "the same organ in different animals under every variety of form and function". Organs as different as a bat's wing, a seal's flipper, a cat's paw and a human hand have a common underlying...
have been found throughout the eukaryotic kingdom, with the exception of plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s. The variety of different shapes that septins can assume within a single cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
is especially apparent in filamentous fungi, where they control aspects of filament
Protein filament
In biology, a filament is a "long chain of proteins, such as those found in hair, muscle, or in flagella". They are often bundled together for strength and rigidity. Some cellular examples include:*Actin filaments*Microtubules*Intermediate filaments...
ous morphology
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
.
Candida albicans
The genomeGenome
In modern molecular biology and genetics, the genome is the entirety of an organism's hereditary information. It is encoded either in DNA or, for many types of virus, in RNA. The genome includes both the genes and the non-coding sequences of the DNA/RNA....
of C. albicans
Candida albicans
Candida albicans is a diploid fungus that grows both as yeast and filamentous cells and a causal agent of opportunistic oral and genital infections in humans. Systemic fungal infections including those by C...
encodes homologues
Homology (biology)
Homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. In 1843, Richard Owen defined homology as "the same organ in different animals under every variety of form and function". Organs as different as a bat's wing, a seal's flipper, a cat's paw and a human hand have a common underlying...
to all S. cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a species of yeast. It is perhaps the most useful yeast, having been instrumental to baking and brewing since ancient times. It is believed that it was originally isolated from the skin of grapes...
septins (CaCDC3, CaCDC10, CaCDC11, CaCDC12, CaSEP7). They form a diffuse band at the base of emerging hyphae, a bright double ring at septation
Septation
Septation may refer to:*Cell division*Formation of the septum during heart development...
sites, an extended diffuse cap at hyphal tips and elongated filament
Protein filament
In biology, a filament is a "long chain of proteins, such as those found in hair, muscle, or in flagella". They are often bundled together for strength and rigidity. Some cellular examples include:*Actin filaments*Microtubules*Intermediate filaments...
s stretching around the spherical chlamydospore
Chlamydospore
A Chlamydospore is the thick-walled big resting spore of several kinds of fungi. It is the life-stage which survives in unfavourable conditions, such as dry or hot seasons....
s. As an effect of maturation, double rings reflect hyphal polarity by disassembling the tip proximal ring. CaCdc3p and CaCdc12p are essential for proliferation in yeast
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic micro-organisms classified in the kingdom Fungi, with 1,500 species currently described estimated to be only 1% of all fungal species. Most reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by an asymmetric division process called budding...
or hyphal forms. Cacdc10Δ and Cacdc11Δ deletion mutant
Mutant
In biology and especially genetics, a mutant is an individual, organism, or new genetic character, arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is a base-pair sequence change within the DNA of a gene or chromosome of an organism resulting in the creation of a new character or trait not...
s are viable but show aberrant chitin
Chitin
Chitin n is a long-chain polymer of a N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose, and is found in many places throughout the natural world...
localization and cannot properly maintain hyphal growth direction.
Aspergillus nidulans
Five septins are found in A. nidulansAspergillus nidulans
Aspergillus nidulans is one of many species of filamentous fungi in the phylum Ascomycota...
(AnAspAp, AnAspBp, AnAspCp, AnAspDp, AnAspEp). AnAspBp forms single rings at septation sites that eventually split into double rings. Additionally, AnAspBp forms a ring at sites of branch emergence which broadens into a band as the branch grows. Like in C. albicans
Candida albicans
Candida albicans is a diploid fungus that grows both as yeast and filamentous cells and a causal agent of opportunistic oral and genital infections in humans. Systemic fungal infections including those by C...
, double rings reflect polarity of the hypha
Hypha
A hypha is a long, branching filamentous structure of a fungus, and also of unrelated Actinobacteria. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium; yeasts are unicellular fungi that do not grow as hyphae.-Structure:A hypha consists of one or...
, but by disassembling the more basal ring. Bases for the various patterns of septin organization could be different modifications and/or localization of different septin interaction partners. Conditional mutant
Mutant
In biology and especially genetics, a mutant is an individual, organism, or new genetic character, arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is a base-pair sequence change within the DNA of a gene or chromosome of an organism resulting in the creation of a new character or trait not...
s of the essential AnAspBp display diffuse chitin
Chitin
Chitin n is a long-chain polymer of a N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose, and is found in many places throughout the natural world...
deposition and a hyper-branching phenotype
Phenotype
A phenotype is an organism's observable characteristics or traits: such as its morphology, development, biochemical or physiological properties, behavior, and products of behavior...
.
Ashbya gossypii

Ashbya gossypii
Ashbya gossypii is a filamentous fungus or mold closely related to yeast, but growing exclusively in a filamentous way. It was originally isolated from cotton as a pathogen causing stigmatomycosis by Ashby and Novell in 1926...
possesses homologues
Homology (biology)
Homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. In 1843, Richard Owen defined homology as "the same organ in different animals under every variety of form and function". Organs as different as a bat's wing, a seal's flipper, a cat's paw and a human hand have a common underlying...
to all S. cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a species of yeast. It is perhaps the most useful yeast, having been instrumental to baking and brewing since ancient times. It is believed that it was originally isolated from the skin of grapes...
septins, with one being duplicated (AgCDC3, AgCDC10, AgCDC11A, AgCDC11B, AgCDC12, AgSEP7). In vivo
In vivo
In vivo is experimentation using a whole, living organism as opposed to a partial or dead organism, or an in vitro controlled environment. Animal testing and clinical trials are two forms of in vivo research...
studies of AgSep7p-GFP
Green fluorescent protein
The green fluorescent protein is a protein composed of 238 amino acid residues that exhibits bright green fluorescence when exposed to blue light. Although many other marine organisms have similar green fluorescent proteins, GFP traditionally refers to the protein first isolated from the...
have revealed that septins assemble into discontinuous hyphal rings close to growing tips and sites of branch formation and into asymmetric
Asymmetry
Asymmetry is the absence of, or a violation of, symmetry.-In organisms:Due to how cells divide in organisms, asymmetry in organisms is fairly usual in at least one dimension, with biological symmetry also being common in at least one dimension....
structures at the base of branching points. Rings are made of filament
Protein filament
In biology, a filament is a "long chain of proteins, such as those found in hair, muscle, or in flagella". They are often bundled together for strength and rigidity. Some cellular examples include:*Actin filaments*Microtubules*Intermediate filaments...
s which are long and diffuse close to growing tips and short and compact further away from the tip. During septum
Septum
In anatomy, a septum is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones.-In human anatomy:...
formation, the septin ring splits into two to form a double ring. Agcdc3Δ, Agcdc10Δ and Agcdc12Δ deletion mutant
Mutant
In biology and especially genetics, a mutant is an individual, organism, or new genetic character, arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is a base-pair sequence change within the DNA of a gene or chromosome of an organism resulting in the creation of a new character or trait not...
s display aberrant morphology
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
and are defective for actin
Actin
Actin is a globular, roughly 42-kDa moonlighting protein found in all eukaryotic cells where it may be present at concentrations of over 100 μM. It is also one of the most highly-conserved proteins, differing by no more than 20% in species as diverse as algae and humans...
-ring formation, chitin
Chitin
Chitin n is a long-chain polymer of a N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose, and is found in many places throughout the natural world...
-ring formation, and sporulation. Due to the lack of septa
Septum
In anatomy, a septum is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones.-In human anatomy:...
, septin deletion mutant
Mutant
In biology and especially genetics, a mutant is an individual, organism, or new genetic character, arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is a base-pair sequence change within the DNA of a gene or chromosome of an organism resulting in the creation of a new character or trait not...
s are highly sensitive, and damage of a single hypha
Hypha
A hypha is a long, branching filamentous structure of a fungus, and also of unrelated Actinobacteria. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium; yeasts are unicellular fungi that do not grow as hyphae.-Structure:A hypha consists of one or...
can result into complete lysis
Lysis
Lysis refers to the breaking down of a cell, often by viral, enzymic, or osmotic mechanisms that compromise its integrity. A fluid containing the contents of lysed cells is called a "lysate"....
of a young mycelium
Mycelium
thumb|right|Fungal myceliaMycelium is the vegetative part of a fungus, consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae. The mass of hyphae is sometimes called shiro, especially within the fairy ring fungi. Fungal colonies composed of mycelia are found in soil and on or within many other...
.
In mitochondria
The septin localized in the mitochondria is called mitochondrial septin (M-septin). It was identified as a CRMP/CRAM-interacting protein in developing mouse brain.Further reading
- "The septins: roles in cytokinesis and other processes." Longtine, M.S., DeMarini, D.J., Valencik, M.L., Al-Awar, O.S., Fares, H., De Virgilio, C., and Pringle, J.R. (1996). Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 8, 106-119.
- "The septin cortex at the yeast mother-bud neck." Gladfelter, A.S., Pringle, J.R., and Lew, D.J. (2001). Curr Opin Microbiol 4, 681-689.
- "Septins: a ring to part mother and daughter." Faty, M., Fink, M., and Barral, Y. (2002). Curr Genet 41, 123-131.
- "Protein-protein interactions governing septin heteropentamer assembly and septin filament organization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae." Versele, M., Gullbrand, B., Shulewitz, M.J., Cid, V.J., Bahmanyar, S., Chen, R.E., Barth, P., Alber, T., and Thorner, J. (2004). Mol Biol Cell 15, 4568-4583.
- "Septin function in yeast model systems and pathogenic fungi." Douglas, L.M., Alvarez, F.J., McCreary, C., and Konopka, J.B. (2005). Eukaryot Cell 4, 1503-1512.
- "Control of filamentous fungal cell shape by septins and formins." Gladfelter, A.S. (2006). Nat Rev Microbiol 4, 223-229.
- "The Septins." Hall, Peter A., Russell, S.E. Hilary, and Pringle, John R. (2008). Chichester, U.K. : Wiley-Blackwell, 2008. 370 p. ISBN 978-0-470-51969-1.

