
Sellmeier equation
Encyclopedia
Empirical relationship
In science, an empirical relationship is one based solely on observation rather than theory. An empirical relationship requires only confirmatory data irrespective of theoretical basis. Sometimes theoretical explanations for what were initially empirical relationships are found, in which case the...
between refractive index
Refractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
and wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
for a particular transparent medium. The equation is used to determine the dispersion
Dispersion (optics)
In optics, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency, or alternatively when the group velocity depends on the frequency.Media having such a property are termed dispersive media...
of light
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
in the medium.
It was first proposed in 1871 by Wolfgang Sellmeier, and was a development of the work of Augustin Cauchy
Augustin Louis Cauchy
Baron Augustin-Louis Cauchy was a French mathematician who was an early pioneer of analysis. He started the project of formulating and proving the theorems of infinitesimal calculus in a rigorous manner, rejecting the heuristic principle of the generality of algebra exploited by earlier authors...
on Cauchy's equation
Cauchy's equation
Cauchy's equation is an empirical relationship between the refractive index and wavelength of light for a particular transparent material. It is named for the mathematician Augustin Louis Cauchy, who defined it in 1836.-The equation:...
for modelling dispersion.
The equation
The usual form of the equation for glasses is
where n is the refractive index, λ is the wavelength, and B1,2,3 and C1,2,3 are experimentally determined Sellmeier coefficient
Coefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of an expression ; it is usually a number, but in any case does not involve any variables of the expression...
s. These coefficients are usually quoted for λ in micrometre
Micrometre
A micrometer , is by definition 1×10-6 of a meter .In plain English, it means one-millionth of a meter . Its unit symbol in the International System of Units is μm...
s. Note that this λ is the vacuum wavelength; not that in the material itself, which is λ/n(λ). A different form of the equation is sometimes used for certain types of materials, e.g. crystal
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituent atoms, molecules, or ions are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern extending in all three spatial dimensions. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography...
s.
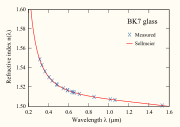
As an example, the coefficients for a common borosilicate
Borosilicate glass
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with the main glass-forming constituents silica and boron oxide. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion , making them resistant to thermal shock, more so than any other common glass...
crown glass
Crown glass (optics)
Crown glass is type of optical glass used in lenses and other optical components. It has relatively low refractive index and low dispersion...
known as BK7 are shown below:
| Coefficient | Value |
|---|---|
| B1 | 1.03961212 |
| B2 | 0.231792344 |
| B3 | 1.01046945 |
| C1 | 6.00069867×10−3 μm2 |
| C2 | 2.00179144×10−2 μm2 |
| C3 | 1.03560653×102 μm2 |
The Sellmeier coefficients for many common optical glasses can be found in the Schott Glass
Schott Glass
SCHOTT AG is a German manufacturer of high-quality industrial glass products, its main markets are household appliances, pharmaceutical industries, solar energy, electronics, optics as well as automotive...
catalogue, or in the Ohara
Ohara Corporation
Ohara Corporation is the U.S. subsidiary of the . The parent company is headquartered in Japan. There are subsidiaries in a number of countries, including Japan, the United States, Germany, Hong Kong, Maylasia, Taiwan, and China....
catalogue.
For common optical glasses, the refractive index calculated with the three-term Sellmeier equation deviates from the actual refractive index by less than 5×10−6 over the wavelengths range of 365 nm to 2.3 µm,http://oharacorp.com/o2.html which is of the order of the homogeneity of a glass sample.http://oharacorp.com/o7.html Additional terms are sometimes added to make the calculation even more precise. In its most general form, the Sellmeier equation is given as

with each term of the sum representing an absorption resonance of strength Bi at a wavelength √Ci. For example, the coefficients for BK7 above correspond to two absorption resonances in the ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
, and one in the mid-infrared
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
region. Close to each absorption peak, the equation gives non-physical values of
 =±∞, and in these wavelength regions a more precise model of dispersion such as Helmholtz's must be used.
=±∞, and in these wavelength regions a more precise model of dispersion such as Helmholtz's must be used.If all terms are specified for a material, at long wavelengths far from the absorption peaks the value of n tends to

where εr is the relative dielectric constant
Dielectric constant
The relative permittivity of a material under given conditions reflects the extent to which it concentrates electrostatic lines of flux. In technical terms, it is the ratio of the amount of electrical energy stored in a material by an applied voltage, relative to that stored in a vacuum...
of the medium.
The Sellmeier equation can also be given in another form:

Here the coefficient A is an approximation of the short-wavelength (e.g., ultraviolet) absorption contributions to the refractive index at longer wavelengths. Other variants of the Sellmeier equation exist that can account for a material's refractive index change due to temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
, pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
, and other parameters.
Coefficients
| Table of coefficients of Sellmeier equationhttp://cvimellesgriot.com/products/Documents/Catalog/Dispersion_Equations.pdf | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | B1 | B2 | B3 | C1 | C2 | C3 |
| borosilicate Borosilicate glass Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with the main glass-forming constituents silica and boron oxide. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion , making them resistant to thermal shock, more so than any other common glass... crown glass Glass Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives... (known as BK7) |
1.03961212 | 0.231792344 | 1.01046945 | 6.00069867×10−3µm2 | 2.00179144×10−2µm2 | 1.03560653×102µm2 |
| sapphire (for ordinary wave) |
1.43134930 | 0.65054713 | 5.3414021 | 5.2799261×10−3µm2 | 1.42382647×10−2µm2 | 3.25017834×102µm2 |
| sapphire (for extraordinary wave) |
1.5039759 | 0.55069141 | 6.5927379 | 5.48041129×10−3µm2 | 1.47994281×10−2µm2 | 4.0289514×102µm2 |
| fused silica Fused quartz Fused quartz and fused silica are types of glass containing primarily silica in amorphous form. They are manufactured using several different processes... |
0.696166300 | 0.407942600 | 0.897479400 | 4.67914826×10−3µm2 | 1.35120631×10−2µm2 | 97.9340025 µm2 |
External links
- A PDF giving Sellmeier coefficients for several common glasses and optical materials
- http://www.schott.com/optics_devices/german/download/opticalglassdatasheetsv101007.xlsAn XLS file with dispersion coefficients and other optical properties of all SchottSchott GlassSCHOTT AG is a German manufacturer of high-quality industrial glass products, its main markets are household appliances, pharmaceutical industries, solar energy, electronics, optics as well as automotive...
] glasses. (Broken link.) - A browser-based calculator giving refractive index from Sellmeier coefficients.
- Annalen der Physik - free Access, digitized by the french national library

