
Screening effect
Encyclopedia
In solids, especially in metals and semiconductors, the electrostatic screening or screening effect reduces the electrostatic field
and Coulomb potential
of an ion inside the solid. Like the electric field of the nucleus is reduced inside an atom or ion due to the shielding effect
, the electric fields of ions in conducting solids are further reduced by the cloud of conduction electrons. The screened Coulomb potential is expressed as

where Z is the atomic number
, e is the elementary unit charge, r is the distance to the nucleus of the embedded ion and q is a screening parameter that determines the range of the potential. The screening parameter q plays an important role in theoretical models in solid-state physics
. The screened electrostatic potential, like the Yukawa potential, has a simple Fourier transform
, expressed as
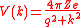
The screened potential determines the inter atomic force and the phonon
dispersion relation in metals
. The screened potential is used to calculate the electronic band structure
of a large variety of materials, often in combination with pseudopotential
models.
Electric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
and Coulomb potential
Coulomb's law
Coulomb's law or Coulomb's inverse-square law, is a law of physics describing the electrostatic interaction between electrically charged particles. It was first published in 1785 by French physicist Charles Augustin de Coulomb and was essential to the development of the theory of electromagnetism...
of an ion inside the solid. Like the electric field of the nucleus is reduced inside an atom or ion due to the shielding effect
Shielding effect
The shielding effect describes the decrease in attraction between an electron and the nucleus in any atom with more than one electron shell. It is also referred to as the screening effect or atomic shielding.-Cause:...
, the electric fields of ions in conducting solids are further reduced by the cloud of conduction electrons. The screened Coulomb potential is expressed as

where Z is the atomic number
Atomic number
In chemistry and physics, the atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom and therefore identical to the charge number of the nucleus. It is conventionally represented by the symbol Z. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element...
, e is the elementary unit charge, r is the distance to the nucleus of the embedded ion and q is a screening parameter that determines the range of the potential. The screening parameter q plays an important role in theoretical models in solid-state physics
Solid-state physics
Solid-state physics is the study of rigid matter, or solids, through methods such as quantum mechanics, crystallography, electromagnetism, and metallurgy. It is the largest branch of condensed matter physics. Solid-state physics studies how the large-scale properties of solid materials result from...
. The screened electrostatic potential, like the Yukawa potential, has a simple Fourier transform
Fourier transform
In mathematics, Fourier analysis is a subject area which grew from the study of Fourier series. The subject began with the study of the way general functions may be represented by sums of simpler trigonometric functions...
, expressed as
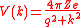
The screened potential determines the inter atomic force and the phonon
Phonon
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, such as solids and some liquids...
dispersion relation in metals
Metallic bond
Metallic bonding is the electrostatic attractive forces between the delocalized electrons, called conduction electrons, gathered in an "electron sea", and the positively charged metal ions...
. The screened potential is used to calculate the electronic band structure
Electronic band structure
In solid-state physics, the electronic band structure of a solid describes those ranges of energy an electron is "forbidden" or "allowed" to have. Band structure derives from the diffraction of the quantum mechanical electron waves in a periodic crystal lattice with a specific crystal system and...
of a large variety of materials, often in combination with pseudopotential
Pseudopotential
In physics, a pseudopotential or effective potential is used as an approximation for the simplified description of complex systems. Applications include atomic physics and neutron scattering.- Atomic physics :...
models.

