
SCFM
Encyclopedia
Standard cubic feet per minute (SCFM) is the volumetric flow rate
of a gas corrected to "standardized" conditions of temperature
and pressure
. It is equivalent to the molar flow rate by the ideal gas law. Conversion of SCFM to mass flow requires knowledge of the mixture averaged gas molecular weight. Consider that one mole of gas (STP) occupies about 22.414 liters. Thus, a one mole/second flow of hydrogen corresponds to 1g/s whereas a one mole/second flow of Krypton, MW=83.8, results in 83.8 g/s flow.
However, great care must be taken, as the "standard" conditions vary between definitions and should therefore always be checked. Worldwide, the "standard" condition for pressure is variously defined as an absolute pressure of 101,325 pascals
, 1.0 bar (i.e., 100,000 pascals), 14.73 psia, or 14.696 psia and the "standard" temperature is variously defined as 68 °F, 60 °F, 0 °C, 15 °C, 20 °C or 25 °C. The relative humidity (e.g., 36% or 0%) is also included in some definitions of standard conditions. There is, in fact, no universally accepted set of standard conditions. (See Standard conditions for temperature and pressure
).
The temperature variation is the most important. In Europe
, the standard temperature is most commonly defined as 0°C, but not always. In the United States
, the standard temperature is most commonly defined as 60 °F or 70 °F, but again, not always. A variation in standard temperature can result in a significant volumetric variation for the same mass flow rate. For example, a mass flow rate of 1,000 kg/h of air at 1 atmosphere of absolute pressure is 455 SCFM when defined at 0 °C (32 °F) but 481 SCFM when defined at 60 °F (15.56 °C).
In countries using the SI metric system of unit, the term "normal cubic metre" (Nm3) is very often used to denote gas volumes at some normalized or standard condition. Again, as noted above, there is no universally accepted set of normalized or standard conditions.
must be created. When positive pressure is applied to a standard cubic foot of gas, it is compressed. When a vacuum is applied to a standard cubic foot of gas, it expands. The volume of gas after it is pressurized or rarefied is referred to as its "actual" volume.
SCF and ACF for any gas are related in accordance with the combined gas law
:
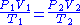
Defining standard conditions by the subscript 1 and actual conditions by the subscript 2, then:

where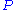 is in absolute pressure units and
is in absolute pressure units and 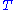
is in absolute temperature units (i.e., either kelvin
s or degrees Rankine).
To be very precise when the gas is air, then the above equation should include correcting for the difference between the relative humidity of the air at the standard and the actual temperature and pressure conditions. In most cases of engineering design, the humidity correction for air is often quite small and hence often ignored.
is a constant CFM device or a constant volume device. This means that, provided the fan speed remains constant, a centrifugal fan will pump a constant volume of air. This is not the same as pumping a constant mass of air. Again, the fan will pump the same volume, though not mass, at any other air density. This means that the air velocity in a system is the same even though mass flow rate through the fan is not.
Volumetric flow rate
The volumetric flow rate in fluid dynamics and hydrometry, is the volume of fluid which passes through a given surface per unit time...
of a gas corrected to "standardized" conditions of temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
and pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
. It is equivalent to the molar flow rate by the ideal gas law. Conversion of SCFM to mass flow requires knowledge of the mixture averaged gas molecular weight. Consider that one mole of gas (STP) occupies about 22.414 liters. Thus, a one mole/second flow of hydrogen corresponds to 1g/s whereas a one mole/second flow of Krypton, MW=83.8, results in 83.8 g/s flow.
However, great care must be taken, as the "standard" conditions vary between definitions and should therefore always be checked. Worldwide, the "standard" condition for pressure is variously defined as an absolute pressure of 101,325 pascals
Pascal (unit)
The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
, 1.0 bar (i.e., 100,000 pascals), 14.73 psia, or 14.696 psia and the "standard" temperature is variously defined as 68 °F, 60 °F, 0 °C, 15 °C, 20 °C or 25 °C. The relative humidity (e.g., 36% or 0%) is also included in some definitions of standard conditions. There is, in fact, no universally accepted set of standard conditions. (See Standard conditions for temperature and pressure
Standard conditions for temperature and pressure
Standard condition for temperature and pressure are standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements established to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data...
).
The temperature variation is the most important. In Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, the standard temperature is most commonly defined as 0°C, but not always. In the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, the standard temperature is most commonly defined as 60 °F or 70 °F, but again, not always. A variation in standard temperature can result in a significant volumetric variation for the same mass flow rate. For example, a mass flow rate of 1,000 kg/h of air at 1 atmosphere of absolute pressure is 455 SCFM when defined at 0 °C (32 °F) but 481 SCFM when defined at 60 °F (15.56 °C).
In countries using the SI metric system of unit, the term "normal cubic metre" (Nm3) is very often used to denote gas volumes at some normalized or standard condition. Again, as noted above, there is no universally accepted set of normalized or standard conditions.
Actual cubic feet per minute
Actual cubic foot per minute (ACFM) is the volume of gas flowing anywhere in a system, independent of its temperature and pressure. If the system were moving a gas at exactly the "standard" condition, then ACFM would equal SCFM. Unfortunately, this usually is not the case as the most important change between these two definitions is the pressure. To move a gas, a positive pressure or a vacuumVacuum
In everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
must be created. When positive pressure is applied to a standard cubic foot of gas, it is compressed. When a vacuum is applied to a standard cubic foot of gas, it expands. The volume of gas after it is pressurized or rarefied is referred to as its "actual" volume.
SCF and ACF for any gas are related in accordance with the combined gas law
Combined gas law
The combined gas law is a gas law which combines Charles's law, Boyle's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. These laws each relate one thermodynamic variable to another mathematically while holding everything else constant. Charles's law states that volume and temperature are directly proportional to each...
:
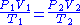
Defining standard conditions by the subscript 1 and actual conditions by the subscript 2, then:

where
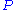 is in absolute pressure units and
is in absolute pressure units and 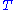
is in absolute temperature units (i.e., either kelvin
Kelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
s or degrees Rankine).
To be very precise when the gas is air, then the above equation should include correcting for the difference between the relative humidity of the air at the standard and the actual temperature and pressure conditions. In most cases of engineering design, the humidity correction for air is often quite small and hence often ignored.
Cubic feet per minute
Cubic feet per minute (CFM) is an often confusing term because it has no single definition that applies to all instances. In the most basic sense, CFM means cubic feet per minute. Unfortunately, gases are compressible, which means that a figure in cubic feet per minute cannot be compared with another figure when it comes the mass of the gas. To further confuse the issue, a centrifugal fanCentrifugal fan
A centrifugal fan is a mechanical device for moving air or other gases. It has a fan wheel composed of a number of fan blades, or ribs, mounted around a hub. As shown in Figure 1, the hub turns on a driveshaft that passes through the fan housing...
is a constant CFM device or a constant volume device. This means that, provided the fan speed remains constant, a centrifugal fan will pump a constant volume of air. This is not the same as pumping a constant mass of air. Again, the fan will pump the same volume, though not mass, at any other air density. This means that the air velocity in a system is the same even though mass flow rate through the fan is not.
See also
- Gas lawsGas lawsThe early gas laws were developed at the end of the 18th century, when scientists began to realize that relationships between the pressure, volume and temperature of a sample of gas could be obtained which would hold for all gases...
- Standard conditions for temperature and pressureStandard conditions for temperature and pressureStandard condition for temperature and pressure are standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements established to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data...
- Standard cubic footStandard cubic footA standard cubic foot is a measure of quantity of gas, equal to a cubic foot of volume at 60 degrees Fahrenheit and either 14.696 psi or 14.73 psi of pressure.A standard cubic foot is thus not a unit of volume but of quantity, and the conversion to normal cubic metres is...
(SCF) - Million standard cubic feet per day (MMSCFD)
External links
- Xchanger Inc, webpage Calculator for SCFM, NM3/hr, lb/hr, kg/hr, ACFM & M3/hr gas flows.
- ACFM versus SCFM for ASME AG-1 HEPA Filters
- SCFM (Standard CFM) vs. ACFM (Actual CFM) (Specifically for air flows only)
- "Standard conditions for gases" from the IUPAC Gold Book.
- "Standard pressure" from the IUPAC Gold Book.
- "STP" from the IUPAC Gold Book.
- "Standard state" from the IUPAC Gold Book.
- Gas Density
- Properties of the Atmosphere

