
Rigvedic rivers
Encyclopedia
River
s, such as the Sapta Sindhu ("seven rivers"), play a prominent part in the hymns of the Rigveda
, and consequently in early Vedic religion
. It is likely that they are derived from older Proto-Indo-Iranian or Proto-Indo-European
hydronyms as cognate names exist in Avestan language
and other Indo-European languages
.
slaying Vritra
(literally "the obstacle"), liberating the rivers; in a variant of the myth, Indra smashes the Vala
cave, releasing the cows that were within. The two myths are separate however, rivers and cows are often poetically correlated in the Rigveda, for example in 3.33, a notable hymn describing the crossing of two swollen rivers by the chariots and wagons of the Bharata
tribe,
and the seven clime
s) of the Avesta. The Avesta
's are generally equated with the Vedic Sapta Sindhavaḥ: in Vendidad
1.18 these are described to be the fifteenth of the sixteen lands created by Mazda
.
, RV 10.75. In 6.61.10, Sarasvati is called "she with seven sisters" (saptasvasā) indicating a group of eight rivers, the number seven being more important than the individual members (see also saptarshi
, hapta karšuuar /haft keshvar in Avestan), so that the list of the Sapta Sindhu may not have been fixed or immutable. In RV 10.64.8 and RV 10.75.1, three groups of seven rivers are referred to ( "thrice seven wandering rivers"), as well as 99 rivers.
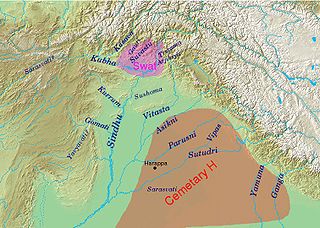 Identification of Rigvedic rivers is the single most important way of establishing the geography of the early Vedic civilization. Rivers with certain identifications stretch from eastern Afghanistan
Identification of Rigvedic rivers is the single most important way of establishing the geography of the early Vedic civilization. Rivers with certain identifications stretch from eastern Afghanistan
to the western Gangetic plain, clustering in the Punjab
. Some river names appear to go back to common Indo-Iranian rivers, with cognate river names in Avestan, notably the Sarasvati
(Avestan Haraxvaiti, Old Persian Hara(h)uvati) and the Sarayu
(Iran. Harayu, Avestan acc. Harōiiūm, mod. Persian Harē).
A number of names can be shown to have been re-applied to other rivers as the center of Vedic culture moved eastward. It is possible to establish a clear picture for the latest phase of the Rigveda, thanks to the Nadistuti sukta
(10.75), which contains a geographically ordered list of rivers. The most prominent river of the Rigveda is the Sarasvati
, next to the Indus
. The Sarasvati river of the Rigveda is commonly identified with the present-day Ghaggar-Hakra, although the Helmand River as a possible locus of early Rigvedic references has been discussed. This is mostly ascribed to the movement of Vedic Aryans from their early seats in Seistan (Arachosia, Avestan Haraēuua), Gandhara
and eastern Afghanistan
into the Indus plains and beyond.
On the other hand archaeologists like B.B. Lal have shown the possibility of reverse westward movements of some Indo-aryan clans from indus basin as well as the absence of the certain archaeological trace for any outside intrusion to the subcontinent.
Northwestern Rivers (western tributaries of the Indus):
The Indus and its minor eastern tributaries:
Central Rivers (rivers of the Punjab):
East-central Rivers (rivers of Haryana
):
Eastern Rivers:
Uncertain / other
River
A river is a natural watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, a lake, a sea, or another river. In a few cases, a river simply flows into the ground or dries up completely before reaching another body of water. Small rivers may also be called by several other names, including...
s, such as the Sapta Sindhu ("seven rivers"), play a prominent part in the hymns of the Rigveda
Rigveda
The Rigveda is an ancient Indian sacred collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns...
, and consequently in early Vedic religion
Historical Vedic religion
The religion of the Vedic period is a historical predecessor of Hinduism. Its liturgy is reflected in the mantra portion of the four Vedas, which are compiled in Sanskrit. The religious practices centered on a clergy administering rites...
. It is likely that they are derived from older Proto-Indo-Iranian or Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European may refer to:*Proto-Indo-European language, the hypothetical common ancestor of the Indo-European languages.*Proto-Indo-Europeans, the hypothetical speakers of the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European language....
hydronyms as cognate names exist in Avestan language
Avestan language
Avestan is an East Iranian language known only from its use as the language of Zoroastrian scripture, i.e. the Avesta, from which it derives its name...
and other Indo-European languages
Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a family of several hundred related languages and dialects, including most major current languages of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and South Asia and also historically predominant in Anatolia...
.
Mythology
A recurring theme in the Rigveda is that of IndraIndra
' or is the King of the demi-gods or Devas and Lord of Heaven or Svargaloka in Hindu mythology. He is also the God of War, Storms, and Rainfall.Indra is one of the chief deities in the Rigveda...
slaying Vritra
Vritra
In the early Vedic religion, Vritra , is an Asura and also a serpent or dragon, the personification of drought and enemy of Indra. Vritra was also known in the Vedas as Ahi...
(literally "the obstacle"), liberating the rivers; in a variant of the myth, Indra smashes the Vala
Vala (Vedic)
Vala , meaning "enclosure" in Vedic Sanskrit, is an Asura of the Rigveda and the Atharvaveda, the brother of Vrtra.Historically, it has the same origin as the Vrtra myth, being derived from the same root, and from the same root also as Varuna, *val-/var- "to cover, to enclose" .Parallel to Vrtra...
cave, releasing the cows that were within. The two myths are separate however, rivers and cows are often poetically correlated in the Rigveda, for example in 3.33, a notable hymn describing the crossing of two swollen rivers by the chariots and wagons of the Bharata
Bharatas
Bhāratas are an Aryan tribe mentioned in the Rigveda, especially in Mandala 3 attributed to the Bharata sage Vishvamitra. In the "river hymn" RV 3.33, the entire Bharata tribe is described as crossing a river. Bharatá is also used as a name of Agni Bhāratas are an Aryan tribe mentioned in the...
tribe,
- 3.33.1cd Like two bright mother cows who lick their youngling, Vipas and Sutudri speed down their waters. (trans. Griffith)
Sapta Sindhu
The Sapta Sindhu are a group of seven chief rivers of uncertain or fluctuating identification (the number seven is of greater importance than the exact members of the group, compare the Saptarishi, and also the (later) seven seasSeven Seas
The phrase "Seven Seas" can refer either to a particular set of seven seas or to a great expanse of water in general. Today in modern times, this also includes the four oceans, and three large seas...
and the seven clime
Clime
The seven climes was a notion of dividing the Earth into zones in Classical Antiquity....
s) of the Avesta. The Avesta
Avesta
The Avesta is the primary collection of sacred texts of Zoroastrianism, composed in the Avestan language.-Early transmission:The texts of the Avesta — which are all in the Avestan language — were composed over the course of several hundred years. The most important portion, the Gathas,...
's are generally equated with the Vedic Sapta Sindhavaḥ: in Vendidad
Vendidad
The Vendidad or Videvdat is a collection of texts within the greater compendium of the Avesta. However, unlike the other texts of the Avesta, the Vendidad is an ecclesiastical code, not a liturgical manual.-Name:...
1.18 these are described to be the fifteenth of the sixteen lands created by Mazda
Ahura Mazda
Ahura Mazdā is the Avestan name for a divinity of the Old Iranian religion who was proclaimed the uncreated God by Zoroaster, the founder of Zoroastrianism...
.
Identity of the seven rivers
It is not entirely clear how the seven rivers were intended to be enumerated. They are often located in the in northtern India / eastern Pakistan. If the Sarasvati and the five major rivers of the Punjab are included (Sutudri, Parusni, Asikni, Vitasta, Vipas(Vipāś), the latter all tributaries of Sindhu), one river is missing probably the Kubha. (The Sindhu is a special case, having feminine or masculine gender). Other possiblilities include the Arjikiya or Sushoma; compare also the list of ten rivers, both east and west of the Indus, in the Nadistuti suktaNadistuti sukta
The Nadistuti sukta ,"hymn of praise of rivers", is hymn 10.75 of the Rigveda.It is important for the reconstruction of the geography of the Vedic civilization...
, RV 10.75. In 6.61.10, Sarasvati is called "she with seven sisters" (saptasvasā) indicating a group of eight rivers, the number seven being more important than the individual members (see also saptarshi
Saptarshi
The Saptarishi are the seven rishis who are extolled at many places in the Vedas and Hindu literature. The Vedic Samhitas never actually enumerate these rishis by name, though later Vedic texts such as the Brahmanas and Upanisads do so. They are regarded in the Vedas as the patriarchs of the...
, hapta karšuuar /haft keshvar in Avestan), so that the list of the Sapta Sindhu may not have been fixed or immutable. In RV 10.64.8 and RV 10.75.1, three groups of seven rivers are referred to ( "thrice seven wandering rivers"), as well as 99 rivers.
Geography of the Rigveda

Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
to the western Gangetic plain, clustering in the Punjab
Punjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
. Some river names appear to go back to common Indo-Iranian rivers, with cognate river names in Avestan, notably the Sarasvati
Sarasvati River
The Sarasvati River is one of the chief Rigvedic rivers mentioned in ancient Hindu texts. The Nadistuti hymn in the Rigveda mentions the Sarasvati between the Yamuna in the east and the Sutlej in the west, and later Vedic texts like Tandya and Jaiminiya Brahmanas as well as the Mahabharata...
(Avestan Haraxvaiti, Old Persian Hara(h)uvati) and the Sarayu
Sarayu
The Sarayu is a river that flows through the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. This river is of ancient significance, finding mentions in the Vedas and the Ramayana. The Sarayu forms at the confluence of the Karnali and Mahakali in Bahraich District...
(Iran. Harayu, Avestan acc. Harōiiūm, mod. Persian Harē).
A number of names can be shown to have been re-applied to other rivers as the center of Vedic culture moved eastward. It is possible to establish a clear picture for the latest phase of the Rigveda, thanks to the Nadistuti sukta
Nadistuti sukta
The Nadistuti sukta ,"hymn of praise of rivers", is hymn 10.75 of the Rigveda.It is important for the reconstruction of the geography of the Vedic civilization...
(10.75), which contains a geographically ordered list of rivers. The most prominent river of the Rigveda is the Sarasvati
Sarasvati River
The Sarasvati River is one of the chief Rigvedic rivers mentioned in ancient Hindu texts. The Nadistuti hymn in the Rigveda mentions the Sarasvati between the Yamuna in the east and the Sutlej in the west, and later Vedic texts like Tandya and Jaiminiya Brahmanas as well as the Mahabharata...
, next to the Indus
Indus River
The Indus River is a major river which flows through Pakistan. It also has courses through China and India.Originating in the Tibetan plateau of western China in the vicinity of Lake Mansarovar in Tibet Autonomous Region, the river runs a course through the Ladakh district of Jammu and Kashmir and...
. The Sarasvati river of the Rigveda is commonly identified with the present-day Ghaggar-Hakra, although the Helmand River as a possible locus of early Rigvedic references has been discussed. This is mostly ascribed to the movement of Vedic Aryans from their early seats in Seistan (Arachosia, Avestan Haraēuua), Gandhara
Gandhara
Gandhāra , is the name of an ancient kingdom , located in northern Pakistan and eastern Afghanistan. Gandhara was located mainly in the vale of Peshawar, the Potohar plateau and on the Kabul River...
and eastern Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
into the Indus plains and beyond.
On the other hand archaeologists like B.B. Lal have shown the possibility of reverse westward movements of some Indo-aryan clans from indus basin as well as the absence of the certain archaeological trace for any outside intrusion to the subcontinent.
List
In the geographical organization of the following list, it has to be kept in mind that some names appearing both in early and in late hymns may have been re-applied to new rivers during the composition of the Rigveda.Northwestern Rivers (western tributaries of the Indus):
- Trstama (GilgitGilgit RiverGilgit River is a tributary of the Indus River, and flows past the town of Gilgit. It is located in the Northern Areas of Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan. The Gilgit starts from Shandur lake. The Gilgit River is also referred to as the Ghizar River....
)? - Susartu
- Anitabha (listed once, in 5.53.9, with the Afghan rivers RasaRasa- Indian culture :* Rasa , a concept in the Indian performing arts* Rasa , a concept of taste or emotional rapture related to Krishna devotion* Rasā, a mythical river mentioned in the Rigveda...
(Avestan Rangha/Raŋhā), Kubha, Krumu, SarayuSarayuThe Sarayu is a river that flows through the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. This river is of ancient significance, finding mentions in the Vedas and the Ramayana. The Sarayu forms at the confluence of the Karnali and Mahakali in Bahraich District...
(Avest. Harōiiu) - RasaRasa- Indian culture :* Rasa , a concept in the Indian performing arts* Rasa , a concept of taste or emotional rapture related to Krishna devotion* Rasā, a mythical river mentioned in the Rigveda...
(on the upper Indus (often a mythical river, Avestan Rangha, Scythian Rha) - Svetya
- Kubha (KabulKabul RiverKabul River , the classical Cophes , is a 700 km long river that starts in the Sanglakh Range of the Hindu Kush Mountains in Afghanistan and ends in the Indus River near Attock, Pakistan. It is the main river in eastern Afghanistan and is separated from the watershed of the Helmand by the Unai Pass...
), Greek Kophēn - Krumu (Kurrum)
- Gomati (GomalGomal RiverGomal River is a river in the historical region of Pashtunistan, consisting of areas in Afghanistan and Pakistan, inhabited by the Pashtuns...
) - SarayuSarayuThe Sarayu is a river that flows through the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. This river is of ancient significance, finding mentions in the Vedas and the Ramayana. The Sarayu forms at the confluence of the Karnali and Mahakali in Bahraich District...
(modern Hari River of HeratHerat ProvinceHerat is one the 34 provinces of Afghanistan; together with Badghis, Farah, and Ghor provinces, it makes up the South-western region of the country...
) - Mehatnu (along with the Gomati and Krumu)
- Suvastu (SwatSwat (Pakistan)Swat is a valley and an administrative district in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province, located close to the Afghan-Pakistan border. It is the upper valley of the Swat River, which rises in the Hindu Kush range. The capital of Swat is Saidu Sharif, but the main town in the Swat valley is Mingora...
) in RV 8.19.37) - Gauri (Panjkora)??
- Kusava (KunarKunar RiverThe Kunar River is about 480 km long, located in eastern Afghanistan and north-western Pakistan. The Kunar river system is fed from melting glaciers and snow of the Hindu Kush mountains....
)??
The Indus and its minor eastern tributaries:
- Sindhu (Indus; (sindhu also means "stream" generically)
- Susoma (SohanSohanSohan is a village and union council of Jhelum District in the Punjab Province of Pakistan. It is part of Jhelum Tehsil, and is located at 33°3'25N 73°26'30E with an altitude of 303 metres . Most of the population belong to the Sohlan....
) - Arjikiya (HaroHaro RiverHaro is the name of a river and its valley in Abbottabad District in the North West Frontier Province of northern Pakistan, identified with the Rigvedic Arjikiya...
)?
Central Rivers (rivers of the Punjab):
- Vitasta (JhelumJhelum RiverJehlum River or Jhelum River , ) is a river that flows in India and Pakistan. It is the largest and most western of the five rivers of Punjab, and passes through Jhelum District...
) - Asikni (Chenab)
- Parusni (RaviRavi RiverThe Ravi is a trans-boundary river flowing through Northwestern India and eastern Pakistan. It is one of the six rivers of the Indus System in Punjab region ....
) - Vipas (BeasBeas RiverThe Beas River is a river in the northern part of India. The river rises in the Himalayas in central Himachal Pradesh, India, and flows for some 470 km to the Sutlej River in the Indian state of Punjab....
) - Sutudri (SutlejSutlejThe Sutlej River is the longest of the five rivers that flow through the historic crossroad region of Punjab in northern India and Pakistan. It is located north of the Vindhya Range, south of the Hindu Kush segment of the Himalayas, and east of the Central Sulaiman Range in Pakistan.The Sutlej...
) - Marudvrdha
East-central Rivers (rivers of Haryana
Haryana
Haryana is a state in India. Historically, it has been a part of the Kuru region in North India. The name Haryana is found mentioned in the 12th century AD by the apabhramsha writer Vibudh Shridhar . It is bordered by Punjab and Himachal Pradesh to the north, and by Rajasthan to the west and south...
):
- SarasvatiSarasvati RiverThe Sarasvati River is one of the chief Rigvedic rivers mentioned in ancient Hindu texts. The Nadistuti hymn in the Rigveda mentions the Sarasvati between the Yamuna in the east and the Sutlej in the west, and later Vedic texts like Tandya and Jaiminiya Brahmanas as well as the Mahabharata...
(References to the Sarasvati river in the Rigveda are identified with the present-day Ghaggar River, although the Arghandāb RiverArghandab RiverArghandab is a river in Afghanistan, about in length. It rises in the Hazarajat country north-west of Ghazni, and flows south-west falls into the Helmand below Girishk. In its lower course it is much used for irrigation, and the valley is cultivated and populous; yet the water is said to be...
(a tributary of the great Helmand RiverHelmand RiverThe Helmand River is the longest river in Afghanistan and the primarily watershed for the endorheic Sistan Basin....
) as a possible locus of early Rigvedic references has been discussed.) - Drsadvati, Apaya (RV 3.23.4, Mahabharata Apaga.)
Eastern Rivers:
- Asmanvati (Assan)?
- YamunaYamunaThe Yamuna is the largest tributary river of the Ganges in northern India...
- GangesGanges RiverThe Ganges or Ganga, , is a trans-boundary river of India and Bangladesh. The river rises in the western Himalayas in the Indian state of Uttarakhand, and flows south and east through the Gangetic Plain of North India into Bangladesh, where it empties into the Bay of Bengal. By discharge it...
Uncertain / other
- Silamavati?
- Urnavati?
- YavyavatiYavyavatiThe Yavyavati is a river of ancient India, mentioned in the Rigveda and in the Pancavimsa Brahmana . In the Pancavimsa Brahmana the river is associated with the Vibhinduka region ....
(Zhob riverZhob RiverZhob River is located in Balochistan, Pakistan. The name is Iranic in its origin and etymologically identical to those of the Little Zab and Great Zab rivers in Iraq and the Pamirs....
?)
See also
- River goddess
- SamudraSamudraSamudra is a Sanskrit term for "ocean", literally the "gathering together of waters" Samudra is a Sanskrit term for "ocean", literally the "gathering together of waters" Samudra is a Sanskrit term for "ocean", literally the "gathering together of waters" (- meaning "together" and -udra meaning...
- Nadistuti suktaNadistuti suktaThe Nadistuti sukta ,"hymn of praise of rivers", is hymn 10.75 of the Rigveda.It is important for the reconstruction of the geography of the Vedic civilization...
- Ap (water)Ap (water)Ap is the Vedic Sanskrit term for "water", in Classical Sanskrit occurring only in the plural, , whence Hindi . The term is from PIE hxap "water"....
- Rigvedic deitiesRigvedic deitiesThere are 1028 hymns in the Rigveda, most of them dedicated to specific deities.Indra, a heroic god, slayer of Vrtra and destroyer of the Vala, liberator of the cows and the rivers; Agni the sacrificial fire and messenger of the gods; and Soma the ritual drink dedicated to Indra are the most...
- Aryan migration
- Out of India theoryOut of India theoryThe Out of India theory is the proposition that the Indo-European language family originated in the Indian subcontinent and spread to the remainder of the Indo-European region through a series of migrations...
- Old European hydronymyOld European hydronymyOld European is the term used by Hans Krahe for the language of the oldest reconstructed stratum of European hydronymy in Central and Western Europe...

