Reversed field pinch
Encyclopedia
A reversed-field pinch is a device used to produce and contain near-thermonuclear plasmas
. It is a toroidal pinch which uses a unique magnetic field configuration as a scheme to magnetically confine a plasma, primarily to study magnetic fusion energy. Its magnetic geometry is somewhat different from that of the more common tokamak
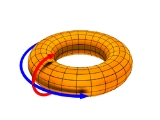
. As one moves out radially, the portion of the magnetic field pointing toroidally (see inset) reverses its direction, giving rise to the term "reversed field". This configuration can be sustained with comparatively lower fields than that of a tokamak of similar power density. One of the disadvantages of this configuration is that it tends to be more susceptible to non-linear effects and turbulence. This makes it a perfect laboratory for non-ideal (resistive) magnetohydrodynamics
. RFPs are also used in the study of astrophysical plasma
s as they share many features.
The largest Reversed Field Pinch device presently in operation is called the Reversed-Field eXperiment (RFX) in Padua
, Italy
. Others include the Madison Symmetric Torus
, EXTRAP T2R in Sweden, and TPE-RX in Japan.
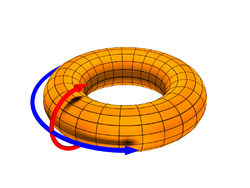
, which has a much larger magnetic field in the toroidal direction than the poloidal direction, an RFP has a comparable field strength in both directions (though the sign of the toroidal field reverses). Moreover, a typical RFP has a field strength approximately one half to one tenth that of a comparable Tokamak. The RFP also relies on driving current in the plasma to reinforce the field from the magnets through the dynamo effect.
.
The magnetic field lines coil loosely around a center torus
. They coil outwards. Near the plasma edge, the toroidal magnetic field reverses and the field lines coil in the reverse direction.
Internal fields are bigger than the fields at the magnet
s.
) use their close fitting shell as a magnetic coil by driving current through the shell itself. This is attractive from a reactor standpoint since a solid copper shell (for example) would be fairly robust against high energy neutrons, compared with superconducting magnets. There is also no established beta
limit for RFPs. There exists a possibility that a reversed field pinch could achieve ignition solely with ohmic power, which would be much simpler than tokamak designs, though it could not be operated in steady state
Despite these advantages, there are many concerns with RFPs. Typically they require a large amount of current to be driven, and although promising experiments are underway, there is no established method of replacing ohmically driven current, which is fundamentally limited by the machine parameters. RFPs are also prone to tearing modes
which lead to overlapping magnetic islands and therefore rapid transport from the core of the plasma to the edge. These problems are areas of active research in the RFP community.
was designed to test this assumption and to learn how good the conductor must be and how close to the plasma it must be placed. In addition, the plasma confinement in the best RFP's is only about 1% as good as in the best tokamaks. One reason for this is that all existing RFP's are relatively small. MST is larger than any previous RFP device, and thus it can test this important size issue.http://sprott.physics.wisc.edu/mstfaq.htm
Plasma (physics)
In physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized. Heating a gas may ionize its molecules or atoms , thus turning it into a plasma, which contains charged particles: positive ions and negative electrons or ions...
. It is a toroidal pinch which uses a unique magnetic field configuration as a scheme to magnetically confine a plasma, primarily to study magnetic fusion energy. Its magnetic geometry is somewhat different from that of the more common tokamak
Tokamak
A tokamak is a device using a magnetic field to confine a plasma in the shape of a torus . Achieving a stable plasma equilibrium requires magnetic field lines that move around the torus in a helical shape...
. As one moves out radially, the portion of the magnetic field pointing toroidally (see inset) reverses its direction, giving rise to the term "reversed field". This configuration can be sustained with comparatively lower fields than that of a tokamak of similar power density. One of the disadvantages of this configuration is that it tends to be more susceptible to non-linear effects and turbulence. This makes it a perfect laboratory for non-ideal (resistive) magnetohydrodynamics
Magnetohydrodynamics
Magnetohydrodynamics is an academic discipline which studies the dynamics of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such fluids include plasmas, liquid metals, and salt water or electrolytes...
. RFPs are also used in the study of astrophysical plasma
Astrophysical plasma
An astrophysical plasma is a plasma the physical properties of which are studied as part of astrophysics. Much of the baryonic matter of the universe is thought to consist of plasma, a state of matter in which atoms and molecules are so hot, that they have ionized by breaking up into their...
s as they share many features.
The largest Reversed Field Pinch device presently in operation is called the Reversed-Field eXperiment (RFX) in Padua
Padua
Padua is a city and comune in the Veneto, northern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Padua and the economic and communications hub of the area. Padua's population is 212,500 . The city is sometimes included, with Venice and Treviso, in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area, having...
, Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
. Others include the Madison Symmetric Torus
Madison Symmetric Torus
The Madison Symmetric Torus is a reversed field pinch physics experiment with applications to both fusion energy research and astrophysical plasmas located at University of Wisconsin-Madison...
, EXTRAP T2R in Sweden, and TPE-RX in Japan.

Characteristics
Unlike the TokamakTokamak
A tokamak is a device using a magnetic field to confine a plasma in the shape of a torus . Achieving a stable plasma equilibrium requires magnetic field lines that move around the torus in a helical shape...
, which has a much larger magnetic field in the toroidal direction than the poloidal direction, an RFP has a comparable field strength in both directions (though the sign of the toroidal field reverses). Moreover, a typical RFP has a field strength approximately one half to one tenth that of a comparable Tokamak. The RFP also relies on driving current in the plasma to reinforce the field from the magnets through the dynamo effect.
Magnetic topology
The reversed-field pinch works towards a state of minimum energyTaylor state
In plasma physics, a Taylor state is the minimum energy state of a plasma satisfying the constraint of conserving magnetic helicity.- Derivation :...
.
The magnetic field lines coil loosely around a center torus
Torus
In geometry, a torus is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three dimensional space about an axis coplanar with the circle...
. They coil outwards. Near the plasma edge, the toroidal magnetic field reverses and the field lines coil in the reverse direction.
Internal fields are bigger than the fields at the magnet
Magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets.A permanent magnet is an object...
s.
Fusion Research
The RFP has many features which make it a promising configuration for a potential fusion reactor. Due to the lower overall fields, an RFP reactor might not need superconducting magnets. This is a large advantage over tokamaks since superconducting magnets are delicate and expensive and so must be shielded from the Neutron rich fusion environment. RFPs are susceptible to surface instabilities and so require a close fitting shell. Some experiments (such as the Madison Symmetric TorusMadison Symmetric Torus
The Madison Symmetric Torus is a reversed field pinch physics experiment with applications to both fusion energy research and astrophysical plasmas located at University of Wisconsin-Madison...
) use their close fitting shell as a magnetic coil by driving current through the shell itself. This is attractive from a reactor standpoint since a solid copper shell (for example) would be fairly robust against high energy neutrons, compared with superconducting magnets. There is also no established beta
Beta (plasma physics)
The beta of a plasma, symbolized by β, is the ratio of the plasma pressure to the magnetic pressure...
limit for RFPs. There exists a possibility that a reversed field pinch could achieve ignition solely with ohmic power, which would be much simpler than tokamak designs, though it could not be operated in steady state
Despite these advantages, there are many concerns with RFPs. Typically they require a large amount of current to be driven, and although promising experiments are underway, there is no established method of replacing ohmically driven current, which is fundamentally limited by the machine parameters. RFPs are also prone to tearing modes
Plasma stability
An important field of plasma physics is the stability of the plasma. It usually only makes sense to analyze the stability of a plasma once it has been established that the plasma is in equilibrium. "Equilibrium" asks whether there are net forces that will accelerate any part of the plasma...
which lead to overlapping magnetic islands and therefore rapid transport from the core of the plasma to the edge. These problems are areas of active research in the RFP community.
Plasma Physics Research
The Reversed Field Pinch is also interesting from a physics standpoint. RFP dynamics are highly turbulent. RFPs also exhibit a strong plasma dynamo, similar to many astrophysical bodies. Basic plasma science is another important aspect of Reversed Field Pinch research.Disadvantages
The RFP is believed to require a shell with high electrical conductivity very close to the boundary of the plasma. This requirement is an unfortunate complication in a reactor. The Madison Symmetric TorusMadison Symmetric Torus
The Madison Symmetric Torus is a reversed field pinch physics experiment with applications to both fusion energy research and astrophysical plasmas located at University of Wisconsin-Madison...
was designed to test this assumption and to learn how good the conductor must be and how close to the plasma it must be placed. In addition, the plasma confinement in the best RFP's is only about 1% as good as in the best tokamaks. One reason for this is that all existing RFP's are relatively small. MST is larger than any previous RFP device, and thus it can test this important size issue.http://sprott.physics.wisc.edu/mstfaq.htm

