
Restriction (mathematics)
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, the notion of restriction of a function is defined as follows:
If f : E → F is a function
from E to F, and A is a subset
of E, then the restriction of f to A is the (partial) function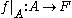 having the graph
having the graph 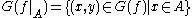 .
.
(In rough words, it is "the same function", but only defined on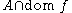 .)
.)
More generally, the restriction (or domain restriction or left-restriction) A ◁ R of a binary relation
R between E and F may be defined as a relation having domain A, codomain F and graph G(A ◁ R) = {(x, y) ∈ G(R) | x ∈ A}. Similarly, one can define a right-restriction or range restriction R ▷ B. (Indeed, one could define a restriction to a subset of E x F, and the same applies to n-ary relations
.
These cases do not fit into the scheme of sheaves
.)
The domain anti-restriction of a function or binary relation R (with domain E and codomain F) by a set A may be defined as (E \ A) ◁ R; it removes all elements of A from the domain E. It is sometimes denoted A ⩤ R. The range anti-restriction R ⩥ B is defined by R ▷ (F \ B).
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, the notion of restriction of a function is defined as follows:
If f : E → F is a function
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...
from E to F, and A is a subset
Subset
In mathematics, especially in set theory, a set A is a subset of a set B if A is "contained" inside B. A and B may coincide. The relationship of one set being a subset of another is called inclusion or sometimes containment...
of E, then the restriction of f to A is the (partial) function
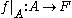 having the graph
having the graph 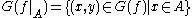 .
.(In rough words, it is "the same function", but only defined on
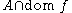 .)
.)More generally, the restriction (or domain restriction or left-restriction) A ◁ R of a binary relation
Binary relation
In mathematics, a binary relation on a set A is a collection of ordered pairs of elements of A. In other words, it is a subset of the Cartesian product A2 = . More generally, a binary relation between two sets A and B is a subset of...
R between E and F may be defined as a relation having domain A, codomain F and graph G(A ◁ R) = {(x, y) ∈ G(R) | x ∈ A}. Similarly, one can define a right-restriction or range restriction R ▷ B. (Indeed, one could define a restriction to a subset of E x F, and the same applies to n-ary relations
Relation (mathematics)
In set theory and logic, a relation is a property that assigns truth values to k-tuples of individuals. Typically, the property describes a possible connection between the components of a k-tuple...
.
These cases do not fit into the scheme of sheaves
Sheaf (mathematics)
In mathematics, a sheaf is a tool for systematically tracking locally defined data attached to the open sets of a topological space. The data can be restricted to smaller open sets, and the data assigned to an open set is equivalent to all collections of compatible data assigned to collections of...
.)
The domain anti-restriction of a function or binary relation R (with domain E and codomain F) by a set A may be defined as (E \ A) ◁ R; it removes all elements of A from the domain E. It is sometimes denoted A ⩤ R. The range anti-restriction R ⩥ B is defined by R ▷ (F \ B).
Examples
- The restriction of the non-injective functionInjective functionIn mathematics, an injective function is a function that preserves distinctness: it never maps distinct elements of its domain to the same element of its codomain. In other words, every element of the function's codomain is mapped to by at most one element of its domain...
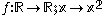 to
to 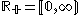 is the injection
is the injection 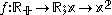 .
. - The inclusion mapInclusion mapIn mathematics, if A is a subset of B, then the inclusion map is the function i that sends each element, x of A to x, treated as an element of B:i: A\rightarrow B, \qquad i=x....
of a set A into a supersetSuperSetSuperSet Software was a group founded by friends and former Eyring Research Institute co-workers Drew Major, Dale Neibaur, Kyle Powell and later joined by Mark Hurst...
E of A is the restriction of the identity functionIdentity functionIn mathematics, an identity function, also called identity map or identity transformation, is a function that always returns the same value that was used as its argument...
on E to A.
See also
- Deformation retractDeformation retractIn topology, a branch of mathematics, a retraction , as the name suggests, "retracts" an entire space into a subspace. A deformation retraction is a map which captures the idea of continuously shrinking a space into a subspace.- Retract :...
- Function (mathematics)#Restrictions and extensions
- Binary relation#Restriction

