
Reformed methanol fuel cell
Encyclopedia
Proton exchange membrane fuel cell
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells, also known as polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells , are a type of fuel cell being developed for transport applications as well as for stationary fuel cell applications and portable fuel cell applications. Their distinguishing features include lower...
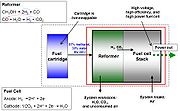
where, the fuel, methanol
Methanol
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, wood alcohol, wood naphtha or wood spirits, is a chemical with the formula CH3OH . It is the simplest alcohol, and is a light, volatile, colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive odor very similar to, but slightly sweeter than, ethanol...
(CH3OH), is reformed, before being fed into the fuel cell
Fuel cell
A fuel cell is a device that converts the chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen or another oxidizing agent. Hydrogen is the most common fuel, but hydrocarbons such as natural gas and alcohols like methanol are sometimes used...
. RMFC systems offer advantages over direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC) systems including higher efficiency, smaller cell stacks, no water management, better operation at low temperatures, and storage at sub-zero temperatures because methanol is a liquid from -97.0 °C to 64.7 °C (-142.6 °F to 148.5 °F). The tradeoff is that RMFC systems operate at hotter temperatures and therefore need more advanced heat management and insulation. The waste products with these types of fuel cells are carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
and water.
Methanol
Methanol
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, wood alcohol, wood naphtha or wood spirits, is a chemical with the formula CH3OH . It is the simplest alcohol, and is a light, volatile, colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive odor very similar to, but slightly sweeter than, ethanol...
is used as a fuel because it is naturally hydrogen dense (a hydrogen carrier) and can be steam reformed
Steam reforming
Fossil fuel reforming is a method of producing hydrogen or other useful products from fossil fuels such as natural gas. This is achieved in a processing device called a reformer which reacts steam at high temperature with the fossil fuel. The steam methane reformer is widely used in industry to...
into hydrogen at low temperatures compared to other hydrocarbon
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons from which one hydrogen atom has been removed are functional groups, called hydrocarbyls....
fuels. Additionally, methanol is naturally occurring, biodegradable, and energy dense.
RMFC systems consist of a fuel processing system (FPS), a fuel cell
Fuel cell
A fuel cell is a device that converts the chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen or another oxidizing agent. Hydrogen is the most common fuel, but hydrocarbons such as natural gas and alcohols like methanol are sometimes used...
, a fuel cartridge, and the BOP (the balance of plant).
Storage
The fuel cartridge stores the methanolMethanol
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, wood alcohol, wood naphtha or wood spirits, is a chemical with the formula CH3OH . It is the simplest alcohol, and is a light, volatile, colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive odor very similar to, but slightly sweeter than, ethanol...
fuel, which is often diluted with up to 40% (by volume) water.
Fuel processing system (FPS) in
MethanolMethanol
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, wood alcohol, wood naphtha or wood spirits, is a chemical with the formula CH3OH . It is the simplest alcohol, and is a light, volatile, colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive odor very similar to, but slightly sweeter than, ethanol...
→Partial oxidation
Partial oxidation
Partial oxidation is a type of chemical reaction. It occurs when a substoichiometric fuel-air mixture is partially combusted in a reformer, creating a hydrogen-rich syngas which can then be put to further use, for example in a fuel cell...
(POX)/Autothermal reforming (ATR)→Water gas shift reaction (WGS)→preferential oxidation (PROX)
The reformer converts methanol to H2 and CO2, a reaction that occurs at temperatures of 250 °C to 300 °C.
Fuel cell
→The membrane electrode assemblyMembrane electrode assembly
A membrane electrode assembly is an assembled stack of proton exchange membranes or alkali anion exchange membrane , catalyst and flat plate electrode used in a fuel cell.-PEM-MEA:...
(MEA) fuel cell stack produces electricity in a reaction that combines H2 (reformed from methanol in the fuel processor) and O2 and produces water (H2O) as a byproduct.
Fuel processing system (FPS) out
→Tail gas combustor (TGC) catalytic combustion afterburner or (catalytic combustion) with a platinumPlatinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pt and an atomic number of 78. Its name is derived from the Spanish term platina del Pinto, which is literally translated into "little silver of the Pinto River." It is a dense, malleable, ductile, precious, gray-white transition metal...
-alumina (Pt–Al2O3) catalyst→condenser
Condenser (heat transfer)
In systems involving heat transfer, a condenser is a device or unit used to condense a substance from its gaseous to its liquid state, typically by cooling it. In so doing, the latent heat is given up by the substance, and will transfer to the condenser coolant...
Balance of plant
The balance of plant (BOP) consists of any fuel pumpFuel pump
A fuel pump is a frequently essential component on a car or other internal combustion engined device. Many engines do not require any fuel pump at all, requiring only gravity to feed fuel from the fuel tank through a line or hose to the engine...
s, air compressors
Gas compressor
A gas compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume.Compressors are similar to pumps: both increase the pressure on a fluid and both can transport the fluid through a pipe. As gases are compressible, the compressor also reduces the volume of a gas...
, and fans
Fan (implement)
A hand-held fan is an implement used to induce an airflow for the purpose of cooling or refreshing oneself. Any broad, flat surface waved back-and-forth will create a small airflow and therefore can be considered a rudimentary fan...
required to circulate the gas and liquid in the system. A control system is also often needed to operate and monitor the RMFC.
State of development
RMFC systems have reached an advanced stage of development. For instance, a small 25 watt RMFC system developed for the military has met environmental tolerance, safety, and performance goals set by the U.S.Army CERDEC, and is commercially available.See also
- Methane reformerMethane reformerA methane refomer is a device based on steam reforming or autothermal reforming and is a type of chemical synthesis, which can produce pure hydrogen gas from natural gas using a catalyst. There are two natural gas reformer technologies — autothermal reforming and steam methane reforming...
- Methanol (data page)Methanol (data page)- Material Safety Data Sheet : The handling of this chemical may incur notable safety precautions. It is highly recommend that you seek the Material Safety Datasheet for this chemical from a reliable source such as , and follow its directions...
- Methanol economyMethanol economyThe methanol economy is a suggested future economy in which methanol replaces fossil fuels as a means of energy storage, ground transportation fuel, and raw material for synthetic hydrocarbons and their products. It offers an alternative to the proposed hydrogen economy or ethanol economy.In the...
- MicropumpMicropumpAlthough any kind of small pump is often referred to as micropump, a more accurate and up-to-date definition restricts this term to pumps with functional dimensions in the micrometre range. Such pumps are of special interest in microfluidic research, and have become available for industrial product...
- Fuel cellFuel cellA fuel cell is a device that converts the chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen or another oxidizing agent. Hydrogen is the most common fuel, but hydrocarbons such as natural gas and alcohols like methanol are sometimes used...
- Glossary of fuel cell termsGlossary of fuel cell termsThe Glossary of fuel cell terms lists the definitions of many terms used within the fuel cell industry. The terms in this fuel cell glossary may be used by fuel cell industry associations, in education material and fuel cell codes and standards to name but a few. –...
- Hydrogen technologiesHydrogen technologiesHydrogen technologies are technologies that relate to the production and use of hydrogen. Hydrogen technologies are applicable for many uses....
- Portable fuel cell applicationsPortable fuel cell applicationsFuel cell applications are stationary fuel cell applications and portable fuel cell plications...

