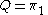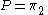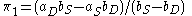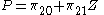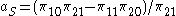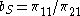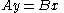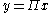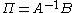Reduced form
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, and particularly in econometrics
, the reduced form of a system of equations is the result of solving the system for the endogenous
variables. This gives the latter as a function of the exogenous
variables, if any. In econometrics, "structural form" models begin from deductive theories of the economy, while "reduced form" models begin by identifying particular relationships between variables.
Let Y and X be random vectors. Y is the vector of the variables to be explained (endogeneous variables) by a statistical model
and X is the vector of explanatory (exogeneous) variables. In addition let be a vector of error terms. Then the general expression of a structural form is
be a vector of error terms. Then the general expression of a structural form is 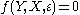 , where f is a function, possibly from vectors to vectors in the case of a multiple-equation model. The reduced form of this model is given by
, where f is a function, possibly from vectors to vectors in the case of a multiple-equation model. The reduced form of this model is given by 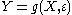 , with g a function.
, with g a function.
of some specific good. The quantity of the demand varies inversely with the price: a higher price decreases demand. The quantity of the supply varies directly with the price: a higher price makes supply more profitable. In formulas:
with positive bS and negative bD. This is the structural form of the equation system: the equations are derived from the theory. (In this case, the economic theory of supply and demand.)
The two endogenous variables are the traded quantity Q and the price P, defined by the two equations of the system. Of course there are always as many endogenous variables as there are equations.
 . This can be written as
. This can be written as 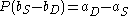 , or
, or 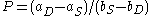 . Thus, P is in fact a fixed number, independent of Q. Below, this number is called
. Thus, P is in fact a fixed number, independent of Q. Below, this number is called 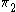 , while the similar number for Q is
, while the similar number for Q is  :
:
The structure of supply and demand has disappeared. The two coefficients are the reduced form coefficients. They are easily identified from data on Q and P. (However, the four structural form coefficients above can not be identified from data: the parameter identification problem
coefficients are the reduced form coefficients. They are easily identified from data on Q and P. (However, the four structural form coefficients above can not be identified from data: the parameter identification problem
.)
It is easily verified that:
In the above set of equations, the choice of the endogenous variables can not be derived from the equations themselves; the modeller might alternatively have chosen for instance Q and Z as endogenous variables, which would make P the exogenous variable.
This structural model can be rewritten in the reduced form:
As before, the four reduced form ( ) coefficients can be derived from the five structural form coefficients. Note that both endogenous variables depend on the exogenous variable Z.
) coefficients can be derived from the five structural form coefficients. Note that both endogenous variables depend on the exogenous variable Z.
By combining the two reduced form equations to eliminate Z, the structural coefficients of the supply side model ( and
and 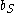 ) can be derived from the four reduced form coefficients (
) can be derived from the four reduced form coefficients (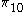 ,
,  ,
,  and
and 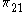 ):
):
Note however, that this still does not allow us to identify the structural parameters of the demand-side model. For that, we would need an exogenous variable which is included in the supply-side of the structural model, but not on the demand-side.
where A and B are matrices
; A is a square M × M matrix. The reduced form of the system is:
Again, each endogenous variable depends on each exogenous variable. It is easily verified that:
Without restrictions on the A and B, the coefficients of A and B can not be identified from data on y and x: each row of the structural model is just a linear relation between y and z with unknown coefficients. (Again the parameter identification problem
.) The M reduced form equations (the rows of the matrix equation y = Π x above) can be identified from the data because each of them contains only one endogenous variable.
might be needed to ensure the reduced form is uniquely determined.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, and particularly in econometrics
Econometrics
Econometrics has been defined as "the application of mathematics and statistical methods to economic data" and described as the branch of economics "that aims to give empirical content to economic relations." More precisely, it is "the quantitative analysis of actual economic phenomena based on...
, the reduced form of a system of equations is the result of solving the system for the endogenous
Endogenous
Endogenous substances are those that originate from within an organism, tissue, or cell. Endogenous retroviruses are caused by ancient infections of germ cells in humans, mammals and other vertebrates...
variables. This gives the latter as a function of the exogenous
Exogenous
Exogenous refers to an action or object coming from outside a system. It is the opposite of endogenous, something generated from within the system....
variables, if any. In econometrics, "structural form" models begin from deductive theories of the economy, while "reduced form" models begin by identifying particular relationships between variables.
Let Y and X be random vectors. Y is the vector of the variables to be explained (endogeneous variables) by a statistical model
Statistical model
A statistical model is a formalization of relationships between variables in the form of mathematical equations. A statistical model describes how one or more random variables are related to one or more random variables. The model is statistical as the variables are not deterministically but...
and X is the vector of explanatory (exogeneous) variables. In addition let
 be a vector of error terms. Then the general expression of a structural form is
be a vector of error terms. Then the general expression of a structural form is 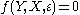 , where f is a function, possibly from vectors to vectors in the case of a multiple-equation model. The reduced form of this model is given by
, where f is a function, possibly from vectors to vectors in the case of a multiple-equation model. The reduced form of this model is given by 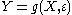 , with g a function.
, with g a function.Structural form
As an example, we use a system of two equations. Both equations are linear. The system models the supply and demandSupply and demand
Supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded by consumers will equal the quantity supplied by producers , resulting in an...
of some specific good. The quantity of the demand varies inversely with the price: a higher price decreases demand. The quantity of the supply varies directly with the price: a higher price makes supply more profitable. In formulas:
- supply:
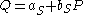
- demand:

with positive bS and negative bD. This is the structural form of the equation system: the equations are derived from the theory. (In this case, the economic theory of supply and demand.)
The two endogenous variables are the traded quantity Q and the price P, defined by the two equations of the system. Of course there are always as many endogenous variables as there are equations.
Reduced form
To find the reduced form, one must solve the equations for the endogenous variables. This reduces the system considerably. For instance, we know that the two right-hand sides of the equations are the same (both equal to Q), and hence . This can be written as
. This can be written as 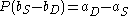 , or
, or 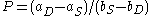 . Thus, P is in fact a fixed number, independent of Q. Below, this number is called
. Thus, P is in fact a fixed number, independent of Q. Below, this number is called 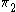 , while the similar number for Q is
, while the similar number for Q is  :
:The structure of supply and demand has disappeared. The two
 coefficients are the reduced form coefficients. They are easily identified from data on Q and P. (However, the four structural form coefficients above can not be identified from data: the parameter identification problem
coefficients are the reduced form coefficients. They are easily identified from data on Q and P. (However, the four structural form coefficients above can not be identified from data: the parameter identification problemParameter identification problem
The parameter identification problem is a problem which can occur in the estimation of multiple-equation econometric models where the equations have variables in common....
.)
It is easily verified that:
Structural and reduced forms with an exogenous variable
Exogenous variables are variables which are not determined by the system. If we assume that demand is influenced not only by price, but also by an exogenous variable, Z. The structural form becomes:- supply:
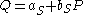
- demand:

In the above set of equations, the choice of the endogenous variables can not be derived from the equations themselves; the modeller might alternatively have chosen for instance Q and Z as endogenous variables, which would make P the exogenous variable.
This structural model can be rewritten in the reduced form:
As before, the four reduced form (
 ) coefficients can be derived from the five structural form coefficients. Note that both endogenous variables depend on the exogenous variable Z.
) coefficients can be derived from the five structural form coefficients. Note that both endogenous variables depend on the exogenous variable Z.By combining the two reduced form equations to eliminate Z, the structural coefficients of the supply side model (
 and
and 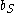 ) can be derived from the four reduced form coefficients (
) can be derived from the four reduced form coefficients (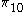 ,
,  ,
,  and
and 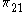 ):
):Note however, that this still does not allow us to identify the structural parameters of the demand-side model. For that, we would need an exogenous variable which is included in the supply-side of the structural model, but not on the demand-side.
The general linear case
Let y be a column vector of M endogenous variables. In the case above with Q and P, we have M = 2. Let x be a column vector of exogenous variables; in the case above x consists only of Z. The structural linear model (without error terms, as above) is:where A and B are matrices
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions. The individual items in a matrix are called its elements or entries. An example of a matrix with six elements isMatrices of the same size can be added or subtracted element by element...
; A is a square M × M matrix. The reduced form of the system is:
Again, each endogenous variable depends on each exogenous variable. It is easily verified that:
Without restrictions on the A and B, the coefficients of A and B can not be identified from data on y and x: each row of the structural model is just a linear relation between y and z with unknown coefficients. (Again the parameter identification problem
Parameter identification problem
The parameter identification problem is a problem which can occur in the estimation of multiple-equation econometric models where the equations have variables in common....
.) The M reduced form equations (the rows of the matrix equation y = Π x above) can be identified from the data because each of them contains only one endogenous variable.
Transformation
From the structural form to the reduced form, a coherency conditionCoherence condition
In mathematics, and particularly category theory a coherence condition is a collection of conditions requiring that various compositions of elementary morphisms are equal...
might be needed to ensure the reduced form is uniquely determined.
See also
- Simultaneous equations modelSimultaneous equations modelSimultaneous equation models are a form of statistical model in the form of a set of linear simultaneous equations. They are often used in econometrics.- Structural and reduced form :...
- System of linear equations
- Simultaneous equationsSimultaneous equationsIn mathematics, simultaneous equations are a set of equations containing multiple variables. This set is often referred to as a system of equations. A solution to a system of equations is a particular specification of the values of all variables that simultaneously satisfies all of the equations...
- Parameter identification problemParameter identification problemThe parameter identification problem is a problem which can occur in the estimation of multiple-equation econometric models where the equations have variables in common....