
Redlich–Kwong equation of state
Encyclopedia
In physics
and thermodynamics
, the Redlich–Kwong equation of state
is an equation that is derived from the van der Waals equation
. It is generally more accurate than the van der Waals equation and the ideal gas equation
, but not used as frequently because the increased difficulty in its derivatives and overall use. It was formulated by Otto Redlich
and Joseph Neng Shun Kwong in 1949, as:
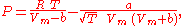
where:
The constants are different depending on which gas is being analyzed. The constants can be calculated from the critical point data of the gas:
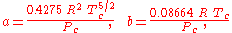
where:
For all Redlich-Kwong gases:
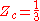
where:
The Redlich–Kwong equation is adequate for calculation of gas phase properties when the ratio of the pressure to the critical pressure (reduced pressure) is less than about one-half of the ratio of the temperature to the critical temperature (reduced temperature):
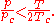
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
and thermodynamics
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a physical science that studies the effects on material bodies, and on radiation in regions of space, of transfer of heat and of work done on or by the bodies or radiation...
, the Redlich–Kwong equation of state
Equation of state
In physics and thermodynamics, an equation of state is a relation between state variables. More specifically, an equation of state is a thermodynamic equation describing the state of matter under a given set of physical conditions...
is an equation that is derived from the van der Waals equation
Van der Waals equation
The van der Waals equation is an equation of state for a fluid composed of particles that have a non-zero volume and a pairwise attractive inter-particle force It was derived by Johannes Diderik van der Waals in 1873, who received the Nobel prize in 1910 for "his work on the equation of state for...
. It is generally more accurate than the van der Waals equation and the ideal gas equation
Ideal gas law
The ideal gas law is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation to the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of Boyle's law and Charles's law...
, but not used as frequently because the increased difficulty in its derivatives and overall use. It was formulated by Otto Redlich
Otto Redlich
Otto Redlich was an Austrian physical chemist and chemical engineer who is best known for his development of equations of state like Redlich-Kwong equation. Besides this he had numerous other contributions to science....
and Joseph Neng Shun Kwong in 1949, as:

where:
- P is the gas pressurePressurePressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
- R is the gas constantGas constantThe gas constant is a physical constant which is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation. It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal,...
, - T is temperatureTemperatureTemperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
, - Vm is the molar volumeMolar volumeThe molar volume, symbol Vm, is the volume occupied by one mole of a substance at a given temperature and pressure. It is equal to the molar mass divided by the mass density...
(V/n), - a is a constant that corrects for attractive potential of molecules, and
- b is a constant that corrects for volume.
The constants are different depending on which gas is being analyzed. The constants can be calculated from the critical point data of the gas:
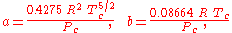
where:
- Tc is the temperature at the critical pointCritical point (thermodynamics)In physical chemistry, thermodynamics, chemistry and condensed matter physics, a critical point, also called a critical state, specifies the conditions at which a phase boundary ceases to exist...
, and - Pc is the pressure at the critical point.
For all Redlich-Kwong gases:
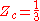
where:
- Zc is the compressibility factorCompressibility factorThe compressibility factor , also known as the compression factor, is a useful thermodynamic property for modifying the ideal gas law to account for the real gas behavior. In general, deviation from ideal behavior becomes more significant the closer a gas is to a phase change, the lower the...
at the critical point
The Redlich–Kwong equation is adequate for calculation of gas phase properties when the ratio of the pressure to the critical pressure (reduced pressure) is less than about one-half of the ratio of the temperature to the critical temperature (reduced temperature):
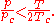
See also
- Soave modification to Redlich-Kwong

