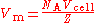Molar volume
Encyclopedia
The molar volume, symbol Vm, is the volume
occupied by one mole
of a substance (chemical element
or chemical compound
) at a given temperature
and pressure
. It is equal to the molar mass
(M) divided by the mass density (ρ). It has the SI unit cubic metre
s per mole (m3/mol), although it is more practical to use the units cubic decimetres per mole (dm3/mol) for gas
es and cubic centimetre
s per mole (cm3/mol) for liquid
s and solid
s.
The molar volume of a substance can be found by measuring its mass and density then applying the relation
If the sample is a mixture
containing N components, the molar volume is calculated using:
For ideal gas
es, the molar volume is given by the ideal gas equation: this is a good approximation for many common gases at standard temperature and pressure. For crystalline solids
, the molar volume can be measured by X-ray crystallography
.
Hence, for a given temperature and pressure, the molar volume is the same for all ideal gases and is known to the same precision as the gas constant
: R = 8.314 4621(75) J mol−1 K−1, that is a relative standard uncertainty of 9.1×10−7, according to the 2010 CODATA recommended value. The molar volume of an ideal gas at 100 kPa
(1 bar
) is
The molar volume of an ideal gas at 1 atmosphere of pressure is
where NA is the Avogadro constant and Z is the number of formula units in the unit cell. The result is normally reported as the "crystallographic density".
are routinely made for the electronics industry, and the measurement of the molar volume of silicon, both by X-ray crystallography and by the ratio of molar mass to mass density, has attracted much attention since the pioneering work at NIST by Deslattes et al. (1974). The interest stems from the fact that accurate measurements of the unit cell volume, atomic weight
and mass density of a pure crystalline solid provide a direct determination of the Avogadro constant. At present (2006 CODATA recommended value), the precision of the value of the Avogadro constant is limited by the uncertainty in the value of the Planck constant
(relative standard uncertainty of 5×10−8).
The 2006 CODATA recommended value for the molar volume of silicon is 12.058 8349(11)×10−6 m3/mol, with a relative standard uncertainty of 9.1×10−8.
Volume
Volume is the quantity of three-dimensional space enclosed by some closed boundary, for example, the space that a substance or shape occupies or contains....
occupied by one mole
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
of a substance (chemical element
Chemical element
A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Familiar examples of elements include carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, gold, mercury, and lead.As of November 2011, 118 elements...
or chemical compound
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
) at a given temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
and pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
. It is equal to the molar mass
Molar mass
Molar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol...
(M) divided by the mass density (ρ). It has the SI unit cubic metre
Cubic metre
The cubic metre is the SI derived unit of volume. It is the volume of a cube with edges one metre in length. An alternative name, which allowed a different usage with metric prefixes, was the stère...
s per mole (m3/mol), although it is more practical to use the units cubic decimetres per mole (dm3/mol) for gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
es and cubic centimetre
Cubic centimetre
A cubic centimetre is a commonly used unit of volume extending the derived SI-unit cubic metre, and corresponds to the volume of a cube measuring 1 cm × 1 cm × 1 cm...
s per mole (cm3/mol) for liquid
Liquid
Liquid is one of the three classical states of matter . Like a gas, a liquid is able to flow and take the shape of a container. Some liquids resist compression, while others can be compressed. Unlike a gas, a liquid does not disperse to fill every space of a container, and maintains a fairly...
s and solid
Solid
Solid is one of the three classical states of matter . It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a...
s.
The molar volume of a substance can be found by measuring its mass and density then applying the relation
-
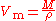 .
.
If the sample is a mixture
Mixture
In chemistry, a mixture is a material system made up by two or more different substances which are mixed together but are not combined chemically...
containing N components, the molar volume is calculated using:
-
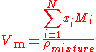 .
.
For ideal gas
Ideal gas
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of a set of randomly-moving, non-interacting point particles. The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanics.At normal conditions such as...
es, the molar volume is given by the ideal gas equation: this is a good approximation for many common gases at standard temperature and pressure. For crystalline solids
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituent atoms, molecules, or ions are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern extending in all three spatial dimensions. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography...
, the molar volume can be measured by X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is a method of determining the arrangement of atoms within a crystal, in which a beam of X-rays strikes a crystal and causes the beam of light to spread into many specific directions. From the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a...
.
Ideal gases
The ideal gas equation can be rearranged to give an expression for the molar volume of an ideal gas:-
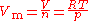 .
.
Hence, for a given temperature and pressure, the molar volume is the same for all ideal gases and is known to the same precision as the gas constant
Gas constant
The gas constant is a physical constant which is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation. It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal,...
: R = 8.314 4621(75) J mol−1 K−1, that is a relative standard uncertainty of 9.1×10−7, according to the 2010 CODATA recommended value. The molar volume of an ideal gas at 100 kPa
Pascal (unit)
The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
(1 bar
Bar (unit)
The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar...
) is
- 22.710 980(38) dm3/mol at 0 °C
- 24.789 598(42) dm3/mol at 25 °C
The molar volume of an ideal gas at 1 atmosphere of pressure is
- 22.414 L/mol at 0 °C
- 24.465 L/mol at 25 °C
Crystalline solids
The unit cell volume (Vcell) may be calculated from the unit cell parameters, whose determination is the first step in an X-ray crystallography experiment (the calculation is performed automatically by the structure determination software). This is related to the molar volume bywhere NA is the Avogadro constant and Z is the number of formula units in the unit cell. The result is normally reported as the "crystallographic density".
Molar volume of silicon
High quality single crystals of ultrapure siliconSilicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
are routinely made for the electronics industry, and the measurement of the molar volume of silicon, both by X-ray crystallography and by the ratio of molar mass to mass density, has attracted much attention since the pioneering work at NIST by Deslattes et al. (1974). The interest stems from the fact that accurate measurements of the unit cell volume, atomic weight
Atomic weight
Atomic weight is a dimensionless physical quantity, the ratio of the average mass of atoms of an element to 1/12 of the mass of an atom of carbon-12...
and mass density of a pure crystalline solid provide a direct determination of the Avogadro constant. At present (2006 CODATA recommended value), the precision of the value of the Avogadro constant is limited by the uncertainty in the value of the Planck constant
Planck constant
The Planck constant , also called Planck's constant, is a physical constant reflecting the sizes of energy quanta in quantum mechanics. It is named after Max Planck, one of the founders of quantum theory, who discovered it in 1899...
(relative standard uncertainty of 5×10−8).
The 2006 CODATA recommended value for the molar volume of silicon is 12.058 8349(11)×10−6 m3/mol, with a relative standard uncertainty of 9.1×10−8.