
Reading Southern railway station
Encyclopedia
Reading Southern railway station was the western terminus of the South Eastern Railway
's route from . It was also used by London and South Western Railway
services from London Waterloo.
The station was situated adjacent to, and to the south-east of, the Great Western Railway
's Reading General station
, which is now simply known as Reading station. The 1989-built concourse of that station now occupies the site of the frontage of the Southern station.
(SER) was from London Bridge station
to Dover, which took a route through in order that several companies could share the same lines. The line from Reading to Redhill was built by the Reading, Guildford and Reigate Railway (RG&RR), and was opened in stages: the section from Reading to Farnborough
was opened on 4 July 1849, with the last section being opened on 15 October 1849. From the start, the RG&RR was worked by the SER, which leased it from 16 July 1846, and absorbed it in 1852. When the first section of line opened, the SER trains served a temporary station north of Forbury Road before moving into a permanent terminal station, about 275 metres (300.7 yd) to the west, on 30 August 1855.
Reading had been served by the Great Western Railway
(GWR) since 1840, and the 1855 SER station was situated west of Vastern Road, on the corner of Blagrave Street and Station Road, adjacent to but south-east of the GWR station, and at a slightly lower level.
The Staines, Wokingham & Woking Junction Railway (SW&WJR) opened a line between and (Staines Junction) on 9 July 1856; the SW&WJR was worked by the London and South Western Railway
(LSWR), and they were authorised to run over the SER into Reading. In this way Reading gained a service into London Waterloo station. The SW&WJR was absorbed by the LSWR in 1878.
The original station did not last long, since it was destroyed by fire in 1859 after being struck by lightning. A replacement was built, which had two platform faces; it was enlarged in 1896 by the provision of two more faces following the resiting of the locomotive shed.
At the opening, there were four trains a day to (then known as Reigate Junction), two of which continued to ; a through service to London Bridge
began in 1852, and in 1853, two more were added.
 In 1899 the South Eastern Railway handed over its operations to a new organisation co-owned with the London, Chatham and Dover Railway
In 1899 the South Eastern Railway handed over its operations to a new organisation co-owned with the London, Chatham and Dover Railway
(LCDR), which traded as the South Eastern and Chatham Railway
(SE&CR); the line and station continued to be owned and maintained by the SER. In 1923, the LSWR and SER amalgamated, together with other railways including the LCDR (and thus the SE&CR), to form the Southern Railway
(SR), which assumed complete control of Reading station and its approaches.
In 1900, there were ten trains each weekday from Waterloo to Reading; by 1914 there were 14, and in 1922, 18. The services tended to be irregular, until the electrification of the inner suburban lines from Waterloo during 1915–16 brought a clock-face pattern to those services, in order to make it easy for people who did not understand timetables; the steam-hauled services, such as those to Reading, had to fit in (there were eight electric trains per hour on the Reading line as far as ) and so became more regular.
During the Dunkirk evacuation (27 May-4 June 1940), 293 special trains arrived at Reading from the Channel ports, most of which were handed over to the GWR.
After the War, there was only one train from Reading to London via the SER route; this was the 7.27am to London Bridge
, which arrived at 9.49, and the 5.25pm return, arriving back at Reading at 7.59. Three coaches sufficed between Reading and Redhill; but by 1960, six were required. The locomotive was normally a Schools class 4-4-0 based at Redhill.
At Nationalisation, the Southern Railway effectively became the Southern Region of British Railways
, and things continued more or less as before; but the station (originally named simply Reading) was renamed Reading South on 26 September 1949, to distinguish it from the adjacent Western Region
(ex-GWR) station (which became Reading General at the same time).
 Reading South was renamed again on 11 September 1961, becoming Reading Southern. The station remained independent of Reading General for several years following Nationalisation, but was transferred to Western Region control in March 1965; within a few months the two stations shared a common station manager. Soon the new management decided to spend £250,000 on improvements at Reading General, which included works to divert the Waterloo and Guildford
Reading South was renamed again on 11 September 1961, becoming Reading Southern. The station remained independent of Reading General for several years following Nationalisation, but was transferred to Western Region control in March 1965; within a few months the two stations shared a common station manager. Soon the new management decided to spend £250,000 on improvements at Reading General, which included works to divert the Waterloo and Guildford
services into the latter station, which would allow the Southern station to be closed.
In the station's final arrangement, there were four platforms; east of Vastern Road were a locomotive depot on the north side of the line, and a goods shed and sidings on the south side.
The passenger station was closed on 6 September 1965, with services being diverted into Reading General; most (including all the electric services) then used a newly-built platform 4A at the latter station, which was long enough for an eight-coach train. It was intended that the non-electric (Guildford line) services would use the older platforms at Reading General; but in practice, these used platform 4A as well. Freight continued to be handled until September 1970, when all goods services were withdrawn except for the Huntley & Palmers
biscuit traffic, which lasted until April 1979.
After demolition the site of the passenger station was used as a car park for Reading General. In 1989 a new concourse for Reading station
was built on the site, and no trace now remains of the former SER station.
A second connection was built to the west of the first one, and was opened on 17 December 1899. This was quite steep.
A third connection to the east of the previous two was opened on 26 May 1941, and like the second allowed trains stopping in the GWR station to run to or from the SER line.
When the SER station closed in 1965, the connection built in 1899 was relaid to allow the services over the former SER line to run into the newly-built Platform 4A at Reading General
.
The 1875 depot was constructed on the north side of the line, situated to the east of Vastern Road between the SER and GWR lines. It had a brick-built shed, with three tracks, one of which was used by the LSWR. The 45 feet (13.7 m) turntable was replaced in 1926 by one of 65 feet (19.8 m) diameter. On 15 October 1898, the SER had 22 locomotives allocated to Reading. Normally, about twenty locomotives were based at Reading; the allocation fell from 22 to 17 upon electrification in 1939. Locomotive classes allocated in 1950 were mostly ex-SECR types: they included eight 2-6-0s of the SR U class; seven 4-4-0s, mostly of the SECR D class
; and two 0-6-0T shunting engines of the SECR R1 class. The duties of the two tank engines included piloting the station, shunting the goods yard and banking goods trains up to . Following Nationalisation, the code 70E was allotted to Reading depot in 1950, which it retained until 1959, when it became a sub-shed of Basingstoke. The depot was reduced in importance in May 1954, when most of the locomotives were transferred away leaving just two shunting engines, but complete closure did not occur until January 1965.
 Since 1903 the Southern Railway and its constituents had pursued a policy of electrification, which began with the routes closest to the London termini and gradually worked outwards. On the LSWR's Waterloo to Reading Line
Since 1903 the Southern Railway and its constituents had pursued a policy of electrification, which began with the routes closest to the London termini and gradually worked outwards. On the LSWR's Waterloo to Reading Line
, electric trains had reached on 25 October 1915 and on 30 January 1916; was reached (the Hounslow Loop Line
) on 12 March 1916. The policy was continued by the Southern Railway from 1923, and on 6 July 1930, electrification was extended to Windsor, which included the Reading line as far as . Electric trains reached on 3 January 1937, and in that year, several electrification schemes were proposed by the Southern Railway
, which included the route from Virginia Water to Reading. As part of these works, new berthing sidings were provided at Reading. The electric service from Waterloo to Reading was introduced on 1 January 1939; trains were every 20 minutes at peak times and every 30 minutes off-peak and on Sundays. Most trains ran non-stop between Waterloo and Staines, and on the outward journey they divided at Ascot (with one portion continuing to Guildford
via ), whilst on the London-bound trip, the two portions would be combined again at Ascot. The total journey time from Waterloo to Reading was reduced from 90 minutes to 75.
New electric trains were built for these services, which consisted of two-coach units; up to four units could be coupled to make a train of up to eight coaches. Each coach of a unit had the seating in compartments, flanked by a driving cab at one end and a lavatory at the other, and there was a side corridor (although there were no gangway connections between the coaches); this was to allow the passengers access to the lavatory. One of the coaches had both first- and third-class compartments, and seated 24 in first-class and 32 in third; the other coach had only third-class, seating 52, but also had a brake section for the guard and luggage, together with the traction motor
s. The units were known as the "2-BIL
" type.
The electric trains bore headcodes to inform both passengers and staff of the route, origin and destination of the train, but not necessarily the direction. Several were used: for example, in March 1939, trains running between Waterloo and Reading bore number 27 if running via Brentford, or 28 if running via Richmond. The main codes remained unchanged for several years but there were occasional amendments particularly for special trains; in the 1950s, specials between Reading and were no. 18, and in 1961, specials between Reading and Bognor
or were no. 41 if running via Ascot, Aldershot, Guildford and ; or 42 if via , and Havant. If the train was equipped to show only letters as headcodes instead of numbers, letter L was used for all services between Reading and Ascot or Waterloo, sometimes with two dots or a bar above the letter to denote different destinations or routes.
The sidings at Reading were used to stable electric trains overnight and at off-peak hours; for example, in Summer 1955, six 2-BIL units would be left in the sidings overnight.
, the North Downs Line
to Redhill was not electrified beyond Wokingham, apart from short stretches shared with other routes. The first Beeching report recommended curtailing the passenger service at Guildford and the closure of all stations between Shalford and Betchworth inclusive. The second Beeching report recommended that the whole of the North Downs Line should be developed as a trunk route for freight services. The passenger service along the entire line was however reprieved, provided that costs could be reduced. The steam-hauled services were to be withdrawn, but money was not available for new Diesel trains. Instead, in 1964, six three-car trains were provided by putting together spare coaches from elsewhere on the network: twelve came from disbanded 6-S
units on the Hastings line, six of which had Diesel engines and driving cabs; there were also six driving trailers from 2-EPB
electric trains available. One coach of each type was coupled together to form a three-car unit; these were officially designated the 3-R units
, but were popularly known as "tadpoles" because the former EMU driving trailer was noticeably wider than the two Hastings coaches.
The Diesel service was introduced between Reading and on 4 January 1965. The Redhill line timetable was totally recast; there was no longer a London service, and most services now ran all the way to . The service was second-class only, with a normal off-peak service interval of 60 minutes. Most trains consisted of one "tadpole" unit, but a few services were operated using BRCW Type 3 Diesel locomotives
hauling three ordinary coaches.
South Eastern Railway (UK)
The South Eastern Railway was a railway company in south-eastern England from 1836 until 1922. The company was formed to construct a route from London to Dover. Branch lines were later opened to Tunbridge Wells, Hastings, Canterbury and other places in Kent...
's route from . It was also used by London and South Western Railway
London and South Western Railway
The London and South Western Railway was a railway company in England from 1838 to 1922. Its network extended from London to Plymouth via Salisbury and Exeter, with branches to Ilfracombe and Padstow and via Southampton to Bournemouth and Weymouth. It also had many routes connecting towns in...
services from London Waterloo.
The station was situated adjacent to, and to the south-east of, the Great Western Railway
Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway was a British railway company that linked London with the south-west and west of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament in 1835 and ran its first trains in 1838...
's Reading General station
Reading railway station
Reading railway station is a major rail transport hub in the English town of Reading. It is situated on the northern edge of the town centre, close to the main retail and commercial areas, and also the River Thames...
, which is now simply known as Reading station. The 1989-built concourse of that station now occupies the site of the frontage of the Southern station.
Construction and early years
The original route of the South Eastern RailwaySouth Eastern Railway (UK)
The South Eastern Railway was a railway company in south-eastern England from 1836 until 1922. The company was formed to construct a route from London to Dover. Branch lines were later opened to Tunbridge Wells, Hastings, Canterbury and other places in Kent...
(SER) was from London Bridge station
London Bridge station
London Bridge railway station is a central London railway terminus and London Underground complex in the London Borough of Southwark, occupying a large area on two levels immediately south-east of London Bridge and 1.6 miles east of Charing Cross. It is one of the oldest railway stations in the...
to Dover, which took a route through in order that several companies could share the same lines. The line from Reading to Redhill was built by the Reading, Guildford and Reigate Railway (RG&RR), and was opened in stages: the section from Reading to Farnborough
Farnborough North railway station
Farnborough North railway station is a railway station in the town of Farnborough in Hampshire, England. The station is managed by First Great Western, who operate services on the North Downs Line from Reading to Guildford, Redhill and Gatwick Airport....
was opened on 4 July 1849, with the last section being opened on 15 October 1849. From the start, the RG&RR was worked by the SER, which leased it from 16 July 1846, and absorbed it in 1852. When the first section of line opened, the SER trains served a temporary station north of Forbury Road before moving into a permanent terminal station, about 275 metres (300.7 yd) to the west, on 30 August 1855.
Reading had been served by the Great Western Railway
Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway was a British railway company that linked London with the south-west and west of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament in 1835 and ran its first trains in 1838...
(GWR) since 1840, and the 1855 SER station was situated west of Vastern Road, on the corner of Blagrave Street and Station Road, adjacent to but south-east of the GWR station, and at a slightly lower level.
The Staines, Wokingham & Woking Junction Railway (SW&WJR) opened a line between and (Staines Junction) on 9 July 1856; the SW&WJR was worked by the London and South Western Railway
London and South Western Railway
The London and South Western Railway was a railway company in England from 1838 to 1922. Its network extended from London to Plymouth via Salisbury and Exeter, with branches to Ilfracombe and Padstow and via Southampton to Bournemouth and Weymouth. It also had many routes connecting towns in...
(LSWR), and they were authorised to run over the SER into Reading. In this way Reading gained a service into London Waterloo station. The SW&WJR was absorbed by the LSWR in 1878.
The original station did not last long, since it was destroyed by fire in 1859 after being struck by lightning. A replacement was built, which had two platform faces; it was enlarged in 1896 by the provision of two more faces following the resiting of the locomotive shed.
At the opening, there were four trains a day to (then known as Reigate Junction), two of which continued to ; a through service to London Bridge
London Bridge station
London Bridge railway station is a central London railway terminus and London Underground complex in the London Borough of Southwark, occupying a large area on two levels immediately south-east of London Bridge and 1.6 miles east of Charing Cross. It is one of the oldest railway stations in the...
began in 1852, and in 1853, two more were added.
The middle period

London, Chatham and Dover Railway
The London, Chatham and Dover Railway was a railway company in south-eastern England from 1859 until the 1923 grouping which united it with other companies to form the Southern Railway. Its lines ran through London and northern and eastern Kent to form a significant part of the Greater London...
(LCDR), which traded as the South Eastern and Chatham Railway
South Eastern and Chatham Railway
The South Eastern and Chatham Railway Companies Joint Management Committee , known by its shorter name of the South Eastern and Chatham Railway was a working union of two neighbouring rival railways, the South Eastern Railway and London, Chatham and Dover Railway , that operated services between...
(SE&CR); the line and station continued to be owned and maintained by the SER. In 1923, the LSWR and SER amalgamated, together with other railways including the LCDR (and thus the SE&CR), to form the Southern Railway
Southern Railway (Great Britain)
The Southern Railway was a British railway company established in the 1923 Grouping. It linked London with the Channel ports, South West England, South coast resorts and Kent...
(SR), which assumed complete control of Reading station and its approaches.
In 1900, there were ten trains each weekday from Waterloo to Reading; by 1914 there were 14, and in 1922, 18. The services tended to be irregular, until the electrification of the inner suburban lines from Waterloo during 1915–16 brought a clock-face pattern to those services, in order to make it easy for people who did not understand timetables; the steam-hauled services, such as those to Reading, had to fit in (there were eight electric trains per hour on the Reading line as far as ) and so became more regular.
During the Dunkirk evacuation (27 May-4 June 1940), 293 special trains arrived at Reading from the Channel ports, most of which were handed over to the GWR.
After the War, there was only one train from Reading to London via the SER route; this was the 7.27am to London Bridge
London Bridge station
London Bridge railway station is a central London railway terminus and London Underground complex in the London Borough of Southwark, occupying a large area on two levels immediately south-east of London Bridge and 1.6 miles east of Charing Cross. It is one of the oldest railway stations in the...
, which arrived at 9.49, and the 5.25pm return, arriving back at Reading at 7.59. Three coaches sufficed between Reading and Redhill; but by 1960, six were required. The locomotive was normally a Schools class 4-4-0 based at Redhill.
At Nationalisation, the Southern Railway effectively became the Southern Region of British Railways
Southern Region of British Railways
The Southern Region was a region of British Railways from 1948. The region ceased to be an operating unit in its own right in the 1980s and was wound up at the end of 1992. The region covered south London, southern England and the south coast, including the busy commuter belt areas of Kent, Sussex...
, and things continued more or less as before; but the station (originally named simply Reading) was renamed Reading South on 26 September 1949, to distinguish it from the adjacent Western Region
Western Region of British Railways
The Western Region was a region of British Railways from 1948. The region ceased to be an operating unit in its own right in the 1980s and was wound up at the end of 1992...
(ex-GWR) station (which became Reading General at the same time).
Later years and closure

Guildford (Surrey) railway station
Guildford railway station is an important railway junction on the Portsmouth Direct Line serving the town of Guildford in Surrey, England. It is 30.3 miles from London Waterloo....
services into the latter station, which would allow the Southern station to be closed.
In the station's final arrangement, there were four platforms; east of Vastern Road were a locomotive depot on the north side of the line, and a goods shed and sidings on the south side.
The passenger station was closed on 6 September 1965, with services being diverted into Reading General; most (including all the electric services) then used a newly-built platform 4A at the latter station, which was long enough for an eight-coach train. It was intended that the non-electric (Guildford line) services would use the older platforms at Reading General; but in practice, these used platform 4A as well. Freight continued to be handled until September 1970, when all goods services were withdrawn except for the Huntley & Palmers
Huntley & Palmers
Huntley & Palmers was a British firm of biscuit makers originally based in Reading, Berkshire. The company created one of the world's first global brands and ran what was once the world’s largest biscuit factory. Over the years, the company was also known as J...
biscuit traffic, which lasted until April 1979.
After demolition the site of the passenger station was used as a car park for Reading General. In 1989 a new concourse for Reading station
Reading railway station
Reading railway station is a major rail transport hub in the English town of Reading. It is situated on the northern edge of the town centre, close to the main retail and commercial areas, and also the River Thames...
was built on the site, and no trace now remains of the former SER station.
Connections between the SER and GWR routes
The first connection, 71 chains (1,428.3 m) in length, was laid in from some sidings on the north side of the GWR line, burrowing under that line, connecting with the SER line facing east; none of it was owned by the SER: the LSWR owned the easternmost 9 chains (181.1 m) and the GWR the remainder. It connected into the GWR main line to the west of the station, and since there were no platforms on the connection, it was primarily used for goods trains, being first used on 1 December 1858.A second connection was built to the west of the first one, and was opened on 17 December 1899. This was quite steep.
A third connection to the east of the previous two was opened on 26 May 1941, and like the second allowed trains stopping in the GWR station to run to or from the SER line.
When the SER station closed in 1965, the connection built in 1899 was relaid to allow the services over the former SER line to run into the newly-built Platform 4A at Reading General
Reading railway station
Reading railway station is a major rail transport hub in the English town of Reading. It is situated on the northern edge of the town centre, close to the main retail and commercial areas, and also the River Thames...
.
Locomotive depot
The SER built an engine shed adjacent to the station in 1852. It was replaced by another structure in 1875, and re-roofed in the early 1950s. Like the station, it closed in 1965.The 1875 depot was constructed on the north side of the line, situated to the east of Vastern Road between the SER and GWR lines. It had a brick-built shed, with three tracks, one of which was used by the LSWR. The 45 feet (13.7 m) turntable was replaced in 1926 by one of 65 feet (19.8 m) diameter. On 15 October 1898, the SER had 22 locomotives allocated to Reading. Normally, about twenty locomotives were based at Reading; the allocation fell from 22 to 17 upon electrification in 1939. Locomotive classes allocated in 1950 were mostly ex-SECR types: they included eight 2-6-0s of the SR U class; seven 4-4-0s, mostly of the SECR D class
SECR D class
The SECR D class was a class of 4-4-0 tender locomotives designed by Harry Wainwright for the South Eastern and Chatham Railway.-Overview:The construction of the initial 20 engines was shared between Ashford railway works and the Glasgow builder, Sharp, Stewart and Company. The first of the class...
; and two 0-6-0T shunting engines of the SECR R1 class. The duties of the two tank engines included piloting the station, shunting the goods yard and banking goods trains up to . Following Nationalisation, the code 70E was allotted to Reading depot in 1950, which it retained until 1959, when it became a sub-shed of Basingstoke. The depot was reduced in importance in May 1954, when most of the locomotives were transferred away leaving just two shunting engines, but complete closure did not occur until January 1965.
Electrification

Waterloo to Reading Line
The Waterloo to Reading Line is a National Rail suburban electric railway line running generally westwards from London, England. It is operated by South West Trains...
, electric trains had reached on 25 October 1915 and on 30 January 1916; was reached (the Hounslow Loop Line
Hounslow Loop Line
The Hounslow Loop Line is a railway line in southwest London which was opened by the London and South Western Railway in 1850. It leaves the Waterloo to Reading Line at Barnes Junction and after some seven and a half miles rejoins it at a triangular junction between and...
) on 12 March 1916. The policy was continued by the Southern Railway from 1923, and on 6 July 1930, electrification was extended to Windsor, which included the Reading line as far as . Electric trains reached on 3 January 1937, and in that year, several electrification schemes were proposed by the Southern Railway
Southern Railway (Great Britain)
The Southern Railway was a British railway company established in the 1923 Grouping. It linked London with the Channel ports, South West England, South coast resorts and Kent...
, which included the route from Virginia Water to Reading. As part of these works, new berthing sidings were provided at Reading. The electric service from Waterloo to Reading was introduced on 1 January 1939; trains were every 20 minutes at peak times and every 30 minutes off-peak and on Sundays. Most trains ran non-stop between Waterloo and Staines, and on the outward journey they divided at Ascot (with one portion continuing to Guildford
Guildford (Surrey) railway station
Guildford railway station is an important railway junction on the Portsmouth Direct Line serving the town of Guildford in Surrey, England. It is 30.3 miles from London Waterloo....
via ), whilst on the London-bound trip, the two portions would be combined again at Ascot. The total journey time from Waterloo to Reading was reduced from 90 minutes to 75.
New electric trains were built for these services, which consisted of two-coach units; up to four units could be coupled to make a train of up to eight coaches. Each coach of a unit had the seating in compartments, flanked by a driving cab at one end and a lavatory at the other, and there was a side corridor (although there were no gangway connections between the coaches); this was to allow the passengers access to the lavatory. One of the coaches had both first- and third-class compartments, and seated 24 in first-class and 32 in third; the other coach had only third-class, seating 52, but also had a brake section for the guard and luggage, together with the traction motor
Traction motor
Traction motor refers to an electric motor providing the primary rotational torque of a machine, usually for conversion into linear motion ....
s. The units were known as the "2-BIL
British Rail Class 401
The Southern Railway gave the designation 2-BIL to the DC third rail electric multiple units built during the 1930s to work long-distance semi-fast services on the newly electrified lines from London to Eastbourne, Portsmouth and Reading...
" type.
The electric trains bore headcodes to inform both passengers and staff of the route, origin and destination of the train, but not necessarily the direction. Several were used: for example, in March 1939, trains running between Waterloo and Reading bore number 27 if running via Brentford, or 28 if running via Richmond. The main codes remained unchanged for several years but there were occasional amendments particularly for special trains; in the 1950s, specials between Reading and were no. 18, and in 1961, specials between Reading and Bognor
Bognor Regis railway station
Bognor Regis railway station is in the town of Bognor Regis, in the English county of West Sussex, England. It is approximately 65 miles south of London Victoria. The station and the trains serving it are operated by Southern railway company...
or were no. 41 if running via Ascot, Aldershot, Guildford and ; or 42 if via , and Havant. If the train was equipped to show only letters as headcodes instead of numbers, letter L was used for all services between Reading and Ascot or Waterloo, sometimes with two dots or a bar above the letter to denote different destinations or routes.
The sidings at Reading were used to stable electric trains overnight and at off-peak hours; for example, in Summer 1955, six 2-BIL units would be left in the sidings overnight.
Dieselisation
Unlike the line to Waterloo via BracknellWaterloo to Reading Line
The Waterloo to Reading Line is a National Rail suburban electric railway line running generally westwards from London, England. It is operated by South West Trains...
, the North Downs Line
North Downs Line
The North Downs Line is the name of the passenger train service connecting Reading, on the Great Western Main Line, to Gatwick Airport, on the Brighton Main Line...
to Redhill was not electrified beyond Wokingham, apart from short stretches shared with other routes. The first Beeching report recommended curtailing the passenger service at Guildford and the closure of all stations between Shalford and Betchworth inclusive. The second Beeching report recommended that the whole of the North Downs Line should be developed as a trunk route for freight services. The passenger service along the entire line was however reprieved, provided that costs could be reduced. The steam-hauled services were to be withdrawn, but money was not available for new Diesel trains. Instead, in 1964, six three-car trains were provided by putting together spare coaches from elsewhere on the network: twelve came from disbanded 6-S
British Rail Class 201
The British Rail Class 201 six-car diesel-electric multiple units were built in 1957-1958 at Eastleigh and Ashford. They were built for use on the London-Hastings line...
units on the Hastings line, six of which had Diesel engines and driving cabs; there were also six driving trailers from 2-EPB
British Rail Class 416
British Rail Class 416 electric multiple units were built between 1953 and 1956. They were intended for inner suburban passenger services on London's Southern Electric network...
electric trains available. One coach of each type was coupled together to form a three-car unit; these were officially designated the 3-R units
British Rail Class 206
The British Rail Class 206 or 3R was a type of Diesel electric multiple unit first created in 1964. They were not 'built' as such but rather re-formed from Class 201 and EPB vehicles for use on -- services...
, but were popularly known as "tadpoles" because the former EMU driving trailer was noticeably wider than the two Hastings coaches.
The Diesel service was introduced between Reading and on 4 January 1965. The Redhill line timetable was totally recast; there was no longer a London service, and most services now ran all the way to . The service was second-class only, with a normal off-peak service interval of 60 minutes. Most trains consisted of one "tadpole" unit, but a few services were operated using BRCW Type 3 Diesel locomotives
British Rail Class 33
The British Rail Class 33 also known as the BRCW Type 3 or Crompton is a class of Bo-Bo diesel-electric locomotives ordered in 1957 and built for the Southern Region of British Railways between 1960 and 1962....
hauling three ordinary coaches.
Accidents
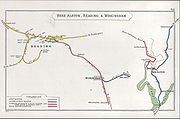
On 12 September 1855, a light engine (ie an engine running alone, without a train) was sent from Reading to Guildford on the down line, even though it was to travel in the up direction. After running for about a mile, it collided with the 4.40 pm service from London Bridge to Reading, which was running correctly on the down line. The driver of the light engine and four passengers were killed; ten more were seriously injured, and three of those died later in hospital.Routes
See also
- London and South Western RailwayLondon and South Western RailwayThe London and South Western Railway was a railway company in England from 1838 to 1922. Its network extended from London to Plymouth via Salisbury and Exeter, with branches to Ilfracombe and Padstow and via Southampton to Bournemouth and Weymouth. It also had many routes connecting towns in...
- Reading railway stationReading railway stationReading railway station is a major rail transport hub in the English town of Reading. It is situated on the northern edge of the town centre, close to the main retail and commercial areas, and also the River Thames...
- Reading West railway stationReading West railway stationReading West is a railway station in Reading in England. It is in West Reading, west of the town centre, about from the main retail and commercial areas. The station is served by local services operated by First Great Western.-History:...
- South Eastern and Chatham RailwaySouth Eastern and Chatham RailwayThe South Eastern and Chatham Railway Companies Joint Management Committee , known by its shorter name of the South Eastern and Chatham Railway was a working union of two neighbouring rival railways, the South Eastern Railway and London, Chatham and Dover Railway , that operated services between...
- South Eastern RailwaySouth Eastern Railway (UK)The South Eastern Railway was a railway company in south-eastern England from 1836 until 1922. The company was formed to construct a route from London to Dover. Branch lines were later opened to Tunbridge Wells, Hastings, Canterbury and other places in Kent...
- Southern RailwaySouthern Railway (Great Britain)The Southern Railway was a British railway company established in the 1923 Grouping. It linked London with the Channel ports, South West England, South coast resorts and Kent...
Further reading
- Nock (1965) The London & South Western Railway
- Williams (1968) The London & South Western Railway, vol. 1
- Williams (1973) The London & South Western Railway, vol. 2

