
Rank product
Encyclopedia
The rank product is a biologically motivated test for the detection of differentially expressed
genes in replicated microarray
experiments.
It is a simple non-parametric
statistical method based on ranks
of fold changes. In addition to its use in expression profiling
, it can be used to combine ranked lists in various application domains, including proteomics
, metabolomics
, statistical meta-analysis
, and general feature selection
.
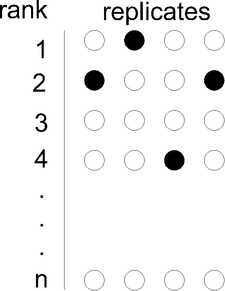 Given n genes and k replicates, let
Given n genes and k replicates, let 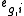 be the fold change and
be the fold change and 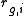 the rank of gene g in the i-th replicate.
the rank of gene g in the i-th replicate.
Compute the rank product via the geometric mean
:
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as ribosomal RNA , transfer RNA or small nuclear RNA genes, the product is a functional RNA...
genes in replicated microarray
DNA microarray
A DNA microarray is a collection of microscopic DNA spots attached to a solid surface. Scientists use DNA microarrays to measure the expression levels of large numbers of genes simultaneously or to genotype multiple regions of a genome...
experiments.
It is a simple non-parametric
Non-parametric statistics
In statistics, the term non-parametric statistics has at least two different meanings:The first meaning of non-parametric covers techniques that do not rely on data belonging to any particular distribution. These include, among others:...
statistical method based on ranks
Ranking
A ranking is a relationship between a set of items such that, for any two items, the first is either 'ranked higher than', 'ranked lower than' or 'ranked equal to' the second....
of fold changes. In addition to its use in expression profiling
Expression profiling
In the field of molecular biology, gene expression profiling is the measurement of the activity of thousands of genes at once, to create a global picture of cellular function. These profiles can, for example, distinguish between cells that are actively dividing, or show how the cells react to a...
, it can be used to combine ranked lists in various application domains, including proteomics
Proteomics
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins, particularly their structures and functions. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, as they are the main components of the physiological metabolic pathways of cells. The term "proteomics" was first coined in 1997 to make an analogy with...
, metabolomics
Metabolomics
Metabolomics is the scientific study of chemical processes involving metabolites. Specifically, metabolomics is the "systematic study of the unique chemical fingerprints that specific cellular processes leave behind", the study of their small-molecule metabolite profiles...
, statistical meta-analysis
Meta-analysis
In statistics, a meta-analysis combines the results of several studies that address a set of related research hypotheses. In its simplest form, this is normally by identification of a common measure of effect size, for which a weighted average might be the output of a meta-analyses. Here the...
, and general feature selection
Feature selection
In machine learning and statistics, feature selection, also known as variable selection, feature reduction, attribute selection or variable subset selection, is the technique of selecting a subset of relevant features for building robust learning models...
.
Calculation of the rank product

 be the fold change and
be the fold change and 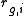 the rank of gene g in the i-th replicate.
the rank of gene g in the i-th replicate.Compute the rank product via the geometric mean
Geometric mean
The geometric mean, in mathematics, is a type of mean or average, which indicates the central tendency or typical value of a set of numbers. It is similar to the arithmetic mean, except that the numbers are multiplied and then the nth root of the resulting product is taken.For instance, the...
:
Determination of significance levels
Simple permutation-based estimation is used to determine how likely a given RP value or better is observed in a random experiment.- generate p permutationPermutationIn mathematics, the notion of permutation is used with several slightly different meanings, all related to the act of permuting objects or values. Informally, a permutation of a set of objects is an arrangement of those objects into a particular order...
s of k rank lists of length n. - calculate the rank products of the n genes in the p permutations.
- count how many times the rank products of the genes in the permutations are smaller or equal to the observed rank product. Set c to this value.
- calculate the average expected value for the rank product by:
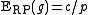 .
. - calculate the percentage of false positives as :
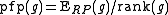 where
where  is the rank of gene g in a list of all n genes sorted by increasing
is the rank of gene g in a list of all n genes sorted by increasing 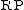 .
.


