
QBD (electronics)
Encyclopedia
QBD is the term applied to the charge-to-breakdown measurement of a semiconductor
device. It is a standard destructive test
method used to determine the quality of gate oxide
s in MOS
devices. It is equal to the total accumulated charge
passing through the dielectric
layer just before failure. Thus QBD is a measure of time-dependent gate oxide breakdown
. As a measure of oxide quality, QBD can also be a useful predictor of product reliability
under specified electrical stress conditions.
is applied to the MOS structure to force a controlled current
through the oxide, i.e. to inject a controlled amount of charge into the dielectric layer. By measuring the time after which the measured voltage drops towards zero (when electrical breakdown
occurs) and integrating the injected current over time, the charge needed to break the gate oxide is determined.
This gate charge integral
is defined as:
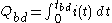
where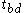 is the measurement time at the step just prior to destructive avalanche breakdown
is the measurement time at the step just prior to destructive avalanche breakdown
.
For the V-ramp test procedure, the measured current
is integrated to obtain QBD. The measured current is also used as a detection criterion for terminating the voltage ramp. One of the defined criteria is the change of logarithmic current slope between successive voltage steps.
of measured QBD is commonly analysed using a Weibull chart.
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
device. It is a standard destructive test
Destructive testing
In destructive testing, tests are carried out to the specimen's failure, in order to understand a specimen's structural performance or material behaviour under different loads...
method used to determine the quality of gate oxide
Gate oxide
The gate oxide is the dielectric layer that separates the gate terminal of a MOSFET from the underlying source and drain terminals as well as the conductive channel that connects source and drain when the transistor is turned on. Gate oxide is formed by oxidizing the silicon of the channel to form...
s in MOS
MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor is a transistor used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. The basic principle of this kind of transistor was first patented by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925...
devices. It is equal to the total accumulated charge
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
passing through the dielectric
Dielectric
A dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material, as in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric...
layer just before failure. Thus QBD is a measure of time-dependent gate oxide breakdown
Time-dependent gate oxide breakdown
Time-dependent gate oxide breakdown is a failure mechanism in MOSFETs, when the gate oxide breaks down as a result of long-time application of relatively low electric field...
. As a measure of oxide quality, QBD can also be a useful predictor of product reliability
Reliability (semiconductor)
Reliability of semiconductor devices can be summarized as follows:# Semiconductor devices are very sensitive to impurities and particles. Therefore, to manufacture these devices it is necessary to manage many processes while accurately controlling the level of impurities and particles...
under specified electrical stress conditions.
Test method
VoltageVoltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
is applied to the MOS structure to force a controlled current
Current source
A current source is an electrical or electronic device that delivers or absorbs electric current. A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current sink is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply...
through the oxide, i.e. to inject a controlled amount of charge into the dielectric layer. By measuring the time after which the measured voltage drops towards zero (when electrical breakdown
Electrical breakdown
The term electrical breakdown or electric breakdown has several similar but distinctly different meanings. For example, the term can apply to the failure of an electric circuit....
occurs) and integrating the injected current over time, the charge needed to break the gate oxide is determined.
This gate charge integral
Integral
Integration is an important concept in mathematics and, together with its inverse, differentiation, is one of the two main operations in calculus...
is defined as:
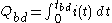
where
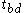 is the measurement time at the step just prior to destructive avalanche breakdown
is the measurement time at the step just prior to destructive avalanche breakdownAvalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown is a phenomenon that can occur in both insulating and semiconducting materials. It is a form of electric current multiplication that can allow very large currents within materials which are otherwise good insulators. It is a type of electron avalanche...
.
Variants
There are five common variants of the QBD test method:- Linear voltage ramp (V-ramp test procedure)
- Constant currentConstant currentConstant current is a term most often used in electronics to describe a system that can vary the voltage across an electronic circuit to maintain a constant electric current....
stress (CCS) - Exponential current ramp (ECR) or (J-ramp test procedure)
- Bounded J-ramp (a variant of the J-ramp procedure, in which the current ramp stops at a defined stress level, and continues as a constant current stress).
- Linear current ramp (LCR)
For the V-ramp test procedure, the measured current
Ammeter
An ammeter is a measuring instrument used to measure the electric current in a circuit. Electric currents are measured in amperes , hence the name. Instruments used to measure smaller currents, in the milliampere or microampere range, are designated as milliammeters or microammeters...
is integrated to obtain QBD. The measured current is also used as a detection criterion for terminating the voltage ramp. One of the defined criteria is the change of logarithmic current slope between successive voltage steps.
Analysis
The cumulative distributionCumulative distribution function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function , or just distribution function, describes the probability that a real-valued random variable X with a given probability distribution will be found at a value less than or equal to x. Intuitively, it is the "area so far"...
of measured QBD is commonly analysed using a Weibull chart.
JEDEC Standard
- JESD35-A – Procedure for the Wafer-Level Testing of Thin Dielectrics, April 2001
See also
- Capacitor - breakdown section
- Field electron emission

