
Pyrimidinedione
Encyclopedia
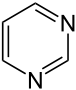
Pyrimidine
Pyrimidine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound similar to benzene and pyridine, containing two nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 of the six-member ring...
ring substituted with two carbonyl
Carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups....
groups.
Examples include naturally occurring metabolite
Metabolite
Metabolites are the intermediates and products of metabolism. The term metabolite is usually restricted to small molecules. A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal growth, development, and reproduction. Alcohol is an example of a primary metabolite produced in large-scale by industrial...
s:
| Trivial name | IUPAC name | Structure | Pathway |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uracil Uracil Uracil is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of RNA that are represented by the letters A, G, C and U. The others are adenine, cytosine, and guanine. In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by thymine.Uracil is a common and... |
Pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione | 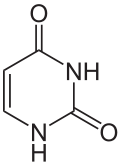 |
Pyrimidine biosynthesis |
| Thymine Thymine Thymine is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine nucleobase. As the name suggests, thymine may be derived by methylation of uracil at... |
5-Methylpyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione | 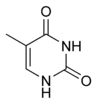 |
Pyrimidine biosynthesis |
| 5,6-Diaminopyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione | Riboflavin biosynthesis |
and drugs:
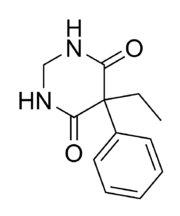
- FluorouracilFluorouracilFluorouracil is a drug that is a pyrimidine analog which is used in the treatment of cancer. It is a suicide inhibitor and works through irreversible inhibition of thymidylate synthase. It belongs to the family of drugs called antimetabolites...
- IdoxuridineIdoxuridineIdoxuridine is an anti-herpesvirus antiviral drug.It is a nucleoside analogue, a modified form of deoxyuridine, similar enough to be incorporated into viral DNA replication, but the iodine atom added to the uracil component blocks base pairing. It is used only topically due to...
- PrimidonePrimidonePrimidone is an anticonvulsant of the pyrimidinedione class, the active metabolites of which, phenobarbital and phenylethylmalonamide , are also anticonvulsants...
- TrifluridineTrifluridineTrifluridine is an anti-herpesvirus antiviral drug, used primarily on the eye. It was sold under the trade name, Viroptic, by Glaxo Wellcome, now merged into GlaxoSmithKline...

