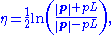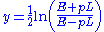Pseudorapidity
Encyclopedia
Particle physics
Particle physics is a branch of physics that studies the existence and interactions of particles that are the constituents of what is usually referred to as matter or radiation. In current understanding, particles are excitations of quantum fields and interact following their dynamics...
, pseudorapidity,
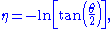
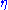 , is a commonly used spatial coordinate describing the angle of a particle relative to the beam axis. It is defined as
, is a commonly used spatial coordinate describing the angle of a particle relative to the beam axis. It is defined as
where
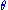 is the angle between the particle momentum
is the angle between the particle momentum  and the beam axis. In terms of the momentum, the pseudorapidity variable can be written as
and the beam axis. In terms of the momentum, the pseudorapidity variable can be written as
where
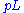 is the component of the momentum along the beam axis. In the limit where the particle is travelling close to the speed of light, or in the approximation that the mass of the particle is nearly zero, pseudorapidity is numerically close to the experimental particle physicist's definition of rapidity,
is the component of the momentum along the beam axis. In the limit where the particle is travelling close to the speed of light, or in the approximation that the mass of the particle is nearly zero, pseudorapidity is numerically close to the experimental particle physicist's definition of rapidity,
This differs slightly from the definition of rapidity
Rapidity
In relativity, rapidity is an alternative to speed as a framework for measuring motion. On parallel velocities rapidities are simply additive, unlike speeds at relativistic velocities. For low speeds, rapidity and speed are proportional, but for high speeds, rapidity takes a larger value. The...
in special relativity
Special relativity
Special relativity is the physical theory of measurement in an inertial frame of reference proposed in 1905 by Albert Einstein in the paper "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies".It generalizes Galileo's...
, which uses
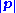 instead of
instead of  . However, pseudorapidity depends only on the polar angle of its trajectory, and not on the energy of the particle.
. However, pseudorapidity depends only on the polar angle of its trajectory, and not on the energy of the particle.In hadron collider physics, the rapidity (or pseudorapidity) is preferred over the polar angle
 because, loosely speaking, particle production is constant as a function of rapidity. One speaks of the "forward" direction in a hadron collider experiment, which refers to regions of the detector that are close to the beam axis, at high
because, loosely speaking, particle production is constant as a function of rapidity. One speaks of the "forward" direction in a hadron collider experiment, which refers to regions of the detector that are close to the beam axis, at high 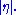
The difference in the rapidity of two particles is independent of Lorentz boosts along the beam axis.
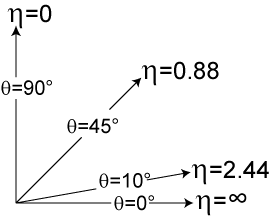
Values
Here are some representative values: 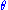 (degrees) (degrees) |
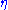 |
|---|---|
| 0 | infinity |
| 5 | 3.13 |
| 10 | 2.44 |
| 20 | 1.74 |
| 30 | 1.32 |
| 45 | 0.88 |
| 60 | 0.55 |
| 80 | 0.175 |
| 90 | 0 |
| 100 | -0.175 |
| 120 | -0.55 |
| ... | ... |
| 175 | -3.13 |
| 180 | -infinity |
Pseudorapidity is odd about
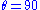 degrees. In other words,
degrees. In other words, 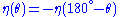 .
.Conversion to Cartesian Momenta
Hadron colliders measure physical momenta in terms of transverse momentum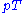 , polar angle in the transverse plane
, polar angle in the transverse plane 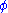 and pseudorapidity
and pseudorapidity  . To obtain cartesian momenta
. To obtain cartesian momenta  (with z being the beam axis) simply use
(with z being the beam axis) simply use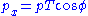
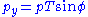
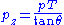 , with
, with  ; alternatively,
; alternatively, 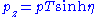 .
.