
Proximity effect (electromagnetism)
Encyclopedia
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
, if currents are flowing through one or more other nearby conductors, such as within a closely wound coil of wire, the distribution of current within the first conductor will be constrained to smaller regions. The resulting current crowding is termed the proximity effect. This crowding gives an increase in the effective resistance of the circuit, which increases with frequency.
Explanation
A changing magnetic fieldMagnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
will influence the distribution of an electric current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
flowing within an electrical conductor
Electrical conductor
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is a material which contains movable electric charges. In metallic conductors such as copper or aluminum, the movable charged particles are electrons...
, by electromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic induction is the production of an electric current across a conductor moving through a magnetic field. It underlies the operation of generators, transformers, induction motors, electric motors, synchronous motors, and solenoids....
. When an alternating current
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
(AC) flows through an isolated conductor, it creates an associated alternating magnetic field around it. The alternating magnetic field induces eddy currents in adjacent conductors, altering the overall distribution of current flowing through them. The result is that the current is concentrated in the areas of the conductor furthest away from nearby conductors carrying current in the same direction.
The proximity effect can significantly increase the AC resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
of adjacent conductors when compared to its resistance to a DC
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
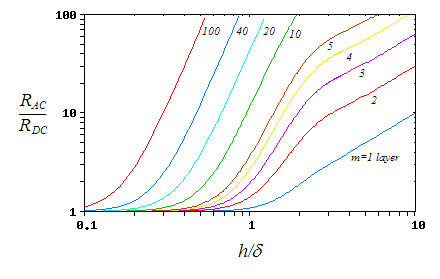
current. The effect increases with frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
. At higher frequencies, the AC resistance of a conductor can easily exceed ten times its DC resistance.
Example
For example, if two wires carrying the same alternating current lie parallel to one another, as would be found in a coil used in an inductorInductor
An inductor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in a magnetic field. An inductor's ability to store magnetic energy is measured by its inductance, in units of henries...
or transformer
Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
, the magnetic field of one wire will induce longitudinal eddy currents in the adjacent wire, that flow in long loops along the wire, in the same direction as the main current on the side of the wire facing away from the other wire, and back in the opposite direction on the side of the wire facing the other wire. Thus the eddy current will reinforce the main current on the side facing away from the first wire, and oppose the main current on the side facing the first wire. The net effect is to redistribute the current in the cross section of the wire into a thin strip on the side facing away from the other wire. Since the current is concentrated into a smaller area of the wire, the resistance is increased.
Similarly, in two adjacent conductors carrying alternating currents flowing in opposite directions, such as are found in power cable
Power cable
A power cable is an assembly of two or more electrical conductors, usually held together with an overall sheath. The assembly is used for transmission of electrical power...
s and pairs of bus bars, the current in each conductor is concentrated into a strip on the side facing the other conductor.
Effects
The additional resistance increases power losses which, in power circuits, can generate undesirable heating. Proximity and skin effectSkin effect
Skin effect is the tendency of an alternating electric current to distribute itself within a conductor with the current density being largest near the surface of the conductor, decreasing at greater depths. In other words, the electric current flows mainly at the "skin" of the conductor, at an...
significantly complicate the design of efficient transformer
Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
s and inductor
Inductor
An inductor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in a magnetic field. An inductor's ability to store magnetic energy is measured by its inductance, in units of henries...
s operating at high frequencies, used for example in switching power supplies.
In radio frequency
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
tuned circuits used in radio equipment, proximity and skin effect losses in the inductor reduce the Q factor
Q factor
In physics and engineering the quality factor or Q factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how under-damped an oscillator or resonator is, or equivalently, characterizes a resonator's bandwidth relative to its center frequency....
, broadening the bandwidth. To minimize this, special construction is used in radio frequency inductors. The winding is usually limited to a single layer, and often the turns are spaced apart to separate the conductors. In multilayer coils, the successive layers are wound in a crisscross pattern to avoid having wires lying parallel to one another; these are sometimes referred to as "basket-weave" or "honeycomb" coils. Since the current flows on the surface of the conductor, high frequency coils are sometimes silver-plated, or made of litz wire
Litz wire
Litz wire is a type of cable used in electronics to carry alternating current. The wire is designed to reduce the skin effect and proximity effect losses in conductors used at frequencies up to about 1 MHz...
.
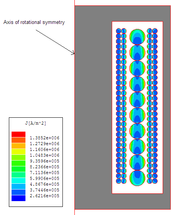
Dowell method for determination of losses
This one-dimensional method for transformers assumes the wires have rectangular cross-section, but can be applied approximately to circular wire by treating it as square with the same cross-sectional area.The windings are divided into 'portions', each portion being a group of layers which contains one position of zero m.m.f.
Magnetomotive force
Magnetomotive force is any physical driving force that produces magnetic flux. In this context, the expression "driving force" is used in a general sense of "work potential", and is analogous, but distinct from force measured in newtons...
For a transformer with a separate primary and secondary winding, each winding is a portion. For a transformer with interleaved (or sectionalised) windings, the innermost and outermost sections are each one portion, while the other sections are each divided into two portions at the point where zero m.m.f occurs.
The total resistance of a portion is given by
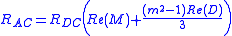
- RDC is the DC resistance of the portion
- Re(.) is the real part of the expression in brackets
- m number of layers in the portion, this should be an integer
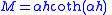
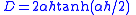

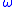 Angular frequencyAngular frequencyIn physics, angular frequency ω is a scalar measure of rotation rate. Angular frequency is the magnitude of the vector quantity angular velocity...
Angular frequencyAngular frequencyIn physics, angular frequency ω is a scalar measure of rotation rate. Angular frequency is the magnitude of the vector quantity angular velocity...
of the current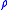 resistivity of the conductor material
resistivity of the conductor material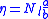
- Nl number of turns per layer
- a width of a square conductor
- b width of the winding window
- h height of a square conductor
Squared-field-derivative method
This can be used for round wire or litz wireLitz wire
Litz wire is a type of cable used in electronics to carry alternating current. The wire is designed to reduce the skin effect and proximity effect losses in conductors used at frequencies up to about 1 MHz...
transformers or inductors with multiple windings of arbitrary geometry with arbitrary current waveforms in each winding. The diameter of each strand should be less than 2 δ. It also assumes the magnetic field is perpendicular to the axis of the wire, which is the case in most designs.
- Find values of the B field due to each winding individually. This can be done using a simple magnetostatic FEA model where each winding is represented as a region of constant current density, ignoring individual turns and litz strands.
- Produce a matrix, D, from these fields. D is a function of the geometry and is independent of the current waveforms.
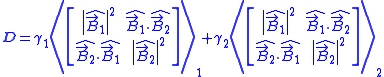
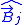 is the field due to a unit current in winding j
is the field due to a unit current in winding j
- <.>j is the spatial average over the region of winding j
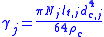
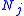 is the number of turns in winding j, for litz wire this is the product of the number of turns and the strands per turn.
is the number of turns in winding j, for litz wire this is the product of the number of turns and the strands per turn.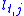 is the average length of a turn
is the average length of a turn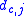 is the wire or strand diameter
is the wire or strand diameter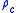 is the resistivity of the wire
is the resistivity of the wire
- AC power loss in all windings can be found using D, and expressions for the instantaneous current in each winding:
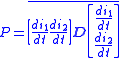
- Total winding power loss is then found by combing this value with the DC loss,
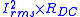
The method can be generalized to multiple windings.
Cables
Proximity effect can also occur within electrical cables. For example, if the conductors are a pair of audio speaker wireSpeaker wire
Speaker wire is used to make the electrical connection between loudspeakers and audio amplifiers. Modern speaker wire consists of two or more electrical conductors individually insulated by plastic such as PVC, PE or Teflon. The two wires are electrically identical, but are marked Speaker wire is...
s, their currents have opposite direction, and currents will preferentially flow along the sides of the wires that are facing each other. The AC resistance of the wires will change (slightly) along with the frequency of the audio signal, though for any frequency, the amplitude of the current will still be linearly proportional to the voltage. Some believe that this will potentially introduce distortion
Distortion
A distortion is the alteration of the original shape of an object, image, sound, waveform or other form of information or representation. Distortion is usually unwanted, and often many methods are employed to minimize it in practice...
and degrade stereo imaging. However, it can be shown that, for reasonable conductor sizes, spacing, and length, this effect is so small as to have an unmeasurable practical impact on audio quality.
External links
- Skin Effect, Proximity Effect, and Litz Wire Electromagnetic effects
- Skin and Proximity Effects and HiFi Cables

