
Proper equilibrium
Encyclopedia
Proper equilibrium is a refinement of Nash Equilibrium
due to Roger B. Myerson.
Proper equilibrium further refines Reinhard Selten
's notion of a
trembling hand perfect equilibrium
by assuming that more costly trembles are made with
significantly smaller probability than less
costly ones.
game and a parameter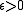 , a totally mixed strategy profile
, a totally mixed strategy profile  is defined to be
is defined to be  -proper if, whenever a player has two pure strategies s and s' such that the expected payoff of playing s is smaller than the expected payoff of
-proper if, whenever a player has two pure strategies s and s' such that the expected payoff of playing s is smaller than the expected payoff of
playing s' (that is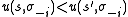 ), then the probability assigned to s
), then the probability assigned to s
is at most times the probability assigned to s'.
times the probability assigned to s'.
A strategy profile of the game is then said to be a proper equilibrium
if it is a limit point, as approaches 0, of a sequence of
approaches 0, of a sequence of  -proper strategy profiles.
-proper strategy profiles.
.
Player 1 (row player) hides a
penny and if Player 2 (column player) guesses correctly whether it is heads up or tails up, he gets the penny. In
this variant, Player 2 has a third option: Grabbing the penny without guessing.
The Nash equilibria
of the game are the strategy profiles where Player 2 grabs the penny
with probability 1. Any mixed strategy of Player 1 is in (Nash) equilibrium with this pure strategy
of Player 2. Any such pair is even trembling hand perfect
.
Intuitively, since Player 1 expects Player 2 to grab the penny, he is not concerned about
leaving Player 2 uncertain about whether it is heads up or tails up. However, it can be seen
that the unique proper equilibrium of this game is the one where Player 1 hides the penny heads up with probability 1/2 and tails up with probability 1/2 (and Player 2 grabs the penny).
This unique proper equilibrium can be motivated
intuitively as follows: Player 1 fully expects Player 2 to grab the penny.
However, Player 1 still prepares for the unlikely event that Player 2 does not grab the
penny and instead for some reason decides to make a guess. Player 1 prepares for this event by
making sure that Player 2 has no information about whether the penny is heads up or tails up,
exactly as in the original Matching Pennies
game.
s in two different ways, completely analogous to the
two different ways trembling hand perfection
is applied to extensive games. This leads to the notions of normal form proper equilibrium
and extensive form proper equilibrium of an extensive form game. It was shown by van
Damme that a normal form proper equilibrium of an extensive form game is behaviorally equivalent to
a quasi-perfect equilibrium
of that game.
Nash equilibrium
In game theory, Nash equilibrium is a solution concept of a game involving two or more players, in which each player is assumed to know the equilibrium strategies of the other players, and no player has anything to gain by changing only his own strategy unilaterally...
due to Roger B. Myerson.
Proper equilibrium further refines Reinhard Selten
Reinhard Selten
-Life and career:Selten was born in Breslau in Lower Silesia, now in Poland, to a Jewish father, Adolf Selten, and Protestant mother, Käthe Luther. For his work in game theory, Selten won the 1994 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences...
's notion of a
trembling hand perfect equilibrium
Trembling hand perfect equilibrium
There are two possible ways of extending the definition of trembling hand perfection to extensive form games.* One may interpret the extensive form as being merely a concise description of a normal form game and apply the concepts described above to this normal form game. In the resulting perturbed...
by assuming that more costly trembles are made with
significantly smaller probability than less
costly ones.
Definition
Given a normal formNormal form
Normal form may refer to:* Normal form * Normal form * Normal form * Normal form In formal language theory:* Beta normal form* Chomsky normal form* Greibach normal form* Kuroda normal form...
game and a parameter
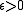 , a totally mixed strategy profile
, a totally mixed strategy profile  is defined to be
is defined to be  -proper if, whenever a player has two pure strategies s and s' such that the expected payoff of playing s is smaller than the expected payoff of
-proper if, whenever a player has two pure strategies s and s' such that the expected payoff of playing s is smaller than the expected payoff ofplaying s' (that is
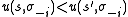 ), then the probability assigned to s
), then the probability assigned to sis at most
 times the probability assigned to s'.
times the probability assigned to s'.A strategy profile of the game is then said to be a proper equilibrium
if it is a limit point, as
 approaches 0, of a sequence of
approaches 0, of a sequence of  -proper strategy profiles.
-proper strategy profiles.Example
The game to the right is a variant of Matching PenniesMatching pennies
Matching pennies is the name for a simple example game used in game theory. It is the two strategy equivalent of Rock, Paper, Scissors. Matching pennies is used primarily to illustrate the concept of mixed strategies and a mixed strategy Nash equilibrium....
.
| Guess heads up | Guess tails up | Grab penny | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hide heads up | -1, 1 | 0, 0 | -1, 1 |
| Hide tails up | 0, 0 | -1, 1 | -1, 1 |
Player 1 (row player) hides a
penny and if Player 2 (column player) guesses correctly whether it is heads up or tails up, he gets the penny. In
this variant, Player 2 has a third option: Grabbing the penny without guessing.
The Nash equilibria
Nash equilibrium
In game theory, Nash equilibrium is a solution concept of a game involving two or more players, in which each player is assumed to know the equilibrium strategies of the other players, and no player has anything to gain by changing only his own strategy unilaterally...
of the game are the strategy profiles where Player 2 grabs the penny
with probability 1. Any mixed strategy of Player 1 is in (Nash) equilibrium with this pure strategy
of Player 2. Any such pair is even trembling hand perfect
Trembling hand perfect equilibrium
There are two possible ways of extending the definition of trembling hand perfection to extensive form games.* One may interpret the extensive form as being merely a concise description of a normal form game and apply the concepts described above to this normal form game. In the resulting perturbed...
.
Intuitively, since Player 1 expects Player 2 to grab the penny, he is not concerned about
leaving Player 2 uncertain about whether it is heads up or tails up. However, it can be seen
that the unique proper equilibrium of this game is the one where Player 1 hides the penny heads up with probability 1/2 and tails up with probability 1/2 (and Player 2 grabs the penny).
This unique proper equilibrium can be motivated
intuitively as follows: Player 1 fully expects Player 2 to grab the penny.
However, Player 1 still prepares for the unlikely event that Player 2 does not grab the
penny and instead for some reason decides to make a guess. Player 1 prepares for this event by
making sure that Player 2 has no information about whether the penny is heads up or tails up,
exactly as in the original Matching Pennies
Matching pennies
Matching pennies is the name for a simple example game used in game theory. It is the two strategy equivalent of Rock, Paper, Scissors. Matching pennies is used primarily to illustrate the concept of mixed strategies and a mixed strategy Nash equilibrium....
game.
Proper equilibria of extensive games
One may apply the properness notion to extensive form gameExtensive form game
An extensive-form game is a specification of a game in game theory, allowing explicit representation of a number of important aspects, like the sequencing of players' possible moves, their choices at every decision point, the information each player has about the other player's moves when he...
s in two different ways, completely analogous to the
two different ways trembling hand perfection
Trembling hand perfect equilibrium
There are two possible ways of extending the definition of trembling hand perfection to extensive form games.* One may interpret the extensive form as being merely a concise description of a normal form game and apply the concepts described above to this normal form game. In the resulting perturbed...
is applied to extensive games. This leads to the notions of normal form proper equilibrium
and extensive form proper equilibrium of an extensive form game. It was shown by van
Damme that a normal form proper equilibrium of an extensive form game is behaviorally equivalent to
a quasi-perfect equilibrium
Quasi-perfect equilibrium
Quasi-perfect equilibrium is a refinement of Nash Equilibrium for extensive form games due to Eric van Damme. Informally, a player playing by a strategy from a quasi-perfect equilibrium takes observed as well as potential future mistakes of his opponents into account but assumes that he himself...
of that game.

