
Matching pennies
Encyclopedia
Matching pennies is the name for a simple example game used in game theory
. It is the two strategy
equivalent of Rock, Paper, Scissors
. Matching pennies is used primarily to illustrate the concept of mixed strategies and a mixed strategy Nash equilibrium
.
The game is played between two players, Player A and Player B. Each player has a penny
and must secretly turn the penny to heads or tails. The players then reveal their choices simultaneously. If the pennies match (both heads or both tails) Player A keeps both pennies, so wins one from Player B (+1 for A, -1 for B). If the pennies do not match (one heads and one tails) Player B keeps both pennies, so receives one from Player A (-1 for A, +1 for B). This is an example of a zero-sum game, where one player's gain is exactly equal to the other player's loss.
The game can be written in a payoff matrix (pictured right). Each cell of the matrix shows the two players' payoffs, with Player A's payoffs listed first.
This game has no pure strategy Nash equilibrium
since there is no pure strategy (heads or tails) that is a best response
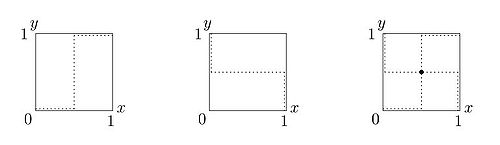
to a best response. In other words, there is no pair of pure strategies such that neither player would want to switch if told what the other would do. Instead, the unique Nash equilibrium of this game is in mixed strategies: each player chooses heads or tails with equal probability. In this way, each player makes the other indifferent between choosing heads or tails, so neither player has an incentive to try another strategy. The best response functions for mixed strategies are depicted on the figure 1 below:
 The matching pennies game is mathematically equivalent to the games "Morra" or "odds and evens", where two players simultaneously display one or two fingers, with the winner determined by whether or not the number of fingers match. Again, the only strategy for these games to avoid being exploited is to play the equilibrium.
The matching pennies game is mathematically equivalent to the games "Morra" or "odds and evens", where two players simultaneously display one or two fingers, with the winner determined by whether or not the number of fingers match. Again, the only strategy for these games to avoid being exploited is to play the equilibrium.
Of course, human players might not faithfully apply the equilibrium strategy, especially if matching pennies is played repeatedly. In a repeated game
, if one is sufficiently adept at psychology, it may be possible to predict the opponent's move and choose accordingly, in the same manner as expert Rock, Paper, Scissors players. In this way, a positive expected payoff
might be attainable, whereas against an opponent who plays the equilibrium, one's expected payoff is zero.
Nonetheless, statistical analysis of penalty kick
s in soccer—a high-stakes real-world situation that closely resembles the matching pennies game—has shown that the decisions of kickers and goalies resemble a mixed strategy equilibrium.
Game theory
Game theory is a mathematical method for analyzing calculated circumstances, such as in games, where a person’s success is based upon the choices of others...
. It is the two strategy
Strategy (game theory)
In game theory, a player's strategy in a game is a complete plan of action for whatever situation might arise; this fully determines the player's behaviour...
equivalent of Rock, Paper, Scissors
Rock, Paper, Scissors
Rock-paper-scissors is a hand game played by two people. The game is also known as roshambo, or another ordering of the three items ....
. Matching pennies is used primarily to illustrate the concept of mixed strategies and a mixed strategy Nash equilibrium
Nash equilibrium
In game theory, Nash equilibrium is a solution concept of a game involving two or more players, in which each player is assumed to know the equilibrium strategies of the other players, and no player has anything to gain by changing only his own strategy unilaterally...
.
The game is played between two players, Player A and Player B. Each player has a penny
Penny
A penny is a coin or a type of currency used in several English-speaking countries. It is often the smallest denomination within a currency system.-Etymology:...
and must secretly turn the penny to heads or tails. The players then reveal their choices simultaneously. If the pennies match (both heads or both tails) Player A keeps both pennies, so wins one from Player B (+1 for A, -1 for B). If the pennies do not match (one heads and one tails) Player B keeps both pennies, so receives one from Player A (-1 for A, +1 for B). This is an example of a zero-sum game, where one player's gain is exactly equal to the other player's loss.
The game can be written in a payoff matrix (pictured right). Each cell of the matrix shows the two players' payoffs, with Player A's payoffs listed first.
This game has no pure strategy Nash equilibrium
Nash equilibrium
In game theory, Nash equilibrium is a solution concept of a game involving two or more players, in which each player is assumed to know the equilibrium strategies of the other players, and no player has anything to gain by changing only his own strategy unilaterally...
since there is no pure strategy (heads or tails) that is a best response
Best response
In game theory, the best response is the strategy which produces the most favorable outcome for a player, taking other players' strategies as given...
to a best response. In other words, there is no pair of pure strategies such that neither player would want to switch if told what the other would do. Instead, the unique Nash equilibrium of this game is in mixed strategies: each player chooses heads or tails with equal probability. In this way, each player makes the other indifferent between choosing heads or tails, so neither player has an incentive to try another strategy. The best response functions for mixed strategies are depicted on the figure 1 below:

Of course, human players might not faithfully apply the equilibrium strategy, especially if matching pennies is played repeatedly. In a repeated game
Repeated game
In game theory, a repeated game is an extensive form game which consists in some number of repetitions of some base game . The stage game is usually one of the well-studied 2-person games...
, if one is sufficiently adept at psychology, it may be possible to predict the opponent's move and choose accordingly, in the same manner as expert Rock, Paper, Scissors players. In this way, a positive expected payoff
Expected value
In probability theory, the expected value of a random variable is the weighted average of all possible values that this random variable can take on...
might be attainable, whereas against an opponent who plays the equilibrium, one's expected payoff is zero.
Nonetheless, statistical analysis of penalty kick
Penalty kick
A penalty kick is a type of direct free kick in association football, taken from twelve yards out from goal and with only the goalkeeper of the defending team between the penalty taker and the goal.Penalty kicks are performed during normal play...
s in soccer—a high-stakes real-world situation that closely resembles the matching pennies game—has shown that the decisions of kickers and goalies resemble a mixed strategy equilibrium.

