Propadiene
Encyclopedia
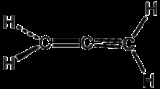
Propadiene is the organic compound
with the formula H2C=C=CH2. It is the simplest allene
, a compound with conjoined C=C double bonds. Propadiene's common name is allene. As a constituent of MAPP gas
, it is used as a fuel for specialized welding
.
Keq = 0.22 (270 °C), 0.1 K (5 °C)
MAPD is produced as a side product, often an undesirable one, of cracking
propane
to produce propene, an important feedstock in the chemical industry
. MAPD interferes with the catalytic
polymerization
of propene.
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
with the formula H2C=C=CH2. It is the simplest allene
Allene
An allene is a compound in which one carbon atom has double bonds with each of its two adjacent carbon centres. Allenes are classified as polyenes with cumulated dienes. The parent compound of allene is propadiene. Compounds with an allene-type structure but with more than three carbon atoms are...
, a compound with conjoined C=C double bonds. Propadiene's common name is allene. As a constituent of MAPP gas
MAPP gas
MAPP gas is a trademarked name belonging to Linde Group, previously to Dow, for a fuel gas based on a stabilized mixture of methylacetylene and propadiene. The name comes from the original chemical composition: methylacetylene-propadiene propane...
, it is used as a fuel for specialized welding
Welding
Welding is a fabrication or sculptural process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by causing coalescence. This is often done by melting the workpieces and adding a filler material to form a pool of molten material that cools to become a strong joint, with pressure sometimes...
.
Production and equilibrium with propyne
Allene exists in equilibrium with propyne, the mixture sometimes being called MAPD for methyl acetylene (alternative name of propyne)-propadiene:- H3CC≡CH H2C=C=CH2
Keq = 0.22 (270 °C), 0.1 K (5 °C)
MAPD is produced as a side product, often an undesirable one, of cracking
Cracking (chemistry)
In petroleum geology and chemistry, cracking is the process whereby complex organic molecules such as kerogens or heavy hydrocarbons are broken down into simpler molecules such as light hydrocarbons, by the breaking of carbon-carbon bonds in the precursors. The rate of cracking and the end products...
propane
Propane
Propane is a three-carbon alkane with the molecular formula , normally a gas, but compressible to a transportable liquid. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, it is commonly used as a fuel for engines, oxy-gas torches, barbecues, portable stoves, and residential central...
to produce propene, an important feedstock in the chemical industry
Chemical industry
The chemical industry comprises the companies that produce industrial chemicals. Central to the modern world economy, it converts raw materials into more than 70,000 different products.-Products:...
. MAPD interferes with the catalytic
Ziegler-Natta catalyst
A Ziegler–Natta catalyst is a catalyst used in the synthesis of polymers of 1-alkenes . Three types of Ziegler–Natta catalysts are currently employed:* Solid and supported catalysts based on titanium compounds...
polymerization
Polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form three-dimensional networks or polymer chains...
of propene.

