
Kaizen
Encyclopedia
, Japanese
for "improvement", or "change for the better" refers to philosophy or practices that focus upon continuous improvement of processes in manufacturing, engineering, game development, and business management. It has been applied in healthcare, psychotherapy
, life-coaching, government, banking, and other industries. When used in the business sense and applied to the workplace, kaizen refers to activities that continually improve all functions, and involves all employees from the CEO to the assembly line
workers. It also applies to processes, such as purchasing and logistics
, that cross organizational boundaries into the supply chain
. By improving standardized activities and processes, kaizen aims to eliminate waste (see lean manufacturing
). Kaizen was first implemented in several Japanese businesses
after the Second World War, influenced in part by American business and quality management teachers who visited the country. It has since spread throughout the world and is now being implemented in many other venues besides just business and productivity.
"), and teaches people how to perform experiments on their work using the scientific method
and how to learn to spot and eliminate waste in business processes. In all, the process suggests a humanized approach to workers and to increasing productivity: "The idea is to nurture the company's human resources as much as it is to praise and encourage participation in kaizen activities." Successful implementation requires "the participation of workers in the improvement."
People at all levels of an organization participate in kaizen, from the CEO down to janitorial staff, as well as external stakeholders when applicable. The format for kaizen can be individual, suggestion system, small group, or large group. At Toyota, it is usually a local improvement within a workstation or local area and involves a small group in improving their own work environment and productivity. This group is often guided through the kaizen process by a line supervisor; sometimes this is the line supervisor's key role. Kaizen on a broad, cross-departmental scale in companies, generates total quality management
, and frees human efforts through improving productivity using machines and computing power.
While kaizen (at Toyota) usually delivers small improvements, the culture of continual aligned small improvements and standardization yields large results in the form of compound productivity improvement. This philosophy differs from the "command and control" improvement programs of the mid-twentieth century. Kaizen methodology includes making changes and monitoring results, then adjusting. Large-scale pre-planning and extensive project scheduling are replaced by smaller experiments, which can be rapidly adapted as new improvements are suggested.
In modern usage, a focused kaizen that is designed to address a particular issue over the course of a week is referred to as a "kaizen blitz" or "kaizen event". These are limited in scope, and issues that arise from them are typically used in later blitzes.
for further training in Statistical Methods.
The Economic and Scientific Section (ESS) group was also tasked with improving Japanese management skills and Edgar McVoy was instrumental in bringing Lowell Mellen to Japan to properly install the Training Within Industry
(TWI) programs in 1951.
Prior to the arrival of Mellen in 1951, the ESS group had a training film to introduce the three TWI "J" programs (Job Instruction, Job Methods and Job Relations)---the film was titled "Improvement in 4 Steps" (Kaizen eno Yon Dankai). Thus the original introduction of "Kaizen" to Japan. For the pioneering, introduction, and implementation of Kaizen in Japan, the Emperor of Japan awarded the 2nd Order Medal of the Sacred Treasure
to Dr. Deming in 1960. Consequently, the Union of Japanese Science and Engineering (JUSE) instituted the annual Deming Prizes for achievement in quality and dependability of products.
On October 18, 1989, JUSE awarded the Deming Prize to Florida Power & Light Co. (FPL), based in the US, for its exceptional accomplishments in process and quality control management. FPL was the first company outside Japan to win the Deming Prize.
Reference:
US National Archives - SCAP collection - PR NewsWire
is known for kaizen, where all line personnel are expected to stop their moving production line in case of any abnormality and, along with their supervisor, suggest an improvement to resolve the abnormality which may initiate a kaizen.
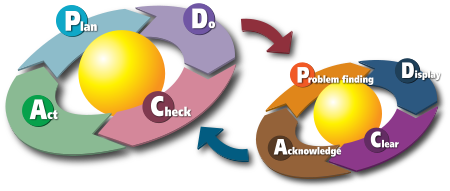 The cycle of kaizen activity can be defined as:
The cycle of kaizen activity can be defined as:
This is also known as the Shewhart cycle, Deming cycle, or PDCA
. Other techniques used in conjunction with PDCA include 5 Whys
, which is a form of root cause analysis in which the user asks "why" to a problem and its answer five successive times. There are normally a series of root causes stemming from one problem, and they can be visualized using fishbone diagrams or tables.
Masaaki Imai
made the term famous in his book Kaizen: The Key to Japan's Competitive Success.
Apart from business applications of the method, both Anthony Robbins and Robert Maurer have popularized the kaizen principles into personal development principles. In his book,One Small Step Can Change Your life: The Kaizen Way and his eight CD set, The Kaizen Way to Success, Dr. Maurer looks at both personal and professional success using the kaizen approach.
In their book The Toyota Way Fieldbook, Jeffrey Liker, and David Meier discuss the kaizen blitz and kaizen burst (or kaizen event) approaches to continuous improvement. A kaizen blitz, or rapid improvement, is a focused activity on a particular process or activity. The basic concept is to identify and quickly remove waste. Another approach is that of the kaizen burst, a specific kaizen activity on a particular process in the value stream.
WebKaizen Events, written by Kate Cornell, condenses the philosophies of kaizen events into a one-day, problem solving method that leads to prioritized solutions. This method combines Kaizen Event tools with PMP
concepts. It introduces the Focused Affinity Matrix and the Cascading Impact Analysis. The Impact/Constraint Diagram and the Dual Constraint Diagram are tools used in this method.
Key elements of kaizen are quality, effort, involvement of all employees, willingness to change, and communication.
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
for "improvement", or "change for the better" refers to philosophy or practices that focus upon continuous improvement of processes in manufacturing, engineering, game development, and business management. It has been applied in healthcare, psychotherapy
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy is a general term referring to any form of therapeutic interaction or treatment contracted between a trained professional and a client or patient; family, couple or group...
, life-coaching, government, banking, and other industries. When used in the business sense and applied to the workplace, kaizen refers to activities that continually improve all functions, and involves all employees from the CEO to the assembly line
Assembly line
An assembly line is a manufacturing process in which parts are added to a product in a sequential manner using optimally planned logistics to create a finished product much faster than with handcrafting-type methods...
workers. It also applies to processes, such as purchasing and logistics
Logistics
Logistics is the management of the flow of goods between the point of origin and the point of destination in order to meet the requirements of customers or corporations. Logistics involves the integration of information, transportation, inventory, warehousing, material handling, and packaging, and...
, that cross organizational boundaries into the supply chain
Supply chain
A supply chain is a system of organizations, people, technology, activities, information and resources involved in moving a product or service from supplier to customer. Supply chain activities transform natural resources, raw materials and components into a finished product that is delivered to...
. By improving standardized activities and processes, kaizen aims to eliminate waste (see lean manufacturing
Lean manufacturing
Lean manufacturing, lean enterprise, or lean production, often simply, "Lean," is a production practice that considers the expenditure of resources for any goal other than the creation of value for the end customer to be wasteful, and thus a target for elimination...
). Kaizen was first implemented in several Japanese businesses
Economy of Japan
The economy of Japan, a free market economy, is the third largest in the world after the United States and the People's Republic of China, and ahead of Germany at 4th...
after the Second World War, influenced in part by American business and quality management teachers who visited the country. It has since spread throughout the world and is now being implemented in many other venues besides just business and productivity.
Introduction
Kaizen is a daily process, the purpose of which goes beyond simple productivity improvement. It is also a process that, when done correctly, humanizes the workplace, eliminates overly hard work ("muriMuri (Japanese term)
Muri is a Japanese term for overburden, unreasonableness or absurdity, which has become popularized in the West by its use as a key concept in the Toyota Production System.-Avoidance of muri in Toyota manufacturing:...
"), and teaches people how to perform experiments on their work using the scientific method
Scientific method
Scientific method refers to a body of techniques for investigating phenomena, acquiring new knowledge, or correcting and integrating previous knowledge. To be termed scientific, a method of inquiry must be based on gathering empirical and measurable evidence subject to specific principles of...
and how to learn to spot and eliminate waste in business processes. In all, the process suggests a humanized approach to workers and to increasing productivity: "The idea is to nurture the company's human resources as much as it is to praise and encourage participation in kaizen activities." Successful implementation requires "the participation of workers in the improvement."
People at all levels of an organization participate in kaizen, from the CEO down to janitorial staff, as well as external stakeholders when applicable. The format for kaizen can be individual, suggestion system, small group, or large group. At Toyota, it is usually a local improvement within a workstation or local area and involves a small group in improving their own work environment and productivity. This group is often guided through the kaizen process by a line supervisor; sometimes this is the line supervisor's key role. Kaizen on a broad, cross-departmental scale in companies, generates total quality management
Total Quality Management
Total quality management or TQM is an integrative philosophy of management for continuously improving the quality of products and processes....
, and frees human efforts through improving productivity using machines and computing power.
While kaizen (at Toyota) usually delivers small improvements, the culture of continual aligned small improvements and standardization yields large results in the form of compound productivity improvement. This philosophy differs from the "command and control" improvement programs of the mid-twentieth century. Kaizen methodology includes making changes and monitoring results, then adjusting. Large-scale pre-planning and extensive project scheduling are replaced by smaller experiments, which can be rapidly adapted as new improvements are suggested.
In modern usage, a focused kaizen that is designed to address a particular issue over the course of a week is referred to as a "kaizen blitz" or "kaizen event". These are limited in scope, and issues that arise from them are typically used in later blitzes.
History
After WWII, to help restore Japan, American occupation forces brought in American experts to help with the rebuilding of Japanese industry while The Civil Communications Section (CCS) developed a Management Training Program that taught statistical control methods as part of the overall material. This course was developed and taught by Homer Sarasohn and Charles Protzman in 1949-50. Sarasohn recommended W. Edwards DemingW. Edwards Deming
William Edwards Deming was an American statistician, professor, author, lecturer and consultant. He is perhaps best known for his work in Japan...
for further training in Statistical Methods.
The Economic and Scientific Section (ESS) group was also tasked with improving Japanese management skills and Edgar McVoy was instrumental in bringing Lowell Mellen to Japan to properly install the Training Within Industry
Training Within Industry
The Training Within Industry service was created by the United States Department of War, running from 1940 to 1945 within the War Manpower Commission. The purpose was to provide consulting services to war-related industries whose personnel were being conscripted into the US Army at the same time...
(TWI) programs in 1951.
Prior to the arrival of Mellen in 1951, the ESS group had a training film to introduce the three TWI "J" programs (Job Instruction, Job Methods and Job Relations)---the film was titled "Improvement in 4 Steps" (Kaizen eno Yon Dankai). Thus the original introduction of "Kaizen" to Japan. For the pioneering, introduction, and implementation of Kaizen in Japan, the Emperor of Japan awarded the 2nd Order Medal of the Sacred Treasure
Order of the Sacred Treasure
The is a Japanese Order, established on January 4, 1888 by Emperor Meiji of Japan as the Order of Meiji. It is awarded in eight classes . It is generally awarded for long and/or meritorious service and considered to be the lowest of the Japanese orders of merit...
to Dr. Deming in 1960. Consequently, the Union of Japanese Science and Engineering (JUSE) instituted the annual Deming Prizes for achievement in quality and dependability of products.
On October 18, 1989, JUSE awarded the Deming Prize to Florida Power & Light Co. (FPL), based in the US, for its exceptional accomplishments in process and quality control management. FPL was the first company outside Japan to win the Deming Prize.
Reference:
US National Archives - SCAP collection - PR NewsWire
Implementation
The Toyota Production SystemToyota Production System
The Toyota Production System is an integrated socio-technical system, developed by Toyota, that comprises its management philosophy and practices. The TPS organizes manufacturing and logistics for the automobile manufacturer, including interaction with suppliers and customers...
is known for kaizen, where all line personnel are expected to stop their moving production line in case of any abnormality and, along with their supervisor, suggest an improvement to resolve the abnormality which may initiate a kaizen.

- Standardize an operation and activities.
- Measure the standardized operation (find cycle time and amount of in-process inventory)
- Gauge measurements against requirements
- Innovate to meet requirements and increase productivity
- Standardize the new, improved operations
- Continue cycle ad infinitum
This is also known as the Shewhart cycle, Deming cycle, or PDCA
PDCA
PDCA is an iterative four-step management method used in business for the control and continuous improvement of processes and products...
. Other techniques used in conjunction with PDCA include 5 Whys
5 Whys
The 5 Whys is a questions-asking method used to explore the cause/effect relationships underlying a particular problem. Ultimately, the goal of applying the 5 Whys method is to determine a root cause of a defect or problem.- Example :...
, which is a form of root cause analysis in which the user asks "why" to a problem and its answer five successive times. There are normally a series of root causes stemming from one problem, and they can be visualized using fishbone diagrams or tables.
Masaaki Imai
Masaaki Imai
Masaaki Imai is a consultant in the field of quality management.Known as the “Lean Guru” and the father of Continuous Improvement Masaaki Imai has been a pioneer and leader in spreading the Kaizen philosophy all over the world....
made the term famous in his book Kaizen: The Key to Japan's Competitive Success.
Apart from business applications of the method, both Anthony Robbins and Robert Maurer have popularized the kaizen principles into personal development principles. In his book,One Small Step Can Change Your life: The Kaizen Way and his eight CD set, The Kaizen Way to Success, Dr. Maurer looks at both personal and professional success using the kaizen approach.
In their book The Toyota Way Fieldbook, Jeffrey Liker, and David Meier discuss the kaizen blitz and kaizen burst (or kaizen event) approaches to continuous improvement. A kaizen blitz, or rapid improvement, is a focused activity on a particular process or activity. The basic concept is to identify and quickly remove waste. Another approach is that of the kaizen burst, a specific kaizen activity on a particular process in the value stream.
WebKaizen Events, written by Kate Cornell, condenses the philosophies of kaizen events into a one-day, problem solving method that leads to prioritized solutions. This method combines Kaizen Event tools with PMP
Project management plan
A project management plan, as defined in the PMBOK Guide Third Edition, is a formal, approved document that defines how the project is executed, monitored and controlled. It may be summary or detailed and may be composed of one or more subsidiary management plans and other planning documents...
concepts. It introduces the Focused Affinity Matrix and the Cascading Impact Analysis. The Impact/Constraint Diagram and the Dual Constraint Diagram are tools used in this method.
Key elements of kaizen are quality, effort, involvement of all employees, willingness to change, and communication.
The five main elements of kaizen
- Teamwork
- Personal discipline
- Improved morale
- Quality circles
- Suggestions for improvement
See also
- 5S
- Business process reengineeringBusiness process reengineeringBusiness process re-engineering is the analysis and design of workflows and processes within an organization.According to Davenport a business process is a set of logically related tasks performed to achieve a defined business outcome....
- MottainaiMOTTAINAIis a Japanese term meaning "a sense of regret concerning waste when the intrinsic value of an object or resource is not properly utilized." The expression "Mottainai!" can be uttered alone as an exclamation when something useful, such as food or time, is wasted, meaning roughly "Oh, what a waste!"...
- Muda
- Overall equipment effectivenessOverall equipment effectivenessOverall equipment effectiveness is a hierarchy of metrics which evaluates and indicates how effectively a manufacturing operation is utilized. The results are stated in a generic form which allows comparison between manufacturing units in differing industries...
- Root cause analysisRoot cause analysisRoot cause analysis is a class of problem solving methods aimed at identifying the root causes of problems or events.Root Cause Analysis is any structured approach to identifying the factors that resulted in the nature, the magnitude, the location, and the timing of the harmful outcomes of one...
- ScrumScrum (development)Scrum is an iterative, incremental framework for project management often seen in agile software development, a type of software engineering....
- Six SigmaSix SigmaSix Sigma is a business management strategy originally developed by Motorola, USA in 1986. , it is widely used in many sectors of industry.Six Sigma seeks to improve the quality of process outputs by identifying and removing the causes of defects and minimizing variability in manufacturing and...
- Statistical process controlStatistical process controlStatistical process control is the application of statistical methods to the monitoring and control of a process to ensure that it operates at its full potential to produce conforming product. Under SPC, a process behaves predictably to produce as much conforming product as possible with the least...
- Theory of ConstraintsTheory of ConstraintsThe theory of constraints adopts the common idiom "A chain is no stronger than its weakest link" as a new management paradigm. This means that processes, organizations, etc., are vulnerable because the weakest person or part can always damage or break them or at least adversely affect the...
- Total productive maintenanceTotal Productive MaintenanceTotal productive maintenance originated in Japan in 1971 as a method for improved machine availability through better utilization of maintenance and production resources....
- TRIZTRIZTRIZ is "a problem-solving, analysis and forecasting tool derived from the study of patterns of invention in the global patent literature". It was developed by the Soviet inventor and science fiction author Genrich Altshuller and his colleagues, beginning in 1946...
- KanbanKanban, also spelled kamban, and literally meaning "signboard" or "billboard", is a concept related to lean and just-in-time production. According to Taiichi Ohno, the man credited with developing Just-in-time, kanban is one means through which JIT is achieved.Kanban is not an inventory control system...
- Visual ControlVisual ControlVisual control is a technique employed in many places where information is communicated by using visual signals instead of texts or other written instructions. The design is deliberate in allowing quick recognition of the information being communicated, in order to increase efficiency and clarity...
- Learning-by-doingLearning-by-doingLearning-by-doing is a concept within economic theory. It refers to the capability of workers to improve their productivity by regularly repeating the same type of action...
- Quality circleQuality circleA quality circle is a volunteer group composed of workers , usually under the leadership of their supervisor , who are trained to identify, analyze and solve work-related problems and present their solutions to management in order to improve the performance of the organization, and motivate and...
External links
- Kaizen and Process Improvement Written by Shmula
- Guide to Kaizen question and answer Written by Mike Wilson
- Toyota stumbles but its "kaizen" cult endures Reuters
- Practice your personal Kaizen Written by Jason Thomas
- Kaizen Implementation Model

