
Precision (statistics)
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, the term precision can mean a quantity defined in a specific way. This is in addition to its more general meaning in the contexts of accuracy and precision
and of precision and recall
.
There can be differences in usage of the term for particular statistical models but, in general statistical usage, the precision is defined to be the reciprocal of the variance
, while the precision matrix is the matrix inverse of the covariance matrix
.
One particular use of the precision matrix is in the context of Bayesian analysis of the multivariate normal distribution: for example, Bernardo & Smith prefer to parameterise the multivariate normal distribution in terms of the precision matrix rather than the covariance matrix because of certain simplifications that then arise.
(1809) “Theoria motus corporum coelestium in sectionibus conicis solem ambientium” (page 212). Gauss’s definition differs from the modern one by a factor of . He writes, for the density function of a normal random variable with precision h,
. He writes, for the density function of a normal random variable with precision h,
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, the term precision can mean a quantity defined in a specific way. This is in addition to its more general meaning in the contexts of accuracy and precision
Accuracy and precision
In the fields of science, engineering, industry and statistics, the accuracy of a measurement system is the degree of closeness of measurements of a quantity to that quantity's actual value. The precision of a measurement system, also called reproducibility or repeatability, is the degree to which...
and of precision and recall
Precision and recall
In pattern recognition and information retrieval, precision is the fraction of retrieved instances that are relevant, while recall is the fraction of relevant instances that are retrieved. Both precision and recall are therefore based on an understanding and measure of relevance...
.
There can be differences in usage of the term for particular statistical models but, in general statistical usage, the precision is defined to be the reciprocal of the variance
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
, while the precision matrix is the matrix inverse of the covariance matrix
Covariance matrix
In probability theory and statistics, a covariance matrix is a matrix whose element in the i, j position is the covariance between the i th and j th elements of a random vector...
.
One particular use of the precision matrix is in the context of Bayesian analysis of the multivariate normal distribution: for example, Bernardo & Smith prefer to parameterise the multivariate normal distribution in terms of the precision matrix rather than the covariance matrix because of certain simplifications that then arise.
History
The term precision (“mensura praecisionis observationum”) first appeared in the works of GaussCarl Friedrich Gauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss was a German mathematician and scientist who contributed significantly to many fields, including number theory, statistics, analysis, differential geometry, geodesy, geophysics, electrostatics, astronomy and optics.Sometimes referred to as the Princeps mathematicorum...
(1809) “Theoria motus corporum coelestium in sectionibus conicis solem ambientium” (page 212). Gauss’s definition differs from the modern one by a factor of
 . He writes, for the density function of a normal random variable with precision h,
. He writes, for the density function of a normal random variable with precision h,
-
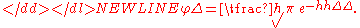
Later Whittaker & Robinson (1924) “Calculus of observations” called this quantity the modulus, but this term has dropped out of use.

