
Polarized glasses
Encyclopedia
Polarized 3D glasses create the illusion of three-dimensional images by restricting the light that reaches each eye
, an example of stereoscopy
which exploits the polarization of light.
To present a stereoscopic motion picture, two images are projected superimposed onto the same screen through different polarizing filters. The viewer wears low-cost eyeglasses which contain a pair of different polarizing filters. As each filter passes only that light which is similarly polarized and blocks the light polarized in the opposite direction, each eye sees a different image. This is used to produce a three-dimensional effect by projecting the same scene into both eyes, but depicted from slightly different perspectives. Several people can view the stereoscopic images at the same time.
filters (Usually at 45 and 135 degrees). The viewer wears linearly polarized eyeglasses which also contain a pair of orthogonal polarizing filters oriented the same as the projector. As each filter only passes light which is similarly polarized and blocks the orthogonally polarized light, each eye only sees one of the projected images, and the 3D effect is achieved. Linearly polarized glasses require the viewer to keep his head level, as tilting of the viewing filters will cause the images of the left and right channels to bleed over to the opposite channel. This can make prolonged viewing uncomfortable as head movement is limited to maintain the 3D effect.
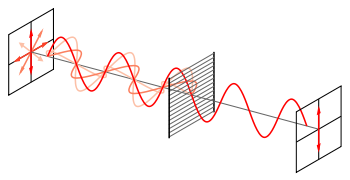
As shown in the figure, the analyzing filters are constructed of a quarter-wave plate (QWP) and a linearly polarized filter (LPF). The QWP always transforms circularly polarized light into linearly polarized light. However, the angle of polarization of the linearly polarized light produced by a QWP depends on the handedness of the circularly polarized light entering the QWP. In the illustration, the left-handed circularly polarized light entering the analyzing filter is transformed by the QWP into linearly polarized light which has its direction of polarization along the transmission axis of the LPF. Therefore, in this case the light passes through the LPF. In contrast, right-handed circularly polarized light would have been transformed into linearly polarized light that had its direction of polarization along the absorbing axis of the LPF, which is at right angles to the transmission axis, and it would have therefore been blocked.
By rotating either the QWP or the LPF by 90 degrees about an axis perpendicular to its surface (i.e. parallel to the direction of propagation of the light wave), one may build an analyzing filter which blocks left-handed, rather than right-handed circularly polarized light. Interestingly, rotating both the QWP and the PLF by the same angle does not change the behaviour of the analyzing filter.
or aluminized screen
is used. This means that a pair of aligned DLP projectors, some polarizing filters, a silver screen, and a computer with a dual-head graphics card can be used to form a relatively high-cost (over US$10,000 in 2010) system for displaying stereoscopic 3D data simultaneously to a group of people wearing polarized glasses.
In the case of RealD
a circularly polarizing liquid crystal filter which can switch polarity many times per second is placed on front of the projector lens. Only one projector is needed, as the left and right eye images are displayed alternately. Sony
features a new system called RealD XLS
, which shows both circularly polarized
images simultaneously: A single 4K projector displays both 2K images above each other, a special lens attachment polarizes and projects the images on top of each other.
Thomson Technicolor have produced a system using a split lens which allows traditional 35mm projectors to be adapted to project in 3D using over/under 35mm film. This is a very cost-effective way to convert a screen as all that is needed is the lens and silver screen rather than converting entirely to digital.
When stereo images are to be presented to a single user, it is practical to construct an image combiner, using partially silvered mirrors and two image screens at right angles to one another. One image is seen directly through the angled mirror whilst the other is seen as a reflection. Polarized filters are attached to the image screens and appropriately angled filters are worn as glasses. A similar technique uses a single screen with an inverted upper image, viewed in a horizontal partial reflector, with an upright image presented below the reflector, again with appropriate polarizers.
One can construct a low cost polarized projection system by using a computer with two projectors and an aluminum foil screen. The dull side of aluminum foil is brighter than most silver screens. This was first demonstrated at PhraJomGlao University, Nônthaburi, Thailand, September 2009.
In 2003 Keigo Iizuka discovered an inexpensive implementation of this principle on laptop computer displays using cellophane
sheets.
first applied it to motion pictures. The so called "3-D movie craze" in the years 1952 through 1955 was almost entirely offered in theaters using polarizing projection and glasses. Only a minute amount of the total 3D films shown in the period used the anaglyph color filter
method.
Linear polarization was also the standard in the 80s.
In the 2000s, computer animation
, digital projection, and the use of sophisticated IMAX 70mm film projectors, have created an opportunity for a new wave of polarized 3D films.
and ophthalmology
, polarized glasses are used for various tests of binocular
depth perception
(i.e. stereopsis
).
s, the use of polarized 3D glasses produces a full-color image that is considerably more comfortable to watch and is not subject to binocular rivalry
. However, it requires a significant increase in expense: even the low cost polarized glasses typically cost 50% more than comparable red-cyan filters, and while anaglyph 3-D films can be printed on one line of film, a polarized film was often done with a special set up that uses two projectors. The use of multiple projectors also raises issues with synchronization
, and a poorly synchronized film would negate any increased comfort from the use of polarization. This problem was solved by a number of single strip polarized systems which were standard in the 1980s.
Particularly with the linear polarization schemes popular since the 1950s, the use of linear polarization meant that a level head was required for any sort of comfortable viewing; any effort to tilt the head sideways would result in the polarization failing, ghosting
, and both eyes seeing both images. Circular polarization has alleviated this problem, allowing viewers to tilt their heads slightly (although any offset between the eye plane and the original camera plane will still interfere with the perception of depth).
Until 2011, home 3D Television and home 3D computer primarily used shutter glasses with LCD or plasma displays.
In 2011, LG was the first TV manufacture to commercialize 3D LCD Television using polarized technology. Using polarized lenses instead of shutter lenses in 3D glasses has many benefits.
Advantages
Human eye
The human eye is an organ which reacts to light for several purposes. As a conscious sense organ, the eye allows vision. Rod and cone cells in the retina allow conscious light perception and vision including color differentiation and the perception of depth...
, an example of stereoscopy
Stereoscopy
Stereoscopy refers to a technique for creating or enhancing the illusion of depth in an image by presenting two offset images separately to the left and right eye of the viewer. Both of these 2-D offset images are then combined in the brain to give the perception of 3-D depth...
which exploits the polarization of light.
To present a stereoscopic motion picture, two images are projected superimposed onto the same screen through different polarizing filters. The viewer wears low-cost eyeglasses which contain a pair of different polarizing filters. As each filter passes only that light which is similarly polarized and blocks the light polarized in the opposite direction, each eye sees a different image. This is used to produce a three-dimensional effect by projecting the same scene into both eyes, but depicted from slightly different perspectives. Several people can view the stereoscopic images at the same time.
Linearly polarized glasses
To present a stereoscopic motion picture, two images are projected superimposed onto the same screen through orthogonal polarizingPolarizer
A polarizer is an optical filter that passes light of a specific polarization and blocks waves of other polarizations. It can convert a beam of light of undefined or mixed polarization into a beam with well-defined polarization. The common types of polarizers are linear polarizers and circular...
filters (Usually at 45 and 135 degrees). The viewer wears linearly polarized eyeglasses which also contain a pair of orthogonal polarizing filters oriented the same as the projector. As each filter only passes light which is similarly polarized and blocks the orthogonally polarized light, each eye only sees one of the projected images, and the 3D effect is achieved. Linearly polarized glasses require the viewer to keep his head level, as tilting of the viewing filters will cause the images of the left and right channels to bleed over to the opposite channel. This can make prolonged viewing uncomfortable as head movement is limited to maintain the 3D effect.

Circularly polarized glasses
To present a stereoscopic motion picture, two images are projected superimposed onto the same screen through circular polarizing filters of opposite handedness. The viewer wears eyeglasses which contain a pair of analyzing filters (circular polarizers mounted in reverse) of opposite handedness. Light that is left-circularly polarized is blocked by the right-handed analyzer, while right-circularly polarized light is extinguished by the left-handed analyzer. The result is similar to that of steroscopic viewing using linearly polarized glasses, except the viewer can tilt his or her head and still maintain left/right separation (although stereoscopic image fusion will be lost due to the mismatch between the eye plane and the original camera plane).As shown in the figure, the analyzing filters are constructed of a quarter-wave plate (QWP) and a linearly polarized filter (LPF). The QWP always transforms circularly polarized light into linearly polarized light. However, the angle of polarization of the linearly polarized light produced by a QWP depends on the handedness of the circularly polarized light entering the QWP. In the illustration, the left-handed circularly polarized light entering the analyzing filter is transformed by the QWP into linearly polarized light which has its direction of polarization along the transmission axis of the LPF. Therefore, in this case the light passes through the LPF. In contrast, right-handed circularly polarized light would have been transformed into linearly polarized light that had its direction of polarization along the absorbing axis of the LPF, which is at right angles to the transmission axis, and it would have therefore been blocked.
By rotating either the QWP or the LPF by 90 degrees about an axis perpendicular to its surface (i.e. parallel to the direction of propagation of the light wave), one may build an analyzing filter which blocks left-handed, rather than right-handed circularly polarized light. Interestingly, rotating both the QWP and the PLF by the same angle does not change the behaviour of the analyzing filter.
System construction and examples
Light reflected from a motion picture screen tends to lose a bit of its polarization, but this problem is eliminated if a silver screenSilver screen
A silver screen, also known as a silver lenticular screen, is a type of projection screen that was popular in the early years of the motion picture industry and passed into popular usage as a metonym for the cinema industry...
or aluminized screen
Aluminized screen
Aluminized screen is a cathode-ray tube screen whose brightness is increased by coating the phosphor with a thin layer of aluminium. Light from an excited part of the phosphor that would normally shine back inside the tube is thus reflected forward, increasing the total light output from the screen...
is used. This means that a pair of aligned DLP projectors, some polarizing filters, a silver screen, and a computer with a dual-head graphics card can be used to form a relatively high-cost (over US$10,000 in 2010) system for displaying stereoscopic 3D data simultaneously to a group of people wearing polarized glasses.
In the case of RealD
Real D Cinema
RealD Cinema is a digital stereoscopic projection technology made and sold by RealD Inc. It is currently the most widely used technology for watching 3-D films in theatres.-Technology:...
a circularly polarizing liquid crystal filter which can switch polarity many times per second is placed on front of the projector lens. Only one projector is needed, as the left and right eye images are displayed alternately. Sony
Sony
, commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues....
features a new system called RealD XLS
Real D Cinema
RealD Cinema is a digital stereoscopic projection technology made and sold by RealD Inc. It is currently the most widely used technology for watching 3-D films in theatres.-Technology:...
, which shows both circularly polarized
Circular polarization
In electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization in which the electric field of the passing wave does not change strength but only changes direction in a rotary type manner....
images simultaneously: A single 4K projector displays both 2K images above each other, a special lens attachment polarizes and projects the images on top of each other.
Thomson Technicolor have produced a system using a split lens which allows traditional 35mm projectors to be adapted to project in 3D using over/under 35mm film. This is a very cost-effective way to convert a screen as all that is needed is the lens and silver screen rather than converting entirely to digital.
When stereo images are to be presented to a single user, it is practical to construct an image combiner, using partially silvered mirrors and two image screens at right angles to one another. One image is seen directly through the angled mirror whilst the other is seen as a reflection. Polarized filters are attached to the image screens and appropriately angled filters are worn as glasses. A similar technique uses a single screen with an inverted upper image, viewed in a horizontal partial reflector, with an upright image presented below the reflector, again with appropriate polarizers.
One can construct a low cost polarized projection system by using a computer with two projectors and an aluminum foil screen. The dull side of aluminum foil is brighter than most silver screens. This was first demonstrated at PhraJomGlao University, Nônthaburi, Thailand, September 2009.
On TV and computer screens
Polarizing techniques are easier to apply with cathode ray technology than with LCD. Ordinary LCD screens already contain polarizers for control of pixel presentation — this can interfere with these techniques.In 2003 Keigo Iizuka discovered an inexpensive implementation of this principle on laptop computer displays using cellophane
Cellophane
Cellophane is a thin, transparent sheet made of regenerated cellulose. Its low permeability to air, oils, greases, bacteria and water makes it useful for food packaging...
sheets.
History
Polarized stereoscopic pictures have been around since 1936, when Edwin H. LandEdwin H. Land
Edwin Herbert Land was an American scientist and inventor, best known as the co-founder of the Polaroid Corporation. Among other things, he invented inexpensive filters for polarizing light, a practical system of in-camera instant photography, and his retinex theory of color vision...
first applied it to motion pictures. The so called "3-D movie craze" in the years 1952 through 1955 was almost entirely offered in theaters using polarizing projection and glasses. Only a minute amount of the total 3D films shown in the period used the anaglyph color filter
Anaglyph image
Anaglyph images are used to provide a stereoscopic 3D effect, when viewed with glasses where the two lenses are different colors, such as red and cyan. Images are made up of two color layers, superimposed, but offset with respect to each other to produce a depth effect...
method.
Linear polarization was also the standard in the 80s.
In the 2000s, computer animation
Computer animation
Computer animation is the process used for generating animated images by using computer graphics. The more general term computer generated imagery encompasses both static scenes and dynamic images, while computer animation only refers to moving images....
, digital projection, and the use of sophisticated IMAX 70mm film projectors, have created an opportunity for a new wave of polarized 3D films.
Health care
In optometryOptometry
Optometry is a health care profession concerned with eyes and related structures, as well as vision, visual systems, and vision information processing in humans. Optometrists, or Doctors of Optometry, are state licensed medical professionals trained to prescribe and fit lenses to improve vision,...
and ophthalmology
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology is the branch of medicine that deals with the anatomy, physiology and diseases of the eye. An ophthalmologist is a specialist in medical and surgical eye problems...
, polarized glasses are used for various tests of binocular
Binocular vision
Binocular vision is vision in which both eyes are used together. The word binocular comes from two Latin roots, bini for double, and oculus for eye. Having two eyes confers at least four advantages over having one. First, it gives a creature a spare eye in case one is damaged. Second, it gives a...
depth perception
Depth perception
Depth perception is the visual ability to perceive the world in three dimensions and the distance of an object. Depth sensation is the ability to move accurately, or to respond consistently, based on the distances of objects in an environment....
(i.e. stereopsis
Stereopsis
Stereopsis refers to impression of depth that is perceived when a scene is viewed with both eyes by someone with normal binocular vision. Binocular viewing of a scene creates two slightly different images of the scene in the two eyes due the the eyes' different positions on the head...
).
Advantages and disadvantages
Compared to anaglyph imageAnaglyph image
Anaglyph images are used to provide a stereoscopic 3D effect, when viewed with glasses where the two lenses are different colors, such as red and cyan. Images are made up of two color layers, superimposed, but offset with respect to each other to produce a depth effect...
s, the use of polarized 3D glasses produces a full-color image that is considerably more comfortable to watch and is not subject to binocular rivalry
Binocular rivalry
Binocular rivalry is a phenomenon of visual perception in which perception alternates between different images presented to each eye.When one image is presented to one eye and a very different image is presented to the other, instead of the two images being seen superimposed, one image is seen for...
. However, it requires a significant increase in expense: even the low cost polarized glasses typically cost 50% more than comparable red-cyan filters, and while anaglyph 3-D films can be printed on one line of film, a polarized film was often done with a special set up that uses two projectors. The use of multiple projectors also raises issues with synchronization
Synchronization
Synchronization is timekeeping which requires the coordination of events to operate a system in unison. The familiar conductor of an orchestra serves to keep the orchestra in time....
, and a poorly synchronized film would negate any increased comfort from the use of polarization. This problem was solved by a number of single strip polarized systems which were standard in the 1980s.
Particularly with the linear polarization schemes popular since the 1950s, the use of linear polarization meant that a level head was required for any sort of comfortable viewing; any effort to tilt the head sideways would result in the polarization failing, ghosting
Ghosting (television)
In television, a ghost is a replica of the transmitted image, offset in position, that is super-imposed on top of the main image on an analogue broadcast.-Common causes:Common causes of ghosts are:...
, and both eyes seeing both images. Circular polarization has alleviated this problem, allowing viewers to tilt their heads slightly (although any offset between the eye plane and the original camera plane will still interfere with the perception of depth).
3D Cinema and 3D Television
3D Cinema has utilized polarized technology for more than 20 years. Polarized light is easy to project using a movie-style projector. This 3D effect preserves true color perception for both eyes.Until 2011, home 3D Television and home 3D computer primarily used shutter glasses with LCD or plasma displays.
In 2011, LG was the first TV manufacture to commercialize 3D LCD Television using polarized technology. Using polarized lenses instead of shutter lenses in 3D glasses has many benefits.
Advantages
- Polarized glasses are inexpensive ( <$20 ), because they contain no electronics.
- Cinema 3D polarized glasses are widely available and compatible with the TV. (The fee to purchase this glasses is usually less than $5.)
- Polarized glasses are not electronic. They do not need to be recharged.
- Shutter glasses have a flicker that some people notice; there is no flicker in polarized glasses.

