
Planck pressure
Encyclopedia
The Planck pressure is the unit of pressure
, denoted by pP, in the system of natural units
known as Planck units
.
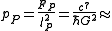 4.63309 × 10113 Pa
4.63309 × 10113 Pa
where
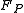 is the Planck force
is the Planck force
 is the speed of light
is the speed of light
in a vacuum
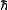 is the reduced Planck's constant
is the reduced Planck's constant
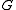 is the gravitational constant
is the gravitational constant
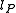 is the Planck length
is the Planck length
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
, denoted by pP, in the system of natural units
Natural units
In physics, natural units are physical units of measurement based only on universal physical constants. For example the elementary charge e is a natural unit of electric charge, or the speed of light c is a natural unit of speed...
known as Planck units
Planck units
In physics, Planck units are physical units of measurement defined exclusively in terms of five universal physical constants listed below, in such a manner that these five physical constants take on the numerical value of 1 when expressed in terms of these units. Planck units elegantly simplify...
.
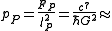 4.63309 × 10113 Pa
4.63309 × 10113 PaPascal (unit)
The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
where
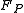 is the Planck force
is the Planck forcePlanck force
Planck force is the derived unit of force resulting from the definition of the base Planck units for time, length, and mass. It is equal to the natural unit of momentum divided by the natural unit of time....
 is the speed of light
is the speed of lightSpeed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
in a vacuum
Vacuum
In everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
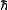 is the reduced Planck's constant
is the reduced Planck's constant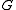 is the gravitational constant
is the gravitational constantGravitational constant
The gravitational constant, denoted G, is an empirical physical constant involved in the calculation of the gravitational attraction between objects with mass. It appears in Newton's law of universal gravitation and in Einstein's theory of general relativity. It is also known as the universal...
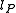 is the Planck length
is the Planck lengthSee also
- Natural unitsNatural unitsIn physics, natural units are physical units of measurement based only on universal physical constants. For example the elementary charge e is a natural unit of electric charge, or the speed of light c is a natural unit of speed...
- Planck's constant

