
Physical Media Dependent
Encyclopedia
Physical Medium Dependent sublayers or PMDs further help to define the physical layer
of computer network
protocols.
They define the details of transmission and reception of individual bits on a physical medium. These responsibilities encompass bit timing, signal encoding, interacting with the physical medium, and the properties of the cable, optical fiber, or wire itself. Common examples are specifications for Fast Ethernet
, Gigabit Ethernet
and 10 Gigabit Ethernet
defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
(IEEE).
For cable modems Physical Medium Dependent sublayers define the physical sub-layer which also includes the MPEG sub-layer.
(PHY). The hierarchy is as follows:
10GBASE-L: was also defined for single mode fiber operations, uses the 1300 nm band allowing it to reach up to 10 km.
10GBASE-S: was defined for use in multimode fiber and ultimately costs less than the other 10GbE standards. It uses 850 nm lasers and only reaches distances ranging between 26 to 82 metres on older fiber technology. In newer optimized multimode fibers (a.k.a OM3) it can reach up to 300 m.
10GBASE-LX4: uses four lasers that each transmit at 3.125 Gbit/s. The receiver is arranged in a wavelength
-division multiplexing manner. On legacy FDDI multimode fiber it can reach up to 300 m while on single mode fiber it can reach up to 10 km.
After these specifications have been laid out, they are then completed with local area network
and wide area network
specifications using different Physical Coding Sublayer
standards.
Physical layer
The physical layer or layer 1 is the first and lowest layer in the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking. The implementation of this layer is often termed PHY....
of computer network
Computer network
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
protocols.
They define the details of transmission and reception of individual bits on a physical medium. These responsibilities encompass bit timing, signal encoding, interacting with the physical medium, and the properties of the cable, optical fiber, or wire itself. Common examples are specifications for Fast Ethernet
Fast Ethernet
In computer networking, Fast Ethernet is a collective term for a number of Ethernet standards that carry traffic at the nominal rate of 100 Mbit/s, against the original Ethernet speed of 10 Mbit/s. Of the fast Ethernet standards 100BASE-TX is by far the most common and is supported by the...
, Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet is a term describing various technologies for transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second , as defined by the IEEE 802.3-2008 standard. It came into use beginning in 1999, gradually supplanting Fast Ethernet in wired local networks where it performed...
and 10 Gigabit Ethernet
10 Gigabit Ethernet
The 10 gigabit Ethernet computer networking standard was first published in 2002. It defines a version of Ethernet with a nominal data rate of 10 Gbit/s , ten times faster than gigabit Ethernet.10 gigabit Ethernet defines only full duplex point to point links which are generally connected by...
defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers is a non-profit professional association headquartered in New York City that is dedicated to advancing technological innovation and excellence...
(IEEE).
For cable modems Physical Medium Dependent sublayers define the physical sub-layer which also includes the MPEG sub-layer.
Description
The Ethernet PMD sublayer is part of the Ethernet physical layerEthernet physical layer
The Ethernet physical layer is the physical layer component of the Ethernet family of computer network standards.The Ethernet physical layer evolved over a considerable time span and encompasses quite a few physical media interfaces and several magnitudes of speed...
(PHY). The hierarchy is as follows:
- Data Link Layer (Layer 2)
- LLC (Logical Link ControlLogical Link ControlThe logical link control data communication protocol layer is the upper sub-layer of the data link layer in the seven-layer OSI reference model...
Sublayer) - MAC (Media Access ControlMedia Access ControlThe media access control data communication protocol sub-layer, also known as the medium access control, is a sublayer of the data link layer specified in the seven-layer OSI model , and in the four-layer TCP/IP model...
Sublayer)- RS (Reconciliation Sublayer) - This sublayer processes PHY Local/Remote Fault messages and handles DDR conversion
- LLC (Logical Link Control
- PHY Layer (Layer 1)
- PCS (Physical Coding SublayerPhysical Coding Sublayer- Description :The Physical Coding Sublayer further helps to define physical layer specifications for networking protocols like Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet....
) - This sublayer performs auto-negotiation and coding such as 8b/10b - PMA (Physical Medium Attachment Sublayer) - This sublayer performs PMA framing, octet synchronization/detection, and
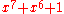 scrambling/descrambling
scrambling/descrambling - PMD (Physical Medium Dependent Sublayer) - This sublayer consists of a transceiver for the physical medium
- PCS (Physical Coding Sublayer
10 Gigabit Ethernet
10GBASE-E: has been defined for single mode fiber operations only. It operates in the 1550 nm band allowing for distances of up to 40 km to be reached.10GBASE-L: was also defined for single mode fiber operations, uses the 1300 nm band allowing it to reach up to 10 km.
10GBASE-S: was defined for use in multimode fiber and ultimately costs less than the other 10GbE standards. It uses 850 nm lasers and only reaches distances ranging between 26 to 82 metres on older fiber technology. In newer optimized multimode fibers (a.k.a OM3) it can reach up to 300 m.
10GBASE-LX4: uses four lasers that each transmit at 3.125 Gbit/s. The receiver is arranged in a wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
-division multiplexing manner. On legacy FDDI multimode fiber it can reach up to 300 m while on single mode fiber it can reach up to 10 km.
After these specifications have been laid out, they are then completed with local area network
Local area network
A local area network is a computer network that interconnects computers in a limited area such as a home, school, computer laboratory, or office building...
and wide area network
Wide area network
A wide area network is a telecommunication network that covers a broad area . Business and government entities utilize WANs to relay data among employees, clients, buyers, and suppliers from various geographical locations...
specifications using different Physical Coding Sublayer
Physical Coding Sublayer
- Description :The Physical Coding Sublayer further helps to define physical layer specifications for networking protocols like Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet....
standards.

