
Physical Coding Sublayer
Encyclopedia
Description
The Physical Coding Sublayer (PCS) further helps to define physical layer specifications(speed and Duplex modes etc..) for networking protocols like Fast EthernetFast Ethernet
In computer networking, Fast Ethernet is a collective term for a number of Ethernet standards that carry traffic at the nominal rate of 100 Mbit/s, against the original Ethernet speed of 10 Mbit/s. Of the fast Ethernet standards 100BASE-TX is by far the most common and is supported by the...
, Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet is a term describing various technologies for transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second , as defined by the IEEE 802.3-2008 standard. It came into use beginning in 1999, gradually supplanting Fast Ethernet in wired local networks where it performed...
and 10 Gigabit Ethernet
10 Gigabit Ethernet
The 10 gigabit Ethernet computer networking standard was first published in 2002. It defines a version of Ethernet with a nominal data rate of 10 Gbit/s , ten times faster than gigabit Ethernet.10 gigabit Ethernet defines only full duplex point to point links which are generally connected by...
.
The Ethernet PCS sublayer is part of the Ethernet PHY layer. The hierarchy is as follows:
- Data Link LayerData link layerThe data link layer is layer 2 of the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking. It corresponds to, or is part of the link layer of the TCP/IP reference model....
(Layer 2)- LLC (Logical Link ControlLogical Link ControlThe logical link control data communication protocol layer is the upper sub-layer of the data link layer in the seven-layer OSI reference model...
Sublayer) - MAC (Media Access ControlMedia Access ControlThe media access control data communication protocol sub-layer, also known as the medium access control, is a sublayer of the data link layer specified in the seven-layer OSI model , and in the four-layer TCP/IP model...
Sublayer)- RS (Reconciliation Sublayer) - This sublayer processes PHY Local/Remote Fault messages and handles DDR conversion
- LLC (Logical Link Control
- PHY LayerPhysical layerThe physical layer or layer 1 is the first and lowest layer in the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking. The implementation of this layer is often termed PHY....
(Layer 1)- PCS (Physical Coding Sublayer) - This sublayer performs autonegotiationAutonegotiationAutonegotiation is an Ethernet procedure by which two connected devices choose common transmission parameters, such as speed, duplex mode, and flow control. In this process, the connected devices first share their capabilities regarding these parameters and then choose the highest performance...
and coding such as 8b/10b encoding8B/10B encodingIn telecommunications, 8b/10b is a line code that maps 8-bit symbols to 10-bit symbols to achieve DC-balance and bounded disparity, and yet provide enough state changes to allow reasonable clock recovery. This means that the difference between the count of 1s and 0s in a string of at least 20 bits... - PMA (Physical Medium Attachment Sublayer) - This sublayer performs PMA framing, octet synchronization/detection, and
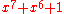 scrambling/descrambling
scrambling/descrambling - PMD (Physical Medium Dependent Sublayer) - This sublayer consists of a transceiver for the physical medium
- PCS (Physical Coding Sublayer) - This sublayer performs autonegotiation
10 Gigabit Ethernet
- 10GBASE-R (LAN) is the serial encoded PCS that allows for Ethernet framing at a rate of approximately 10.3 Gbit/s (MAC= 10,000 Gbit/s, overhead= 64 B/66 B effective rate= 10,000 * 66/64= 10,312.5 - see also 64b/66b encoding64b/66b encodingIn data networking and transmission, 64b/66b is a line code that transforms 64-bit data to 66-bit line code to provide enough state changes to allow reasonable clock recovery and facilitate alignment of the data stream at the receiver....
). This rate does not match the rate 9.953 Gbit/s used in SONET and SDH and is not supported over a WAN based on SONET or SDH.
- 10GBASE-X (LAN) uses similar coding methods as 10GBASE-R but is only used in the definition of 10GBASE-LX4. This is mainly because LX4 operates on both single and multimode fibers, giving it a unique set of specifications as defined in its PMDPhysical Media DependentPhysical Medium Dependent sublayers or PMDs further help to define the physical layer of computer network protocols.They define the details of transmission and reception of individual bits on a physical medium. These responsibilities encompass bit timing, signal encoding, interacting with the...
.
- 10GBASE-W (WAN) defines WAN encoding for 10GbE, it encodes the frames so that they are compatible with SONET STS-192c data rates and SDH VC-4-64 transmission standards allowing for 10 Gbit/s transmission across a WAN. It does this by wrapping the 64/66b payload into a SONET frame, making the effective rate 9.95 Gbit/s.

