
Photoanalysis
Encyclopedia
Photoanalysis (or photo analysis) refers to the study of pictures to compile various types of data, for example, to measure the size distribution of virtually anything that can be captured by photo. Photoanalysis technology has changed the way mines and mills quantify fragmented material.http://www.c-core.ca/Mining06.pdf
Images are a good way to document conditions before, after, and even during blasting activities. The technology is advancing at a high rate, and lenses, storage media memory, light sensitivity and resolution
Image resolution
Image resolution is an umbrella term that describes the detail an image holds. The term applies to raster digital images, film images, and other types of images. Higher resolution means more image detail....
have been improving steadily. Today's digital cameras and camcorders include high-resolution optics, compact size, automatic time and date stamps, good battery life, shutters to freeze motion, and computers to autofocus
Autofocus
An autofocus optical system uses a sensor, a control system and a motor to focus fully automatic or on a manually selected point or area. An electronic rangefinder has a display instead of the motor; the adjustment of the optical system has to be done manually until indication...
and eliminate jitter using image stabilization
Image stabilization
Image stabilization is a family of techniques used to reduce blurring associated with the motion of a camera during exposure. Specifically, it compensates for pan and tilt of a camera or other imaging device. It is used in image-stabilized binoculars, still and video cameras, and astronomical...
.
Mining
Photoanalysis in miningMining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the earth, from an ore body, vein or seam. The term also includes the removal of soil. Materials recovered by mining include base metals, precious metals, iron, uranium, coal, diamonds, limestone, oil shale, rock...
operations can provide an automated system that forewarns a company of potential problems with materials, leading to economies and reduced damage caused from over-sized materials. It can also help determine the effectiveness of blasts.
A company can use this technology to monitor materials moving on a conveyor belt
Conveyor belt
A conveyor belt consists of two or more pulleys, with a continuous loop of material - the conveyor belt - that rotates about them. One or both of the pulleys are powered, moving the belt and the material on the belt forward. The powered pulley is called the drive pulley while the unpowered pulley...
in an underground environment, to measure piles left over from a blast, and even measure the amount of material being carried by dump trucks or vessels to a destination.
Photoanalysis is being used on SAG mills worldwide to control the size of rock being crushed. Companies are using this technology to determine the size of particles being processed in the SAG Mill.http://www.dynonobel.com/dynonobelcom/en/global/consulting/technicallibrary/sagmillthroughput.htm Having oversize material entering the SAG mill makes an operation less efficient, costing companies money in electrical and maintenance costs. Photoanalysis technology can eliminate unwanted material before it enters the mill, keeping rock crushing costs low.
Forestry
Wood chipWoodchips
Woodchips are a medium-sized solid material made by cutting, or chipping, larger pieces of wood. Woodchips may be used as a biomass solid fuel. They may also be used as an organic mulch in gardening, landscaping, restoration ecology and mushroom cultivation...
size can affect the overall quality of a product. With automated photoanalysis systems, companies can remove any unwanted wrong-size particles without stopping their mill process.
Photoanalysis can have an impact on how efficiently forestry companies operate. In mills worldwide, photoanalysis technology is improving the use of lumber products, cutting back on the amount of trees being used to operate, and saving companies money through quality control
Quality control
Quality control, or QC for short, is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. This approach places an emphasis on three aspects:...
optimization.http://www.thefreelibrary.com/Mining,+forestry+suppliers+unite+to+offer+industry+%22packaged...-a0123583683
With the current downturn in the North American forestry industry, operators are looking at making their mills more efficient and effective when processing materials. Photoanalysis technology helps identify any weaknesses in the process by continuously monitoring different sections of an operation.
Agriculture

- Automated removal of any unwanted material on food conveyor
- Improved quality control for the most important parts of the agricultural process
- Pinpoint accuracy that helps the efficiency and effectiveness of product handling techniques
The importance of photoanalysis technology is being noticed by the agricultural industry as it identifies any unwanted materials going through the process. In an example, if a mouse is on a conveyor of corn, photoanalysis technology would be able to identify the unwanted object and remove it before it contaminates the whole process.
Origins of photoanalysis technology
Photoanalysis technology was created by using the Waterloo Image Enhancement Process in the 1980s. After further development of the imaging process with explosives producer DuPont, engineers Tom Palangio and Takis Katsabanis began selling photoanalysis software commercially. They later renamed the process WipFrag, standing for Waterloo Image Process FragmentationToday, photoanalysis technology has evolved into stabilized and portable systems that can automatically capture and analyze results instantly. Thousands of these products are currently being used around the world to measure fragmented material.
Fragmentation analysis
Fragmentation analysis is becoming a popular term in mining, agricultural and forestry industries. With the majority of money in these industries directed towards the proper sizing of materials, companies are using fragmentation analysis to determine various factors within an operation.http://www.isee.org/2008%20Abstracts/08v127g.pdfThe two main ways a company keeps track of fragmented material are through manual and automated sieving
Sieve analysis
A sieve analysis is a practice or procedure used to assess the particle size distribution of a granular material....
procedures. Manual sieving involves extracting a sample of material to analyze the size distribution. The results can be tabulated within two days. Automated sieving is an advanced way of sieving materials running through a process. Without having to extract the material, photoanalysis can take place, allowing for immediate results with pinpoint accuracy.
Blast Fragmentation Software
Operators are using fragmentation analysis to determine the effectiveness of various blastsRock blasting
Rock blasting is the controlled use of explosives to excavate, break down or remove rock. It is practised most often in mining, quarrying and civil engineering such as dam or road construction...
. With automated sieving technology, workers can track the success of these blasts and receive instant results. Companies are using these results to determine what blasting method yielded the best results for their specific operation.
"It is necessary to realize that the size of fragmented material after a blast is not dependant on the amount of explosives being used, but rather the position of the explosives" states Tom Palangio, engineer and co-inventor of automated fragmentation technology. "If a company can use less explosives and maintain the same size of fragmented material post-blast, they can become more efficient."
By using photoanalysis the fragmented materials can be monitored, offering pinpoint accuracy and allowing mine operators to make adjustments to future blasting procedures. See Optical Granulometry
Optical Granulometry
Optical granulometry is the process of measuring the different grain sizes in a granular material, based on a photograph. Technology has been created to analyze a photograph and create statistics based on what the picture portrays. This information is vital in maintaining machinery in various...
to view the automated sieving process.
Pre-crushing analysis

Having an analysis taking place at every major point in an operation allows for the proper tracking of material being processed. Engineers can then determine what part of the process needs improving based solely on the size of material.
Post-crushing analysis
Meeting the material standards set by governments and large companies can be hard. Having a post-crushing analysis taking place ensures that no oversize material gets shipped; eliminating the chance of getting fined for not meeting industry specifications.
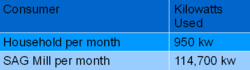
Household energy consumption estimate:
SAG Mill energy consumption estimate:

