
Phased adoption
Encyclopedia
Phased adoption is a strategy of implementing an innovation (i.e., information system
s, new technologies, processes, etc.) in an organization in a phased way, so that different parts of the organization are implemented in different subsequent time slots. Other concepts that are used are: phased implementation, phased conversion, phased approach, phased strategy, phased introduction and staged conversion.
Systems (ERP), Content Management System
s (CMS), Customer
and Supplier Relationship Management
Systems (CRM and SRM), came the task to implement these systems in the organizations that are about to use it. The following entry will discuss just a small fraction of what has to be done or can be done when implementing such a system in the organization.
The phased approach takes the conversion one step at a time. The implementation requires a thoroughly thought out scenario for starting to use the new system. And at every milestone one has to instruct the employees and other users. The old system is taken over by the new system in predefined steps until it is totally abounded. The actual installation of the new system will be done in several ways, per module or per product and several instances can be carried out. This may be done by introducing some of the functionalities of the system before the rest or by introducing some functionalities to certain users before introducing them to all the users. This gives the users the time to cope with the changes caused by the system.
It is common to organize an implementation team that moves from department to department. By moving, the team learns and so gains expertise and knowledge, so that each subsequent implementation will be a lot faster than the first one.
 The visualising technique used in this entry is a technique developed by the O&I group of the University of Utrecht (Weerd, 2005). The technique is described in the following Wiki: Meta-modeling technique.
The visualising technique used in this entry is a technique developed by the O&I group of the University of Utrecht (Weerd, 2005). The technique is described in the following Wiki: Meta-modeling technique.
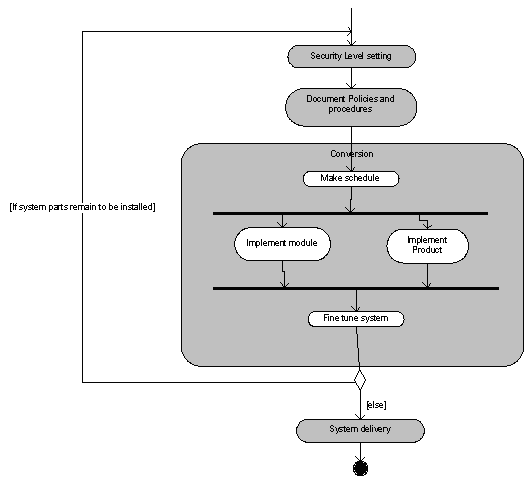
As can be seen in figure 1, phased adoption has a loop in it. Every department that is to be connected to the system is going through the same process. First based on the previous training sessions security levels are set (see ITIL
) In this way every unique user has its own profile which describes, which parts of the system are visible and/or usable to that specific user. Then the document and policies are documented. Al processes and procedures are described in process descriptions, can be in paper or on the intranet. Then the actual conversion is depicted. As described in the above text, certain departments and or parts of an organization may be implemented in different time slots. In figure 1 that is depicted by implementing an additional module or even a total product. HRM needs different modules of an ERP system than Finance (module) or Finance may need an additional accounting software package (Product). Tuning of the system occurs to solve existing problems. After the certain department has been conversed the loop starts over, and another department or user group may be conversed. If all of the departments or organization parts are conversed and the system is totally implemented the system is officially delivered to the organization and the implementation team may be dissolved.
Phased adoption makes it possible to introduce modules that are ready whilst programming the other future modules. This does make the implementation scenario more critical, since certain modules depend on one another. Project Management techniques can be adopted to tackle these problems. See the techniques section below.
However, the actual adoption of the system by the users can be more problematic. The system may work just fine but if it is not used it’s worthless. Users base their attitude towards the system on their first experience (Eason, 1988). As this creates an extra weight on the first interaction, the implementers should be concerned with making the first interaction especially a pleasant one.
In the technique used in this entry each CONCEPT requires a proper definition which is preferably copied from a standard glossary of which the source is given, if applicable. All CONCEPT names in the text are with capital characters. In Table 1 the concept definition list is presented.
Table 1: Concept Diagram
Pros:
Cons:
Risks:
 The following sections are supplemental to the entry about adoption (software implementation)
The following sections are supplemental to the entry about adoption (software implementation)
and are specific to phased adoption:
The configuration and specification of the hardware in place used by the legacy system and to run the new system is delivered in the hardware specifications. The hardware configuration is tested to assure proper functioning. This is reported in the hardware configuration report.
The configuration and specification of the software in place, i.e., the legacy system and the future new system is made clear to assure proper functioning once the system is installed. The act of specifying the system already installed is key to the implementation. Which parts or even total systems will be taken over by the new system? All this is reported in the software installation and software test reports.
The actual installation of the software of the new system is also done here in a confined area to support the training sessions described in the following section.
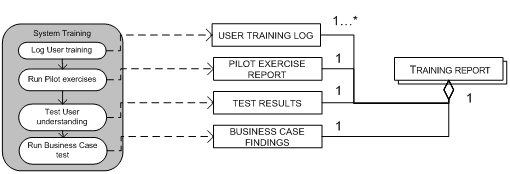 The system training will teach users the keystrokes and transactions required to run the system (Umble, 2003) . The pilot exercises the systems and tests the users understanding of the system. The project team creates a skeletal business case test environment which takes the business processes from the beginning, when a customer order is received, to the end, when the customer order is shipped.
The system training will teach users the keystrokes and transactions required to run the system (Umble, 2003) . The pilot exercises the systems and tests the users understanding of the system. The project team creates a skeletal business case test environment which takes the business processes from the beginning, when a customer order is received, to the end, when the customer order is shipped.
Training as such is not enough for adopting an information system. The users have learning needs (Eason, 1988). Known learning needs are the emotional guidance. Users need to make emotional steps in order to make cognitive
steps. If they fear the system due to its difficult handling they may not be able to understand the cognitive steps needed to successfully carry out the tasks.
. Other techniques are the SAP Implementation method, which is adapted to implementing SAP
systems. Systems are installed in several different ways. Different organizations may have their own methods, When implementing a system, it is considered a project and thus must be handled as such. Well known theories and methods are used in the field such as the PRINCE2
method with all of its underlying techniques, such as a PERT diagram, Gantt chart
and critical path method
s.
and Brooklyn
, New York
.
The University Physicians Group in New York went with a complete technical installation of an EMR (Electronic Medical Record) software package. The UPG found that some vendors of the EMR package recommended a rolling out that would be done all-at-one, also called the Big Bang. But they found out that the Big Bang would have overwhelmed the physicians and staff due to the following factors:
Thus they chose a phased approach: “Hence, a phased adoption to us, offered the greatest chance of success, staff adoption, and opportunity for the expected return-on-investment once the system was completely adopted.” (J. Hyman, M.D.)
There also was a group who were somewhat reluctant about any new systems. By introducing the system to certain early adopters (Rogers, 1995) the late majority would be able to get to know the system. As it was introduced phased through the organisation. Per loop (see figure 5, A) the UPG was introduced to the system.
Information system
An information system - or application landscape - is any combination of information technology and people's activities that support operations, management, and decision making. In a very broad sense, the term information system is frequently used to refer to the interaction between people,...
s, new technologies, processes, etc.) in an organization in a phased way, so that different parts of the organization are implemented in different subsequent time slots. Other concepts that are used are: phased implementation, phased conversion, phased approach, phased strategy, phased introduction and staged conversion.
Overview
Information Technology has revolutionized the way of working in organizations (Eason, 1988). With the introduction of high-tech Enterprise Resource PlanningEnterprise resource planning
Enterprise resource planning systems integrate internal and external management information across an entire organization, embracing finance/accounting, manufacturing, sales and service, customer relationship management, etc. ERP systems automate this activity with an integrated software application...
Systems (ERP), Content Management System
Content management system
A content management system is a system providing a collection of procedures used to manage work flow in a collaborative environment. These procedures can be manual or computer-based...
s (CMS), Customer
Customer relationship management
Customer relationship management is a widely implemented strategy for managing a company’s interactions with customers, clients and sales prospects. It involves using technology to organize, automate, and synchronize business processes—principally sales activities, but also those for marketing,...
and Supplier Relationship Management
Supplier relationship management
“SRM is a discipline of working collaboratively with those suppliers that are vital to the success of your organisation to maximise the potential value of those relationships.” - Reference - Overview :...
Systems (CRM and SRM), came the task to implement these systems in the organizations that are about to use it. The following entry will discuss just a small fraction of what has to be done or can be done when implementing such a system in the organization.
The phased approach takes the conversion one step at a time. The implementation requires a thoroughly thought out scenario for starting to use the new system. And at every milestone one has to instruct the employees and other users. The old system is taken over by the new system in predefined steps until it is totally abounded. The actual installation of the new system will be done in several ways, per module or per product and several instances can be carried out. This may be done by introducing some of the functionalities of the system before the rest or by introducing some functionalities to certain users before introducing them to all the users. This gives the users the time to cope with the changes caused by the system.
It is common to organize an implementation team that moves from department to department. By moving, the team learns and so gains expertise and knowledge, so that each subsequent implementation will be a lot faster than the first one.
The Process Data Diagram

As can be seen in figure 1, phased adoption has a loop in it. Every department that is to be connected to the system is going through the same process. First based on the previous training sessions security levels are set (see ITIL
Information Technology Infrastructure Library
The Information Technology Infrastructure Library , is a set of good practices for IT service management that focuses on aligning IT services with the needs of business. In its current form , ITIL is published in a series of five core publications, each of which covers an ITSM lifecycle stage...
) In this way every unique user has its own profile which describes, which parts of the system are visible and/or usable to that specific user. Then the document and policies are documented. Al processes and procedures are described in process descriptions, can be in paper or on the intranet. Then the actual conversion is depicted. As described in the above text, certain departments and or parts of an organization may be implemented in different time slots. In figure 1 that is depicted by implementing an additional module or even a total product. HRM needs different modules of an ERP system than Finance (module) or Finance may need an additional accounting software package (Product). Tuning of the system occurs to solve existing problems. After the certain department has been conversed the loop starts over, and another department or user group may be conversed. If all of the departments or organization parts are conversed and the system is totally implemented the system is officially delivered to the organization and the implementation team may be dissolved.
Phased adoption makes it possible to introduce modules that are ready whilst programming the other future modules. This does make the implementation scenario more critical, since certain modules depend on one another. Project Management techniques can be adopted to tackle these problems. See the techniques section below.
However, the actual adoption of the system by the users can be more problematic. The system may work just fine but if it is not used it’s worthless. Users base their attitude towards the system on their first experience (Eason, 1988). As this creates an extra weight on the first interaction, the implementers should be concerned with making the first interaction especially a pleasant one.
In the technique used in this entry each CONCEPT requires a proper definition which is preferably copied from a standard glossary of which the source is given, if applicable. All CONCEPT names in the text are with capital characters. In Table 1 the concept definition list is presented.
Table 1: Concept Diagram
| Concept | Definition |
| Management Decision Report | The description of the selection of the process carried out before the actual implementation start of the new system are described here. Decisions and requirements are described in the report too. (Eason, 1988) |
| Critical Implementation factors | Factors that rose in the selection of the system and are critical during the implementation process. (Umble, 2003) |
| Hardware specifications | The configuration and specification of the hardware in place used by the legacy system and to run the new system. |
| Hardware test report | The results of the tested hardware in place. |
| Software specification | The configuration and specification of the software in place, i.e., the legacy system and the future new system. |
| Software test report | Software tests examine the complete software system. (ISO 9000 ISO 9000 The ISO 9000 family of standards relates to quality management systems and is designed to help organizations ensure they meet the needs of customers and other stakeholders . The standards are published by ISO, the International Organization for Standardization, and available through National... ) |
| User training log | A log concerning the training of the employees involved with the new system (Eason, 1988) |
| Pilot Exercise report | The report of the pilot exercise carried out with the newly installed system in a controlled single environment. |
| Test result | Tests results of the users knowledge of the system. Real users bashing on a prototype long enough to get thoroughly acquainted with it, with careful monitoring and followup of the results. (The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language is an American dictionary of the English language published by Boston publisher Houghton Mifflin, the first edition of which appeared in 1969... , Fourth Edition, 2000) |
| Business case findings | The project team creates a skeletal business case test environment which takes the business processes from the beginning, when a customer order is received, to the end, when the customer order is shipped. The findings concerned with this test are logged and reported. (Umble, 2003) |
| Security level report | Once the training phase is finished, the setting of the security and permissions levels are necessary to ensure that everyone has access to the information they need. (Cazemier, J.A., Overbeek, P.L., Peters, L.M., 2000) |
| Documentation | The organized collection of records that describe the structure, purpose, operation, maintenance, and data requirements for a computer program, operating system, or hardware device. (The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition, 2000) |
| Conversion scenario | The redefined implementation script, taking into account the Conformity tot the requirements. Furthermore the conversion scenario consists of a workaround and rollback plan. The conversion scenario is the blueprint of the implementation project. (Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Module Implementation Plan | A plan concerning the implementation of a specific module in the system of the organization’s processes is described here. (The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition, 2000) |
| Product Implementation Plan | A plan concerning the implementation of a specific product of the system into the processes of the organization is described here. (The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition, 2000) |
| Tuning report | During the implementation the implementers might want to change the system due to findings in the implementation increments. |
| System Acceptation | The system gets accepted by the organization. (Umble, 2003) |
| Catch-up | An approach or strategy intended to overcome a disadvantage or lead (The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition, 2000) |
Advantages, disadvantages and risks of Phased Adoption
The Phased adoption method has certain pros, cons and risks (Koop, R., Rooimans, R. & Theye, M. de (2003), Eason (1988))Pros:
- The conversion will be done in parts. Time is available for adjustments
- Negative influences that arise at the start are less critical
- No ‘catch-up’ period is needed.
- Time for the users to adapt is longer
- Technical staff can concentrate on part of the system or some of the users.
Cons:
- Several adjustments are needed
- Training sessions are confusing for users as they are asked to work with the new and the old system
- Several changes in documentation
- The duration of the project
- System delivery milestone is unclear
- Correctness and completeness of the dataset has to be checked several times
- A ‘fall back’ to the old system is becoming more difficult every new phase.
- The implementation may appear unclear to the employees and other users.
Risks:
- Complexity of the implementation
- Prone to make mistakes
- Fall back impossible in later phases
Hardware and software installation

Adoption (software implementation)
Adoption deals with the transfer between an old system to a target system in an organization. So if a company works with an old software system, it may want to use a new system which is more efficient, has more work capacity etc. So then a new system needs to be adopted, where after it can be...
and are specific to phased adoption:
The configuration and specification of the hardware in place used by the legacy system and to run the new system is delivered in the hardware specifications. The hardware configuration is tested to assure proper functioning. This is reported in the hardware configuration report.
The configuration and specification of the software in place, i.e., the legacy system and the future new system is made clear to assure proper functioning once the system is installed. The act of specifying the system already installed is key to the implementation. Which parts or even total systems will be taken over by the new system? All this is reported in the software installation and software test reports.
The actual installation of the software of the new system is also done here in a confined area to support the training sessions described in the following section.
Training

Training as such is not enough for adopting an information system. The users have learning needs (Eason, 1988). Known learning needs are the emotional guidance. Users need to make emotional steps in order to make cognitive
steps. If they fear the system due to its difficult handling they may not be able to understand the cognitive steps needed to successfully carry out the tasks.
Techniques
In the implementation field several techniques are used. A well-known method, and specifically oriented on the implementation field, is the Regatta method by SogetiSogeti
Sogeti is a wholly owned subsidiary of Cap Gemini Group. It is an international information technology consultancy specializing in local professional services. Sogeti employs 20,000 people in 15 countries. Sogeti developed Test Management Approach....
. Other techniques are the SAP Implementation method, which is adapted to implementing SAP
SAP AG
SAP AG is a German software corporation that makes enterprise software to manage business operations and customer relations. Headquartered in Walldorf, Baden-Württemberg, with regional offices around the world, SAP is the market leader in enterprise application software...
systems. Systems are installed in several different ways. Different organizations may have their own methods, When implementing a system, it is considered a project and thus must be handled as such. Well known theories and methods are used in the field such as the PRINCE2
PRINCE2
PRojects IN Controlled Environments 2 is a structured project management method endorsed by the UK government as the project management standard for public projects. The methodology encompasses the management, control and organisation of a project...
method with all of its underlying techniques, such as a PERT diagram, Gantt chart
Gantt chart
A Gantt chart is a type of bar chart that illustrates a project schedule. Gantt charts illustrate the start and finish dates of the terminal elements and summary elements of a project. Terminal elements and summary elements comprise the work breakdown structure of the project. Some Gantt charts...
and critical path method
Critical path method
The critical path method is an algorithm for scheduling a set of project activities. It is an important tool for effective project management.-History:...
s.
Example
The EMR implementation at the University Physicians Group (UPG) in Staten IslandStaten Island
Staten Island is a borough of New York City, New York, United States, located in the southwest part of the city. Staten Island is separated from New Jersey by the Arthur Kill and the Kill Van Kull, and from the rest of New York by New York Bay...
and Brooklyn
Brooklyn
Brooklyn is the most populous of New York City's five boroughs, with nearly 2.6 million residents, and the second-largest in area. Since 1896, Brooklyn has had the same boundaries as Kings County, which is now the most populous county in New York State and the second-most densely populated...
, New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
.
The University Physicians Group in New York went with a complete technical installation of an EMR (Electronic Medical Record) software package. The UPG found that some vendors of the EMR package recommended a rolling out that would be done all-at-one, also called the Big Bang. But they found out that the Big Bang would have overwhelmed the physicians and staff due to the following factors:
- Ongoing workload during the key lessons prevented them to fully pay attention.
- Urgent need to complete some records caused the users to fall back to the old system
- Information overload on the physicians side.
- No time to play around with the system.
- 100% availability was not assured by the vendor.
Thus they chose a phased approach: “Hence, a phased adoption to us, offered the greatest chance of success, staff adoption, and opportunity for the expected return-on-investment once the system was completely adopted.” (J. Hyman, M.D.)
There also was a group who were somewhat reluctant about any new systems. By introducing the system to certain early adopters (Rogers, 1995) the late majority would be able to get to know the system. As it was introduced phased through the organisation. Per loop (see figure 5, A) the UPG was introduced to the system.
See also
- PRINCE2PRINCE2PRojects IN Controlled Environments 2 is a structured project management method endorsed by the UK government as the project management standard for public projects. The methodology encompasses the management, control and organisation of a project...
- Regatta method by Sogeti
- Parallel adoptionParallel adoptionParallel adoption is a method for transferring between an old system to a target system in an organization. In order to reduce risk, the old and new system run simultaneously for some period of time after which, if the criteria for the new system are met, the old system is disabled...
- ERPEnterprise resource planningEnterprise resource planning systems integrate internal and external management information across an entire organization, embracing finance/accounting, manufacturing, sales and service, customer relationship management, etc. ERP systems automate this activity with an integrated software application...
- SRMSupplier relationship management“SRM is a discipline of working collaboratively with those suppliers that are vital to the success of your organisation to maximise the potential value of those relationships.” - Reference - Overview :...
- CRMCustomer relationship managementCustomer relationship management is a widely implemented strategy for managing a company’s interactions with customers, clients and sales prospects. It involves using technology to organize, automate, and synchronize business processes—principally sales activities, but also those for marketing,...
- Software packageSoftware package (installation)In package management systems, which are commonly used with Linux-based operating systems, a package is a specific piece of software which the system can install and uninstall....

