.gif)
Adoption (software implementation)
Encyclopedia
Adoption deals with the transfer (conversion) between an old system to a target system in an organization. So if a company works with an old software system, it may want to use a new system which is more efficient, has more work capacity etc. So then a new system needs to be adopted, where after it can be used.
There are several types of adoption that can be used to implement a system. The types ‘big bang’, ‘parallel adoption’ and ‘phased adoption’ form the main types that are used to adopt a system. The big bang relates to the cosmological theory (Big bang
) where the start of the cosmos happened at one moment in time. This is also the case with the big bang adoption type where the new system is adopted on one date. In case of parallel adoption the old and the new system are running parallel so all the users can get used to the new system, but still can do their work using the old system. Phased adoption means that the adoption will happen in several phases, so after each phase the system is a little closer to be fully adopted by the organization
The actual selection is done by prioritizing the goals to be achieved and then matching a strategy against it (Eason, 1988). Eason defines the following goals:
If a large critical mass is needed for the system to work a big bang strategy might seem the answer. (Rogers, 1995)
Minimising risk to operation of the organization is key. Parallel and phased introduction might control this risk.
The organization has to be ready for the changeover. Socio-technical preparations such as training sessions and ready-made scenarios must be clear.
The speed of in which the organization is changing over to the new system.
The system might be adjusted to the users needs. In this the chosen strategy must provide the opportunity to do so.
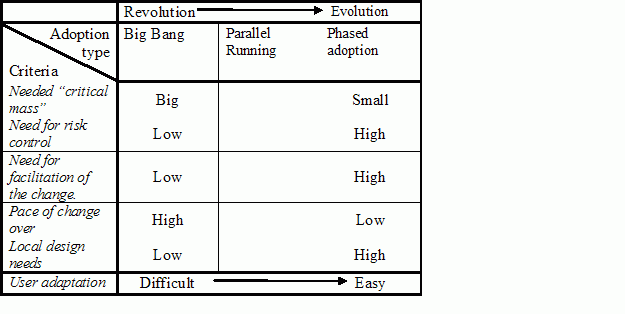
Table Eason Matrix
The actual selection of adoption type depends on far more factors then these goals, but they create a window to choose one of the types. Other criteria are called variables (Gallivan, 1996). Gallivan suggests that the appropriate adoption types depends on:
These variables are of a higher level then the criteria of Eason and should be handled as such. Based on table 1 and on the mentioned higher level variables by Gallivan, one can make a selection of an appropriate strategy to choose.
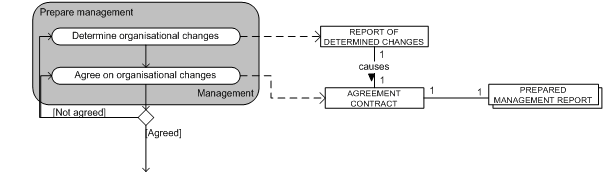
Figure 1: Organization preparation Process
In order to prepare the organization for the adoption of the new system, the changes that will take place need to be determined. This is necessary to be able to have a plan or an overview of the changeover, and can be done by creating requirements for the system. Once the management has determined the requirements in a report of determined changes, they need to agree upon them to be able to move on with the change-process. If there is no agreement, the management needs to discuss the requirements again and again until they do agree. If agreement is achieved and the agreement contract is signed, the organization can take further steps. So now the test-phase can be prepared, in which the validity of the data that will be used will be checked and in which trials will be held (Eason, 1988).
There are several types of adoption that can be used to implement a system. The types ‘big bang’, ‘parallel adoption’ and ‘phased adoption’ form the main types that are used to adopt a system. The big bang relates to the cosmological theory (Big bang
Big Bang
The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model that explains the early development of the Universe. According to the Big Bang theory, the Universe was once in an extremely hot and dense state which expanded rapidly. This rapid expansion caused the young Universe to cool and resulted in...
) where the start of the cosmos happened at one moment in time. This is also the case with the big bang adoption type where the new system is adopted on one date. In case of parallel adoption the old and the new system are running parallel so all the users can get used to the new system, but still can do their work using the old system. Phased adoption means that the adoption will happen in several phases, so after each phase the system is a little closer to be fully adopted by the organization
Define the wanted type of adoption
The adoption type has to be defined in front of the adoption phase and will be chosen based on the goals to be achieved and on the type of system to be implemented. The three types of adoption, Big Bang, parallel adoption and phased adoption, are ranging from an instant switch to a strategy where users progressively start using the new system over a certain period of time (can be weeks, months or even years).The actual selection is done by prioritizing the goals to be achieved and then matching a strategy against it (Eason, 1988). Eason defines the following goals:
- Possible existence of needed “critical mass” to make the system work.
If a large critical mass is needed for the system to work a big bang strategy might seem the answer. (Rogers, 1995)
- Need for risk control, if risk is involved.
Minimising risk to operation of the organization is key. Parallel and phased introduction might control this risk.
- Need for facilitation of the change.
The organization has to be ready for the changeover. Socio-technical preparations such as training sessions and ready-made scenarios must be clear.
- Pace of change over
The speed of in which the organization is changing over to the new system.
- Local design needs
The system might be adjusted to the users needs. In this the chosen strategy must provide the opportunity to do so.
Table Eason Matrix

The actual selection of adoption type depends on far more factors then these goals, but they create a window to choose one of the types. Other criteria are called variables (Gallivan, 1996). Gallivan suggests that the appropriate adoption types depends on:
Innovativeness of the individuals
Attributes of the ones that are to adopt the innovation/systemThe type of innovation
Is it a process or product innovation?Attributes of the innovation itself
Preparedness, communicability and divisibilityThe implementation complexity.
How complex is the implementation or what is it is extent?
These variables are of a higher level then the criteria of Eason and should be handled as such. Based on table 1 and on the mentioned higher level variables by Gallivan, one can make a selection of an appropriate strategy to choose.
Prepare an organization for adoption

Figure 1: Organization preparation Process
In order to prepare the organization for the adoption of the new system, the changes that will take place need to be determined. This is necessary to be able to have a plan or an overview of the changeover, and can be done by creating requirements for the system. Once the management has determined the requirements in a report of determined changes, they need to agree upon them to be able to move on with the change-process. If there is no agreement, the management needs to discuss the requirements again and again until they do agree. If agreement is achieved and the agreement contract is signed, the organization can take further steps. So now the test-phase can be prepared, in which the validity of the data that will be used will be checked and in which trials will be held (Eason, 1988).
See also
- Direct changeoverDirect changeoverDirect changeover is one of the methods to change from an existing system to a new one. This is the simplest methods of changeover. Imagine a new checkout system for a supermarket...
- Phased implementationPhased implementationPhased implementation is a method of changing from an existing system to a new one. Phased implementation is a changeover process that takes place in stages. Think of a supermarket for example. Imagine that only the vegetable section is changed over to the new system while the rest carries on with...
- Big bang adoptionBig bang adoptionBig bang adoption is the adoption type of the instant changeover, when everybody associated with the new system moves to the fully functioning new system on a given date ....
- Phased adoptionPhased adoptionPhased adoption is a strategy of implementing an innovation in an organization in a phased way, so that different parts of the organization are implemented in different subsequent time slots...
- Parallel adoptionParallel adoptionParallel adoption is a method for transferring between an old system to a target system in an organization. In order to reduce risk, the old and new system run simultaneously for some period of time after which, if the criteria for the new system are met, the old system is disabled...
- SAP ImplementationSAP ImplementationSAP implementation is the whole of processes that defines a complete method to implement the SAP ERP enterprise resource planning software in an organization. The SAP implementation method described in this entry is a generic method and not a specific implementation method as such...

