Phase fired controllers
Encyclopedia
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
voltages. It works by modulating a thyristor
Thyristor
A thyristor is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating N and P-type material. They act as bistable switches, conducting when their gate receives a current trigger, and continue to conduct while they are forward biased .Some sources define silicon controlled rectifiers and...
, SCR
Silicon-controlled rectifier
A silicon-controlled rectifier is a four-layer solid state device that controls current. The name "silicon controlled rectifier" or SCR is General Electric's trade name for a type of thyristor. The SCR was developed by a team of power engineers led by Gordon Hall and commercialized by Frank W...
, triac
TRIAC
TRIAC, from Triode for Alternating Current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered , and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs belong to the thyristor family and are...
, thyratron
Thyratron
A thyratron is a type of gas filled tube used as a high energy electrical switch and controlled rectifier. Triode, tetrode and pentode variations of the thyratron have been manufactured in the past, though most are of the triode design...
, or other such gated diode
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
-like devices into and out of conduction at a predetermined phase of the applied waveform.
Overview
Phase fired control is often used to control the amount of voltageVoltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
, current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
or power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
that a power supply
Power supply
A power supply is a device that supplies electrical energy to one or more electric loads. The term is most commonly applied to devices that convert one form of electrical energy to another, though it may also refer to devices that convert another form of energy to electrical energy...
feeds to its load. It does this in much the same way that a pulse width modulated
Pulse-width modulation
Pulse-width modulation , or pulse-duration modulation , is a commonly used technique for controlling power to inertial electrical devices, made practical by modern electronic power switches....
(PWM) supply would pulse on and off to create an average value at its output. If the supply has a DC output, its time base is of no importance in deciding when to pulse the supply on or off, as the value that will be pulsed on and off is continuous.
PFC differs from PWM in that it addresses supplies that output a modulated waveform, such as the sinusoidal AC
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
waveform that the national grid outputs. Here, it becomes important for the supply to pulse on and off at the correct position in the modulation cycle for a known value to be achieved; for example, the controller could turn on at the peak of a waveform or at its base if the cycle's time base were not taken into consideration.
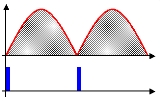
Phase fired controllers take their name from that fact that they trigger a pulse of output at a certain phase of the input's modulation cycle. In essence, a PFC is a PWM controller that can synchronise itself with the modulation present at the input.
Most phase fired controllers use thyristors or other solid state switching devices as their control elements. Thyristor based controllers may utilise Gate Turn Off (GTO) thyristors, allowing the controller to not only decide when to pulse the output on but also when to turn it off, rather than having to wait for the waveform to pass within the element's Zero Cross Point
Zero cross circuit
A zero cross circuit is an electrical circuit that starts operation with the AC load voltage at close to zero-phase. This is in relation to solid state relays, such as triacs and silicon controlled rectifiers...
.
Output reduction by bucking
A phase fired controller, like a buck topology switched-mode power supplySwitched-mode power supply
A switched-mode power supply is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator in order to be highly efficient in the conversion of electrical power...
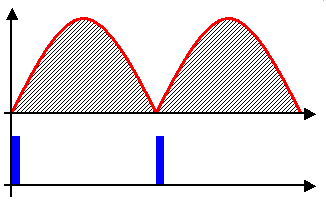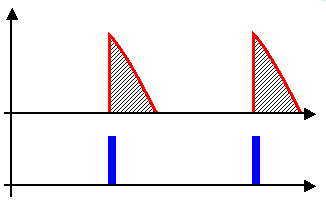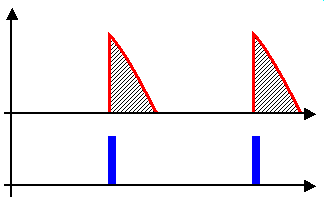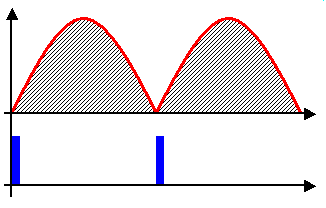
, is only able to deliver an output maximum equal to that which is present at its input, minus any losses occurring in the control elements themselves. Provided the modulation during each cycle is predictable or repetitive, as it is on the national grid's AC mains, to obtain an output lower than its input, a phase fired control simply switches off for a given phase angle of the input's modulation cycle. By triggering the device into conduction at a phase angle greater than 0 degrees, a point after the modulation cycle starts, a fraction of the total energy within each cycle is present at the output.
'Boosting' by derating
To achieve a 'boost' like effect, the PFC designs must be derated such that maximum present at the input is higher than the nominal output requirements. When the supply is first turned on or operating under nominal conditions, the controller will continually be delivering less than 100% of its input. When a boost is required, the controller delivers a percentage closer to 100% of the maximum input available.Derating of mains powered, phase fired controllers is important as they are often used to control resistive
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
loads, such as heating elements. Over time, the resistance of heating elements can increase. To account for this, a phase fired control must be able to provide some degree of extra voltage to draw the same heating current through the element. The only way of achieving this is to purposely design the supply to require less than 100% of the input's modulation cycle when the elements are first put in place, progressively opening the supply up towards delivering 100% of the input modulation cycle as the elements age.
Applications
Previously, extremely expensive and heavy multi-tapped transformerTransformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
s were used as the supplies for such elements, with the corresponding winding tap being connected to the element to produce the desired temperature. This limited the temperature resolution to the number of tap combinations available. They often find their way into controllers designed for equipment such as electric ovens and furnaces.
In modern, usually high power, equipment, the transformer is replaced with phase fired controllers connecting the load directly to the mains, resulting in a substantially cheaper and lighter system. However, the method is usually limited to use in equipment that would be unrealistic without it. This is because removal of the mains transformer means that the load is in direct galvanic contact with the input. For industrial ovens and furnaces the input is often the national grid AC, which is itself galvanically referenced to the Earth. With the controller's output referenced to the Earth, a user need only be in contact with the Earth and one of the output terminals to risk receiving an electrical shock. With many high power pieces of equipment running from three phase 415 V, high current capable inputs and having the entirety of any metallic housing or framework present Earthed (grounded), this is a serious risk that must be assessed with care.
History
The first patent for phase fired controllers derives from 1912. However realization was first possible in the 1920s, when mercury arc valveMercury arc valve
A mercury-arc valve is a type of electrical rectifier used for converting high-voltage or high-current alternating current into direct current . Rectifiers of this type were used to provide power for industrial motors, electric railways, streetcars, and electric locomotives, as well as for...
rectifiers with control grids became available.
However, this method of voltage regulation was not very common at the time, because of the limitations of mercury arc valves. It became widespread with the invention of solid-state thyristor
Thyristor
A thyristor is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating N and P-type material. They act as bistable switches, conducting when their gate receives a current trigger, and continue to conduct while they are forward biased .Some sources define silicon controlled rectifiers and...
s at the end of the 1950s.

