
Penalty method
Encyclopedia
Penalty methods are a certain class of algorithm
s for solving constrained
optimization
problems.
A penalty method replaces a constrained optimization problem by a series of unconstrained problems whose solutions ideally converge to the solution of the original constrained problem. The unconstrained problems are formed by adding a term to the objective function that consists of a penalty parameter and a measure of violation of the constraints. The measure of violation is nonzero when the constraints are violated and is zero in the region where constraints are not violated.
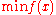
subject to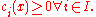
This problem can be solved as a series of unconstrained minimization problems
where
In the above equations,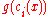 is the penalty function while
is the penalty function while 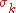 are the penalty coefficients. In each iteration k of the method, we increase the penalty coefficient
are the penalty coefficients. In each iteration k of the method, we increase the penalty coefficient 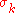 (e.g. by a factor of 10), solve the unconstrained problem and use the solution as the initial guess for the next iteration. Solutions of the successive unconstrained problems will eventually converge to the solution of the original constrained problem.
(e.g. by a factor of 10), solve the unconstrained problem and use the solution as the initial guess for the next iteration. Solutions of the successive unconstrained problems will eventually converge to the solution of the original constrained problem.
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
s for solving constrained
Constraint (mathematics)
In mathematics, a constraint is a condition that a solution to an optimization problem must satisfy. There are two types of constraints: equality constraints and inequality constraints...
optimization
Optimization (mathematics)
In mathematics, computational science, or management science, mathematical optimization refers to the selection of a best element from some set of available alternatives....
problems.
A penalty method replaces a constrained optimization problem by a series of unconstrained problems whose solutions ideally converge to the solution of the original constrained problem. The unconstrained problems are formed by adding a term to the objective function that consists of a penalty parameter and a measure of violation of the constraints. The measure of violation is nonzero when the constraints are violated and is zero in the region where constraints are not violated.
Example
Let us say we are solving the following constrained problem: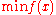
subject to
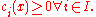
This problem can be solved as a series of unconstrained minimization problems

where

In the above equations,
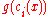 is the penalty function while
is the penalty function while 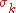 are the penalty coefficients. In each iteration k of the method, we increase the penalty coefficient
are the penalty coefficients. In each iteration k of the method, we increase the penalty coefficient 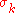 (e.g. by a factor of 10), solve the unconstrained problem and use the solution as the initial guess for the next iteration. Solutions of the successive unconstrained problems will eventually converge to the solution of the original constrained problem.
(e.g. by a factor of 10), solve the unconstrained problem and use the solution as the initial guess for the next iteration. Solutions of the successive unconstrained problems will eventually converge to the solution of the original constrained problem.
