Pelger-Huet anomaly
Encyclopedia
Pelger-Huet anomaly is a blood laminopathy
associated with the lamin B receptor
.
It is characterized by a white blood cell
type known as a neutrophil whose nucleus is hyposegmented.
 It is a genetic disorder
It is a genetic disorder
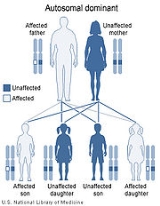
with an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. Heterozygotes are clinically normal, although their neutrophils may be mistaken for immature cells which may cause mistreatment in a clinical setting. Homozygotes tend to have neutrophils with rounded nuclei
that do have some functional problems.
(LBR) gene. The characteristic leukocyte appearance was first reported in 1928 by Pelger, a Dutch hematologist, who described leukocytes with dumbbell-shaped bilobed nuclei, a reduced number of nuclear segments, and coarse clumping of the nuclear chromatin. In 1931 Huet, a pediatrician, identified it as an inherited disorder.
It is a genetic disorder with an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. Heterozygotes are clinically normal, although their neutrophils may be mistaken for immature cells, which may cause mistreatment in a clinical setting. Homozygotes tend to have neutrophils with rounded nuclei
that do have some functional problems. Homozygous individuals inconsistently have skeletal anomalies such as post-axial polydactyly, short metacarpals, short upper limbs, short stature, or hyperkyphosis.
Identifying Pelger-Huët anomaly (PHA)is important to differentiate from bandemia
with a left-shifted peripheral blood smear and neutrophilic band forms and from an increase in young neutrophilic forms that can be observed in association with infection.
, multiple myeloma, enteroviral infections, malaria, muscular dystrophy, leukemoid reactions secondary to metastases to the bone marrow, and drug sensitivity, sulfa and valproate toxicities are examples. In some of these conditions, especially the drug-induced cases, identifying the change as Pelger-Huet anomaly is important because it obviates the need for further unnecessary testing for cancer.
Peripheral blood smear shows a predominance of neutrophils with bilobed nuclei which are composed of two nuclear masses connected with a thin filament of chromatin. It resembles the pince-nez glasses, so it is often referred to as pince-nez
appearance. Usually the congenital form is not associated with thrombocytopenia and leukopenia, so if these features are present more detailed search for myelodysplasia is warranted, as pseudo-pelger-Huet anomaly can be an early feature of myelodysplasia.
Laminopathy
Laminopathies are a group of rare genetic disorders caused by mutations in genes encoding proteins of the nuclear lamina. They are included in the more generic term nuclear envelopathies that was coined in 2000 for diseases associated with defects of the nuclear envelope...
associated with the lamin B receptor
Lamin B receptor
Lamin-B receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LBR gene.-Clinical significance:There is evidence tying it to Greenberg dysplasia and Pelger-Huet anomaly.-Interactions:Lamin B receptor has been shown to interact with CBX3 and CBX5....
.
It is characterized by a white blood cell
White blood cell
White blood cells, or leukocytes , are cells of the immune system involved in defending the body against both infectious disease and foreign materials. Five different and diverse types of leukocytes exist, but they are all produced and derived from a multipotent cell in the bone marrow known as a...
type known as a neutrophil whose nucleus is hyposegmented.

Genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is an illness caused by abnormalities in genes or chromosomes, especially a condition that is present from before birth. Most genetic disorders are quite rare and affect one person in every several thousands or millions....
with an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. Heterozygotes are clinically normal, although their neutrophils may be mistaken for immature cells which may cause mistreatment in a clinical setting. Homozygotes tend to have neutrophils with rounded nuclei
Cell nucleus
In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
that do have some functional problems.
Congenital Pelger-Huet anomaly
Is a benign dominantly inherited defect of terminal neutrophil differentiation secondary to mutations in the lamin B receptorLamin B receptor
Lamin-B receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LBR gene.-Clinical significance:There is evidence tying it to Greenberg dysplasia and Pelger-Huet anomaly.-Interactions:Lamin B receptor has been shown to interact with CBX3 and CBX5....
(LBR) gene. The characteristic leukocyte appearance was first reported in 1928 by Pelger, a Dutch hematologist, who described leukocytes with dumbbell-shaped bilobed nuclei, a reduced number of nuclear segments, and coarse clumping of the nuclear chromatin. In 1931 Huet, a pediatrician, identified it as an inherited disorder.
It is a genetic disorder with an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. Heterozygotes are clinically normal, although their neutrophils may be mistaken for immature cells, which may cause mistreatment in a clinical setting. Homozygotes tend to have neutrophils with rounded nuclei
Cell nucleus
In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
that do have some functional problems. Homozygous individuals inconsistently have skeletal anomalies such as post-axial polydactyly, short metacarpals, short upper limbs, short stature, or hyperkyphosis.
Identifying Pelger-Huët anomaly (PHA)is important to differentiate from bandemia
Bandemia
Bandemia refers to an excess of band cells released by the bone marrow into the blood. The ICD diagnosis code for bandemia is 288.66.It is a signifier of infection or inflammation....
with a left-shifted peripheral blood smear and neutrophilic band forms and from an increase in young neutrophilic forms that can be observed in association with infection.
Acquired or Pseudo-Pelger-Huet anomaly
Develops in the course of acute or chronic myelogenous leukemia and in myelodysplastic syndromes. In patients with these conditions, the pseudo–Pelger-Huët cells tend to appear late in the disease and often appear after considerable chemotherapy has been administered. The morphologic changes have also been described in myxedema associated with panhypopituitarism, vitamin B-12 and folate deficiencyFolate deficiency
Folate deficiency is a lack of folic acid in the diet and the signs are often subtle. Folate deficiency anemia is the medical name given for the condition. -Symptoms:Loss of appetite, and weight loss can occur...
, multiple myeloma, enteroviral infections, malaria, muscular dystrophy, leukemoid reactions secondary to metastases to the bone marrow, and drug sensitivity, sulfa and valproate toxicities are examples. In some of these conditions, especially the drug-induced cases, identifying the change as Pelger-Huet anomaly is important because it obviates the need for further unnecessary testing for cancer.
Peripheral blood smear shows a predominance of neutrophils with bilobed nuclei which are composed of two nuclear masses connected with a thin filament of chromatin. It resembles the pince-nez glasses, so it is often referred to as pince-nez
Pince-nez
Pince-nez are a style of spectacles, popular in the 19th century, which are supported without earpieces, by pinching the bridge of the nose. The name comes from French pincer, to pinch, and nez, nose....
appearance. Usually the congenital form is not associated with thrombocytopenia and leukopenia, so if these features are present more detailed search for myelodysplasia is warranted, as pseudo-pelger-Huet anomaly can be an early feature of myelodysplasia.

