
Oxygenation (medical)
Encyclopedia
Oxygenation occurs when oxygen
molecules enter the tissues
of the body. For example, blood
is oxygenated in the lung
s, where oxygen molecules travel from the air and into the blood. Oxygenation is commonly used to refer to medical oxygen saturation.
The opposite of the process is called de-oxygenation.
 In medicine
In medicine
, oxygen saturation (SO2), commonly referred to as "sats", measures the percentage of hemoglobin
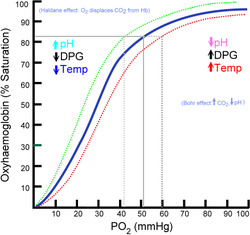
binding sites in the bloodstream occupied by oxygen. At low partial pressures of oxygen, most hemoglobin is deoxygenated. At around 90% (the value varies according to the clinical context) oxygen saturation increases according to an oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve and approaches 100% at partial oxygen pressures of >10 kPa. A pulse oximeter
relies on the light absorption characteristics of saturated hemoglobin to give an indication of oxygen saturation.
(which can also be caused by anemia
). Hypoxemia due to low SaO2 is indicated by cyanosis
.
Venous oxygen saturation (SvO2) is measured to see how much oxygen the body consumes. Under clinical treatment, a SvO2 below 60% indicates that the body is in lack of oxygen, and ischemic diseases occur. This measurement is often used under treatment with a heart-lung machine (extracorporeal circulation), and can give the perfusionist an idea of how much flow the patient needs to stay healthy.
Tissue oxygen saturation (StO2) can be measured by near infrared spectroscopy
. Although the measurements are still widely discussed, they give an idea of tissue oxygenation in various conditions.
Saturation of peripheral oxygen (SpO2) is an estimation of the oxygen saturation level usually measured with a pulse oximeter
device. It can be calculated with the pulse oximetry
according to the following formula:

(which can also be caused by anemia
). Hypoxemia due to low SaO2 is indicated by cyanosis
, but oxygen saturation does not directly reflect tissue oxygenation. The affinity of hemoglobin to oxygen may impair or enhance oxygen release at the tissue level. Oxygen is more readily released to the tissues when pH is decreased, body temperature is increased, arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) is increased, and 2,3-DPG levels (a byproduct of glucose metabolism also found in stored blood products) are increased. When the hemoglobin has greater affinity for oxygen, less is available to the tissues. Conditions such as increased pH, decreased temperature, decreased
PaCO2, and decreased 2,3-DPG will increase oxygen binding to the hemoglobin and limit its release to the tissue.
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
molecules enter the tissues
Tissue (biology)
Tissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning...
of the body. For example, blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
is oxygenated in the lung
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
s, where oxygen molecules travel from the air and into the blood. Oxygenation is commonly used to refer to medical oxygen saturation.
The opposite of the process is called de-oxygenation.
Oxygen saturation

Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
, oxygen saturation (SO2), commonly referred to as "sats", measures the percentage of hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells of all vertebrates, with the exception of the fish family Channichthyidae, as well as the tissues of some invertebrates...
binding sites in the bloodstream occupied by oxygen. At low partial pressures of oxygen, most hemoglobin is deoxygenated. At around 90% (the value varies according to the clinical context) oxygen saturation increases according to an oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve and approaches 100% at partial oxygen pressures of >10 kPa. A pulse oximeter
Pulse oximeter
A pulse oximeter is a medical device that indirectly monitors the oxygen saturation of a patient's blood and changes in blood volume in the skin, producing a photoplethysmograph. It is often attached to a medical monitor so staff can see a patient's oxygenation at all times...
relies on the light absorption characteristics of saturated hemoglobin to give an indication of oxygen saturation.
Measurements
An SaO2 (arterial oxygen saturation) value below 90% causes hypoxemiaHypoxemia
Hypoxemia is generally defined as decreased partial pressure of oxygen in blood, sometimes specifically as less than or causing hemoglobin oxygen saturation of less than 90%.-Distinction from anemia and hypoxia:...
(which can also be caused by anemia
Anemia
Anemia is a decrease in number of red blood cells or less than the normal quantity of hemoglobin in the blood. However, it can include decreased oxygen-binding ability of each hemoglobin molecule due to deformity or lack in numerical development as in some other types of hemoglobin...
). Hypoxemia due to low SaO2 is indicated by cyanosis
Cyanosis
Cyanosis is the appearance of a blue or purple coloration of the skin or mucous membranes due to the tissues near the skin surface being low on oxygen. The onset of cyanosis is 2.5 g/dL of deoxyhemoglobin. The bluish color is more readily apparent in those with high hemoglobin counts than it is...
.
Venous oxygen saturation (SvO2) is measured to see how much oxygen the body consumes. Under clinical treatment, a SvO2 below 60% indicates that the body is in lack of oxygen, and ischemic diseases occur. This measurement is often used under treatment with a heart-lung machine (extracorporeal circulation), and can give the perfusionist an idea of how much flow the patient needs to stay healthy.
Tissue oxygen saturation (StO2) can be measured by near infrared spectroscopy
Near infrared spectroscopy
Near-infrared spectroscopy is a spectroscopic method that uses the near-infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum...
. Although the measurements are still widely discussed, they give an idea of tissue oxygenation in various conditions.
Saturation of peripheral oxygen (SpO2) is an estimation of the oxygen saturation level usually measured with a pulse oximeter
Pulse oximeter
A pulse oximeter is a medical device that indirectly monitors the oxygen saturation of a patient's blood and changes in blood volume in the skin, producing a photoplethysmograph. It is often attached to a medical monitor so staff can see a patient's oxygenation at all times...
device. It can be calculated with the pulse oximetry
Pulse oximetry
Pulse oximetry is a non-invasive method allowing the monitoring of the oxygenation of a patient's hemoglobin.A sensor is placed on a thin part of the patient's body, usually a fingertip or earlobe, or in the case of an infant, across a foot....
according to the following formula:

Medical significance
Healthy individuals at sea level usually exhibit oxygen saturation values between 96% and 99%. An SaO2 (arterial oxygen saturation) value below 90% causes hypoxemiaHypoxemia
Hypoxemia is generally defined as decreased partial pressure of oxygen in blood, sometimes specifically as less than or causing hemoglobin oxygen saturation of less than 90%.-Distinction from anemia and hypoxia:...
(which can also be caused by anemia
Anemia
Anemia is a decrease in number of red blood cells or less than the normal quantity of hemoglobin in the blood. However, it can include decreased oxygen-binding ability of each hemoglobin molecule due to deformity or lack in numerical development as in some other types of hemoglobin...
). Hypoxemia due to low SaO2 is indicated by cyanosis
Cyanosis
Cyanosis is the appearance of a blue or purple coloration of the skin or mucous membranes due to the tissues near the skin surface being low on oxygen. The onset of cyanosis is 2.5 g/dL of deoxyhemoglobin. The bluish color is more readily apparent in those with high hemoglobin counts than it is...
, but oxygen saturation does not directly reflect tissue oxygenation. The affinity of hemoglobin to oxygen may impair or enhance oxygen release at the tissue level. Oxygen is more readily released to the tissues when pH is decreased, body temperature is increased, arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) is increased, and 2,3-DPG levels (a byproduct of glucose metabolism also found in stored blood products) are increased. When the hemoglobin has greater affinity for oxygen, less is available to the tissues. Conditions such as increased pH, decreased temperature, decreased
PaCO2, and decreased 2,3-DPG will increase oxygen binding to the hemoglobin and limit its release to the tissue.

