Organogenesis
Encyclopedia
Embryogenesis
Embryogenesis is the process by which the embryo is formed and develops, until it develops into a fetus.Embryogenesis starts with the fertilization of the ovum by sperm. The fertilized ovum is referred to as a zygote...
, organogenesis (organo-genesis, compound of the Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
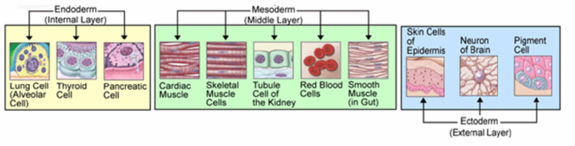
words όργανον "that with which one works", and γένεσις "origin, creation, generation") is the process by which the ectoderm
Ectoderm
The "ectoderm" is one of the three primary germ cell layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the mesoderm and endoderm , with the ectoderm as the most exterior layer...
, endoderm
Endoderm
Endoderm is one of the three primary germ cell layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm and mesoderm , with the endoderm as the intermost layer...
, and mesoderm
Mesoderm
In all bilaterian animals, the mesoderm is one of the three primary germ cell layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm and endoderm , with the mesoderm as the middle layer between them.The mesoderm forms mesenchyme , mesothelium, non-epithelial blood corpuscles and...
develop into the internal organs of the organism. Internal organs initiate development in humans within the 3rd to 8th weeks in utero. The germ layer
Germ layer
A germ layer, occasionally referred to as a germinal epithelium, is a group of cells, formed during animal embryogenesis. Germ layers are particularly pronounced in the vertebrates; however, all animals more complex than sponges produce two or three primary tissue layers...
s in organogenesis differ by three processes: folds, splits, and condensation. Developing early during this stage in chordate
Chordate
Chordates are animals which are either vertebrates or one of several closely related invertebrates. They are united by having, for at least some period of their life cycle, a notochord, a hollow dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, an endostyle, and a post-anal tail...
animals are the neural tube
Neural tube
In the developing vertebrate, the neural tube is the embryo's precursor to the central nervous system, which comprises the brain and spinal cord...
and notochord
Notochord
The notochord is a flexible, rod-shaped body found in embryos of all chordates. It is composed of cells derived from the mesoderm and defines the primitive axis of the embryo. In some chordates, it persists throughout life as the main axial support of the body, while in most vertebrates it becomes...
. Vertebrate
Vertebrate
Vertebrates are animals that are members of the subphylum Vertebrata . Vertebrates are the largest group of chordates, with currently about 58,000 species described. Vertebrates include the jawless fishes, bony fishes, sharks and rays, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and birds...
animals all differentiate from the gastrula the same way. Vertebrates develop a neural crest
Neural crest
Neural crest cells are a transient, multipotent, migratory cell population unique to vertebrates that gives rise to a diverse cell lineage including melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage and bone, smooth muscle, peripheral and enteric neurons and glia....
that differentiates into many structures, including some bones, muscles, and components of the peripheral nervous system
Peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system consists of the nerves and ganglia outside of the brain and spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the central nervous system to the limbs and organs. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the bone of spine and skull, or by the blood–brain...
. The coelom
Coelom
The coelom is a fluid-filled cavity formed within the mesoderm. Coeloms developed in triploblasts but were subsequently lost in several lineages. Loss of coelom is correlated with reduction in body size...
of the body forms from a split of the mesoderm along the somite axis.
In plants, organogenesis can occur from totipotent callus cells.
See also
- EctodermEctodermThe "ectoderm" is one of the three primary germ cell layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the mesoderm and endoderm , with the ectoderm as the most exterior layer...
- EmbryogenesisEmbryogenesisEmbryogenesis is the process by which the embryo is formed and develops, until it develops into a fetus.Embryogenesis starts with the fertilization of the ovum by sperm. The fertilized ovum is referred to as a zygote...
- EndodermEndodermEndoderm is one of the three primary germ cell layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm and mesoderm , with the endoderm as the intermost layer...
- Eye developmentEye developmentThe eye develops from the neural tube, the epidermis, and the periocular mesenchyme, which receives contributions from both the neural crest and mesoderm lineages.-Sequential inductions:...
- Germ layerGerm layerA germ layer, occasionally referred to as a germinal epithelium, is a group of cells, formed during animal embryogenesis. Germ layers are particularly pronounced in the vertebrates; however, all animals more complex than sponges produce two or three primary tissue layers...
- Germ line developmentGerm line developmentThe cells that give rise to the gametes are often set aside during cleavage. During development, these cells will differentiate into primordial germ cells, migrate to the location of the gonad, and form the germ line of the animal....
- Heart developmentHeart developmentThe heart is the first functional organ in a vertebrate embryo. There are 5 stages to heart development.- Specification of cardiac precursor cells :...
- HistogenesisHistogenesisHistogenesis is the formation of different tissues from undifferentiated cells. These cells are constituents of three primary germ layers, the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm...
- Limb developmentLimb developmentLimb development in tetrapods — animals with four limbs — is an area of active research in developmental biology. Limb formation begins in the limb field, as a limb "bud." Fibroblast growth factor induces formation of an organizer, called the apical ectodermal ridge , which guides further...
- MesodermMesodermIn all bilaterian animals, the mesoderm is one of the three primary germ cell layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm and endoderm , with the mesoderm as the middle layer between them.The mesoderm forms mesenchyme , mesothelium, non-epithelial blood corpuscles and...
- MorphogenesisMorphogenesisMorphogenesis , is the biological process that causes an organism to develop its shape...

