
Organogallium chemistry
Encyclopedia

Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
of organometallic compounds containing a carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
to gallium
Gallium
Gallium is a chemical element that has the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Elemental gallium does not occur in nature, but as the gallium salt in trace amounts in bauxite and zinc ores. A soft silvery metallic poor metal, elemental gallium is a brittle solid at low temperatures. As it liquefies...
(Ga) chemical bond
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction...
. Despite their high toxicity organogallium compounds have some use in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the construction of organic compounds via organic reactions. Organic molecules can often contain a higher level of complexity compared to purely inorganic compounds, so the synthesis of organic compounds has...
. The compound trimethylgallium
Trimethylgallium
Trimethylgallium, Ga3, often abbreviated to TMG or TMGa, is the preferred metalorganic source of gallium for metalorganic vapour phase epitaxy of gallium-containing compound semiconductors, such as GaAs, GaN, GaP, GaSb, InGaAs, InGaN, AlGaInP, InGaP and AlInGaNP.-Properties:TMG is a clear,...
is of some relevance to MOCVD as a precursor to gallium arsenide:
- Ga(CH3)3 + AsH3 → GaAs + 3CH4
with arsine
Arsine
Arsine is the chemical compound with the formula AsH3. This flammable, pyrophoric, and highly toxic gas is one of the simplest compounds of arsenic...
at 700 °C. Gallium trichloride
Gallium trichloride
Gallium trichloride is the chemical compound with the formula GaCl3. Solid gallium trichloride exists as a dimer with the formula Ga2Cl6. It is colourless and soluble in virtually all solvents, which is unusual for a metal halide. It is the main precursor to most derivatives of gallium and a...
is an important reagent for the introduction of gallium into organic compounds.
The main gallium oxidation state
Oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state is an indicator of the degree of oxidation of an atom in a chemical compound. The formal oxidation state is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Oxidation states are typically represented by...
is Ga(III) as in all higher group 13 elements notably aluminium
Aluminium
Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances....
.
Organogallium(III) chemistry
Compounds of the type R3Ga are monomeric. Lewis acidityLewis acid
]The term Lewis acid refers to a definition of acid published by Gilbert N. Lewis in 1923, specifically: An acid substance is one which can employ a lone pair from another molecule in completing the stable group of one of its own atoms. Thus, H+ is a Lewis acid, since it can accept a lone pair,...
decreases in the order Al > Ga > In and as a result organogallium compound do not form bridged dimers as organoaluminum compounds do. Organogallium compounds are also less reactive then organoaluminum compounds.
Organogallium compounds can be synthesized by transmetallation, for example the reaction of gallium metal with dimethylmercury
Dimethylmercury
Dimethylmercury is an organomercury compound. This colorless liquid is one of the strongest known neurotoxins. It is described as having a slightly sweet smell, although inhaling enough vapor to detect its odor would be hazardous....
:
- 2Ga + 2Me2Hg → 2Me3Ga + 3 Hg
or via organolithium compounds or Grignard
Grignard
Grignard can be a French last name, or refers to an organic chemical reaction.* Victor Grignard, a French organic chemist.* The Grignard Company a chemical manufacturer.* Grignard reaction, an organic chemical reaction developed by Victor Grignard....
s:
- GaCl3 + 3MeMgBr → Me3Ga + 3MgBrCl
The electron-deficient nature of gallium can be removed by complex formation, for example
- Me2GaCl + NH3 → [Me2Ga(NH3)Cl]+Cl-
Pi complex formation with alkyne
Alkyne
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that have a triple bond between two carbon atoms, with the formula CnH2n-2. Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name acetylene also refers specifically to C2H2, known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature...
s is also known.
Organogallium compounds are reagents or intermediates in several classes of organic reactions:
- Barbier-typeBarbier reactionThe Barbier reaction is an organic reaction between an alkyl halide and a carbonyl group as an electrophilic substrate in the presence of magnesium, aluminium, zinc, indium, tin or its salts. The reaction product is a primary, secondary or tertiary alcohol...
reactions with elemental gallium, allylic substrates and carbonyl compounds - Carbometallation (carbogallation) reactions
Higher group 13 organometallic chemistry
The chemistry of organoindium (In) and organothallium (Tl) compounds parallel that of organogallium in many regards. IndiumIndium
Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. This rare, very soft, malleable and easily fusible post-transition metal is chemically similar to gallium and thallium, and shows the intermediate properties between these two...
and thallium
Thallium
Thallium is a chemical element with the symbol Tl and atomic number 81. This soft gray poor metal resembles tin but discolors when exposed to air. The two chemists William Crookes and Claude-Auguste Lamy discovered thallium independently in 1861 by the newly developed method of flame spectroscopy...
in oxidation state
Oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state is an indicator of the degree of oxidation of an atom in a chemical compound. The formal oxidation state is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Oxidation states are typically represented by...
+1 are more common, for example the metallocene
Metallocene
A metallocene is a compound typically consisting of two cyclopentadienyl anions bound to a metal center in the oxidation state II, with the resulting general formula 2M. Closely related to the metallocenes are the metallocene derivatives, e.g. titanocene dichloride, vanadocene dichloride...
s cyclopentadienylindium(I)
Cyclopentadienylindium(I)
Cyclopentadienylindium, C5H5In, is an organoindium compound containing indium in the +1 oxidation state. Commonly abbreviated to CpIn, it is a cyclopentadienyl complex with a half-sandwich structure....
and cyclopentadienyl thallium
Cyclopentadienyl thallium
Cyclopentadienylthallium, also known as thallium cyclopentadienide, is an organothallium compound with formula C5H5Tl. This light yellow solid is insoluble in most organic solvents, but sublimes readily, and is useful as a precursor to transition metal and main group Cp compounds, as well as...
. Trimethylindium
Trimethylindium
Trimethylindium , In3, is the preferred metalorganic source of Indium for metalorganic vapour phase epitaxy of indium-containing compound semiconductors, such as InP, InAs, InN, InSb, GaInAs, InGaN, AlGaInP, AlInP, AlInGaNP etc. TMI is a white, crystalline and sublimable solid, with melting point...
is important in the semiconductor industry. A special thallium feature is electrophilic
Electrophilic substitution
Electrophilic substitution reactions are chemical reactions in which an electrophile displaces a group in a compound, typically but not always hydrogen. Electrophilic aromatic substitution is characteristic of aromatic compounds and is an important way of introducing functional groups onto benzene...
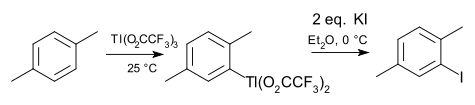
thallation of arene compounds, reminiscent of mercuration (the group 12 neighbor). A common reagent for this purpose is thalium(III) trifluoroacetate. The intermediate arylthallium bisfluoroacetate can be isolated and converted to an aryl halide, aryl cyanide, aryl thiol or nitroarene. An example is the iodation of para-xylene .
 :
:
See also
- Chemical bonds of carbon with other elements in the periodic table:

