
Optical sectioning
Encyclopedia
Optical sectioning is the process by which a suitably designed microscope
can produce clear images of a focal planes deep within a thick sample. This is used to reduce the need for thin section
ing using instruments such as the microtome
. Many different techniques for optical sectioning are used and several microscopy
techniques are specifically designed to improve the quality of optical sectioning.
Good optical sectioning, often referred to as good depth or z resolution, is popular in modern microscopy as it allows the three dimensional reconstruction of a sample from images captured at different focal planes.
) producing a clear image of the plane of the sample the microscope is focused on. Unfortunately a microscope is not this specific and light from sources outside the focal plane also reaches the detector; in a thick sample there may be a significant amount of material, and so spurious signal, between the focal plane and the objective lens.
With no modification to the microscope, i.e. with a simple wide field light microscope, the quality of optical sectioning is governed by the same physics as the depth of field
effect in photography
. For a high numerical aperture
lens, equivalent to a wide aperture
, the depth of field is small (shallow focus
) and gives good optical sectioning. High magnification
objective lenses typically have higher numerical apertures (and so better optical sectioning) than low magnification objectives. Oil immersion
objectives typically have even larger numerical apertures so improved optical sectioning.
The resolution
in the depth direction (the "z resolution") of a standard wide field microscope depends on the numerical aperture and the wavelength of the light and can be approximated as:
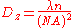 where λ is the wavelength, n the refractive index of the objective lens immersion media and NA the numerical aperture.
where λ is the wavelength, n the refractive index of the objective lens immersion media and NA the numerical aperture.
In comparison the lateral resolution can be approximated as:
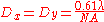
limits.
Differential interference contrast (DIC) provides modest improvements to optical sectioning. In DIC the sample is effectively illuminated by two slightly offset light sources which then interfere to produce an image resulting from the phase differences of the two sources. As the offset in the light sources is small the only difference in phase results from the material close to the focal plane.
Confocal microscopy
uses a scanning point or points of light to illuminate the sample. In conjunction with a pinhole at a conjugate focal plane
this acts fo filter out light from sources outside the focal plane to improve optical sectioning.
Dual and multi-photon excitation techniques take advantage of the fact that fluorophores can be excited not just by a single photon
of the correct energy
but also by multiple photons, which together provide the correct energy. The additional "concentration
"-dependent effect of requiring multiple photons to simultaneously interact with a fluorophore gives stimulation only very close to the focal plane. These techniques are normally used in conjunction with confocal microscopy.
Further improvements in optical sectioning are under active development, these principally work through methods to circumvent the diffraction limit of light. Examples include single photon interferometry
through two objective lenses to give extremely accurate depth information about a single fluorophore and three dimensional structured illumination microscopy.
The optical sectioning of normal wide field microscopes can be improved significantly by deconvolution
, an image processing technique to remove blur from the image according to a measured or calculated point spread function
.
and electron microscope
s typically have a large depth of field (poor optical sectioning) and so thin sectioning of samples is still widely used.
Scanning probe microscopes and scanning electron microscope
s cannot do any form of optical sectioning as these microscopes only interact with the surface of a sample. Total internal reflection microscopy is a fluorescent microscopy technique, which intentionally restricts observation to either the top or bottom surfaces of a sample, but with extremely high depth resolution.
Microscope
A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy...
can produce clear images of a focal planes deep within a thick sample. This is used to reduce the need for thin section
Thin section
In optical mineralogy and petrography, a thin section is a laboratory preparation of a rock, mineral, soil, pottery, bones, or even metal sample for use with a polarizing petrographic microscope, electron microscope and electron microprobe. A thin sliver of rock is cut from the sample with a...
ing using instruments such as the microtome
Microtome
A microtome is a sectioning instrument that allows for the cutting of extremely thin slices of material, known as sections. Microtomes are an important device in microscopy preparation, allowing for the preparation of samples for observation under transmitted light or electron radiation...
. Many different techniques for optical sectioning are used and several microscopy
Microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view samples and objects that cannot be seen with the unaided eye...
techniques are specifically designed to improve the quality of optical sectioning.
Good optical sectioning, often referred to as good depth or z resolution, is popular in modern microscopy as it allows the three dimensional reconstruction of a sample from images captured at different focal planes.
Optical sectioning in traditional light microscopes
In an ideal microscope, only light from the focal plane would be allowed to reach the detector (typically an observer or a CCDCharge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device is a device for the movement of electrical charge, usually from within the device to an area where the charge can be manipulated, for example conversion into a digital value. This is achieved by "shifting" the signals between stages within the device one at a time...
) producing a clear image of the plane of the sample the microscope is focused on. Unfortunately a microscope is not this specific and light from sources outside the focal plane also reaches the detector; in a thick sample there may be a significant amount of material, and so spurious signal, between the focal plane and the objective lens.
With no modification to the microscope, i.e. with a simple wide field light microscope, the quality of optical sectioning is governed by the same physics as the depth of field
Depth of field
In optics, particularly as it relates to film and photography, depth of field is the distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene that appear acceptably sharp in an image...
effect in photography
Photography
Photography is the art, science and practice of creating durable images by recording light or other electromagnetic radiation, either electronically by means of an image sensor or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film...
. For a high numerical aperture
Numerical aperture
In optics, the numerical aperture of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, NA has the property that it is constant for a beam as it goes from one...
lens, equivalent to a wide aperture
Aperture
In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture of an optical system is the opening that determines the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane. The aperture determines how collimated the admitted rays are,...
, the depth of field is small (shallow focus
Shallow focus
Shallow focus is a photographic and cinematographic technique incorporating a small depth of field. In shallow focus one plane of the image is in focus while the rest is out of focus. Shallow focus is typically used to emphasize one part of the image over another...
) and gives good optical sectioning. High magnification
Magnification
Magnification is the process of enlarging something only in appearance, not in physical size. This enlargement is quantified by a calculated number also called "magnification"...
objective lenses typically have higher numerical apertures (and so better optical sectioning) than low magnification objectives. Oil immersion
Oil immersion
In light microscopy, oil immersion is a technique used to increase the resolution of a microscope. This is achieved by immersing both the objective lens and the specimen in a transparent oil of high refractive index, thereby increasing the numerical aperture of the objective lens.Immersion oils are...
objectives typically have even larger numerical apertures so improved optical sectioning.
The resolution
Optical resolution
Optical resolution describes the ability of an imaging system to resolve detail in the object that is being imaged.An imaging system may have many individual components including a lens and recording and display components...
in the depth direction (the "z resolution") of a standard wide field microscope depends on the numerical aperture and the wavelength of the light and can be approximated as:
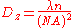 where λ is the wavelength, n the refractive index of the objective lens immersion media and NA the numerical aperture.
where λ is the wavelength, n the refractive index of the objective lens immersion media and NA the numerical aperture.In comparison the lateral resolution can be approximated as:
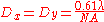
Bright-field light microscopy
Beyond increasing numerical aperture, there are few techniques available to improve optical sectioning in bright-field light microscopy. Most microscopes with oil immersion objectives are reaching the limits of numerical aperture possible due to refractionRefraction
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its speed. It is essentially a surface phenomenon . The phenomenon is mainly in governance to the law of conservation of energy. The proper explanation would be that due to change of medium, the phase velocity of the wave is changed...
limits.
Differential interference contrast (DIC) provides modest improvements to optical sectioning. In DIC the sample is effectively illuminated by two slightly offset light sources which then interfere to produce an image resulting from the phase differences of the two sources. As the offset in the light sources is small the only difference in phase results from the material close to the focal plane.
Fluorescence microscopy
In fluorescence microscopy objects out of the focal plane only interfere with the image if they are illuminated and fluoresce. This adds an extra way in which optical sectioning can be improved by making illumination specific to only the focal plane.Confocal microscopy
Confocal microscopy
Confocal microscopy is an optical imaging technique used to increase optical resolution and contrast of a micrograph by using point illumination and a spatial pinhole to eliminate out-of-focus light in specimens that are thicker than the focal plane. It enables the reconstruction of...
uses a scanning point or points of light to illuminate the sample. In conjunction with a pinhole at a conjugate focal plane
Conjugate focal plane
In optics, a conjugate focal plane of a given plane, P, is a plane P′ such that points on P are imaged at P′. In a telescope, the subject focal plane is at infinity and the conjugate image plane, at which the image sensor is placed, is said to be an infinite conjugate...
this acts fo filter out light from sources outside the focal plane to improve optical sectioning.
Dual and multi-photon excitation techniques take advantage of the fact that fluorophores can be excited not just by a single photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
of the correct energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
but also by multiple photons, which together provide the correct energy. The additional "concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
"-dependent effect of requiring multiple photons to simultaneously interact with a fluorophore gives stimulation only very close to the focal plane. These techniques are normally used in conjunction with confocal microscopy.
Further improvements in optical sectioning are under active development, these principally work through methods to circumvent the diffraction limit of light. Examples include single photon interferometry
Interferometry
Interferometry refers to a family of techniques in which electromagnetic waves are superimposed in order to extract information about the waves. An instrument used to interfere waves is called an interferometer. Interferometry is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy,...
through two objective lenses to give extremely accurate depth information about a single fluorophore and three dimensional structured illumination microscopy.
The optical sectioning of normal wide field microscopes can be improved significantly by deconvolution
Deconvolution
In mathematics, deconvolution is an algorithm-based process used to reverse the effects of convolution on recorded data. The concept of deconvolution is widely used in the techniques of signal processing and image processing...
, an image processing technique to remove blur from the image according to a measured or calculated point spread function
Point spread function
The point spread function describes the response of an imaging system to a point source or point object. A more general term for the PSF is a system's impulse response, the PSF being the impulse response of a focused optical system. The PSF in many contexts can be thought of as the extended blob...
.
Other
Optical sectioning is underdeveloped in non-light microscopes. X-rayX-ray microscope
An X-ray microscope uses electromagnetic radiation in the soft X-ray band to produce images of very small objects.Unlike visible light, X-rays do not reflect or refract easily, and they are invisible to the human eye. Therefore the basic process of an X-ray microscope is to expose film or use a...
and electron microscope
Electron microscope
An electron microscope is a type of microscope that uses a beam of electrons to illuminate the specimen and produce a magnified image. Electron microscopes have a greater resolving power than a light-powered optical microscope, because electrons have wavelengths about 100,000 times shorter than...
s typically have a large depth of field (poor optical sectioning) and so thin sectioning of samples is still widely used.
Scanning probe microscopes and scanning electron microscope
Scanning electron microscope
A scanning electron microscope is a type of electron microscope that images a sample by scanning it with a high-energy beam of electrons in a raster scan pattern...
s cannot do any form of optical sectioning as these microscopes only interact with the surface of a sample. Total internal reflection microscopy is a fluorescent microscopy technique, which intentionally restricts observation to either the top or bottom surfaces of a sample, but with extremely high depth resolution.
Alternatives
The primary alternatives to optical sectioning are:- Thin sectionThin sectionIn optical mineralogy and petrography, a thin section is a laboratory preparation of a rock, mineral, soil, pottery, bones, or even metal sample for use with a polarizing petrographic microscope, electron microscope and electron microprobe. A thin sliver of rock is cut from the sample with a...
ing of the sample, for example as used in histologyHistological sectionHistological section refers to thin slices of tissue applied to a microscopic slide, usually around 5 to 10 micrometres thick, which are viewed under a microscope...
. - TomographyTomographyTomography refers to imaging by sections or sectioning, through the use of any kind of penetrating wave. A device used in tomography is called a tomograph, while the image produced is a tomogram. The method is used in radiology, archaeology, biology, geophysics, oceanography, materials science,...
, which is particularly well developed for transmission electron microscopyElectron tomographyElectron Tomography is a tomography technique for obtaining detailed 3D structures of subcellular macromolecular objects. Electron tomography is an extension of traditional transmission electron microscopy and uses a transmission electron microscope to collect the data...
.

