Operating reserve
Encyclopedia
Grid (electricity)
An electrical grid is a vast, interconnected network for delivering electricity from suppliers to consumers. It consists of three main components: 1) generating plants that produce electricity from combustible fuels or non-combustible fuels ; 2) transmission lines that carry electricity from power...
, the operating reserve is the generating capacity available to the system operator within a short interval of time to meet demand in case a generator
Electrical generator
In electricity generation, an electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. A generator forces electric charge to flow through an external electrical circuit. It is analogous to a water pump, which causes water to flow...
goes down or there is another disruption to the supply. Most power systems are designed so that, under normal conditions, the operating reserve is always at least the capacity of the largest generator plus a fraction of the peak load.
The operating reserve is made up of the spinning reserve as well as the non-spinning or supplemental reserve:
- The spinning reserve is the extra generating capacity that is available by increasing the power output of generators that are already connected to the power system. For most generators, this increase in power output is achieved by increasing the torqueTorqueTorque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
applied to the turbine's rotorTurbineA turbine is a rotary engine that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work.The simplest turbines have one moving part, a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades, or the blades react to the flow, so that they move and...
.
- The non-spinning or supplemental reserve is the extra generating capacity that is not currently connected to the system but can be brought online after a short delay. In isolated power systems, this typically equates to the power available from fast-start generators. However, in interconnected power systems, this may include the power available on short notice by importing power from other systems or retracting power that is currently being exported to other systems.
Generators that intend to provide either spinning and non-spinning reserve should be able to reach their promised capacity within ten or so minutes. Most power system guidelines require a significant fraction of their operating reserve to come from spinning reserve. This is because the spinning reserve is slightly more reliable (it doesn't suffer from start-up issues) and can respond immediately whereas with non-spinning reserve generators there is a delay as the generator starts-up offline.
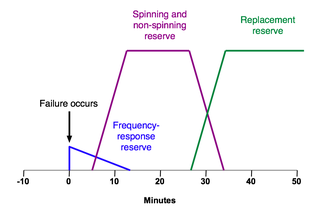
In addition, there are two other kinds of reserve power that are often discussed in combination with the operating reserve: the frequency-response reserve and the replacement reserve.
- The frequency-response reserve (also known as regulating reserve) is provided as an automatic reaction to a loss in supply. It occurs because immediately following a loss of supply, the generators slow down due to the increased load. To combat this slowing, many generators have a governorGovernor (device)A governor, or speed limiter, is a device used to measure and regulate the speed of a machine, such as an engine. A classic example is the centrifugal governor, also known as the Watt or fly-ball governor, which uses a rotating assembly of weights mounted on arms to determine how fast the engine...
. By helping the generators to speed up, these governors provide a small boost to both the output frequency and the power of each generator. However, because the frequency-response reserve is often small and not at the discretion of the system operator it is not considered part of the operating reserve.
- The replacement reserve (also known as contingency reserve) is reserve power provided by generators that require a longer start-up time (typically thirty to sixty minutes). It is used to relieve the generators providing the spinning or non-spinning reserve and thus restore the operating reserve (confusingly the replacement reserve is sometimes known as the 30 or 60-minute operating reserve).
The time periods over which all four kinds of reserve power operate is illustrated in the diagram that accompanies this article.

