
Open circuit test
Encyclopedia
The Open circuit test, or "no-load test", is one of the methods used in electrical engineering
to determine the no load impedance
in the excitation branch of a real transformer
.
is connected to the primary. An ammeter
is connected in series with the primary winding. A voltmeter
is optional since the applied voltage is same as the voltmeter reading. Rated voltage is applied at primary.
If the applied voltage is normal voltage then normal flux will be set up. As the Iron loss is a function of applied voltage, normal iron loss will occur. Hence the iron loss is maximum at rated voltage. This maximum iron loss is measured using the wattmeter. Since the impedance of the series
winding of the transformer is very small compared to that of the excitation branch, all of the input voltage is dropped
across the excitation branch. Thus the wattmeter measures only the iron loss.
Since the secondary of the transformer is open, the primary draws only no load current. This no load current is negligible. As the copper losses depend on current they can be neglected.
Current
, voltage
and power
are measured at the primary winding to ascertain the admittance
and power factor angle
.
Another method of determining the series impedance of a real transformer is the short circuit test
.
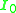 is very small.
is very small.
If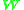 is the wattmeter reading then,
is the wattmeter reading then,
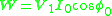
The above equation can be rewritten as,
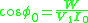
Thus,
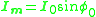
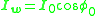
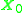 and
and 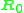 can be calculated as,
can be calculated as,
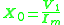
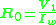
Thus,
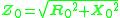
or
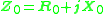

The conductance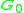 can be calculated as,
can be calculated as,
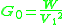
Hence the susceptance,
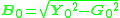
or
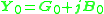
Here,
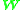 is the wattmeter reading
is the wattmeter reading
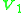 is the applied rated voltage
is the applied rated voltage
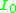 is the no load current
is the no load current
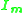 is the magnetizing component of no load current
is the magnetizing component of no load current
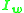 is the core loss component of no load current
is the core loss component of no load current
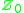 is the exciting impedance
is the exciting impedance
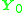 is the exciting admittance
is the exciting admittance
Electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
to determine the no load impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
in the excitation branch of a real transformer
Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
.
Method
The secondary of the transformer is left open-circuited. A wattmeterWattmeter
The wattmeter is an instrument for measuring the electric power in watts of any given circuit.An instrument which measures electrical energy in watt hours is essentially a wattmeter which accumulates or averages readings; many such instruments measure and can display many parameters and can be...
is connected to the primary. An ammeter
Ammeter
An ammeter is a measuring instrument used to measure the electric current in a circuit. Electric currents are measured in amperes , hence the name. Instruments used to measure smaller currents, in the milliampere or microampere range, are designated as milliammeters or microammeters...
is connected in series with the primary winding. A voltmeter
Voltmeter
A voltmeter is an instrument used for measuring electrical potential difference between two points in an electric circuit. Analog voltmeters move a pointer across a scale in proportion to the voltage of the circuit; digital voltmeters give a numerical display of voltage by use of an analog to...
is optional since the applied voltage is same as the voltmeter reading. Rated voltage is applied at primary.
If the applied voltage is normal voltage then normal flux will be set up. As the Iron loss is a function of applied voltage, normal iron loss will occur. Hence the iron loss is maximum at rated voltage. This maximum iron loss is measured using the wattmeter. Since the impedance of the series
Series and parallel circuits
Components of an electrical circuit or electronic circuit can be connected in many different ways. The two simplest of these are called series and parallel and occur very frequently. Components connected in series are connected along a single path, so the same current flows through all of the...
winding of the transformer is very small compared to that of the excitation branch, all of the input voltage is dropped
Voltage drop
Voltage drop is the reduction in voltage in the passive elements of an electrical circuit. Voltage drops across conductors, contacts, connectors and source internal resistances are undesired as they reduce the supplied voltage while voltage drops across loads and other electrical and electronic...
across the excitation branch. Thus the wattmeter measures only the iron loss.
Since the secondary of the transformer is open, the primary draws only no load current. This no load current is negligible. As the copper losses depend on current they can be neglected.
Current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
, voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
and power
Electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.-Circuits:Electric power, like mechanical power, is represented by the letter P in electrical equations...
are measured at the primary winding to ascertain the admittance
Admittance
In electrical engineering, the admittance is a measure of how easily a circuit or device will allow a current to flow. It is defined as the inverse of the impedance . The SI unit of admittance is the siemens...
and power factor angle
Power factor
The power factor of an AC electric power system is defined as the ratio of the real power flowing to the load over the apparent power in the circuit, and is a dimensionless number between 0 and 1 . Real power is the capacity of the circuit for performing work in a particular time...
.
Another method of determining the series impedance of a real transformer is the short circuit test
Short circuit test
The purpose of a short circuit test is to determine the series branch parameters of the equivalent circuit. As the name suggests, in this test primary applied voltage, the current and power input are measured keeping the secondary terminals short circuited. Let these values be Vsc, Isc and Wsc...
.
Calculations
The current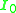 is very small.
is very small.If
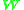 is the wattmeter reading then,
is the wattmeter reading then,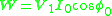
The above equation can be rewritten as,
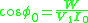
Thus,
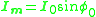
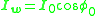
Impedance
By using the above equations,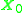 and
and 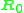 can be calculated as,
can be calculated as,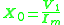
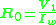
Thus,
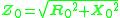
or
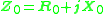
Admittance
The admittance is the inverse of impedance. Therefore,
The conductance
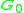 can be calculated as,
can be calculated as,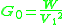
Hence the susceptance,
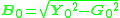
or
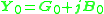
Here,
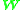 is the wattmeter reading
is the wattmeter reading 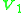 is the applied rated voltage
is the applied rated voltage 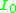 is the no load current
is the no load current 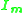 is the magnetizing component of no load current
is the magnetizing component of no load current 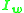 is the core loss component of no load current
is the core loss component of no load current 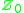 is the exciting impedance
is the exciting impedance 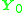 is the exciting admittance
is the exciting admittance

