
OT-64 SKOT
Encyclopedia
The OT-64 SKOT is an amphibious
armored personnel carrier (8x8
), developed jointly by Poland
and Czechoslovakia
(ČSSR
) well into the 1960s.
from World War II
. The first prototype
was built in 1959. In 1961 the first sample series were built and starting from October 1963 the vehicles were produced in Lublin
, Poland by Fabryka Samochodów Ciężarowych
. Czechoslovakia
supplied the driveline components, i.e. the engine, transmission and axles.
The first production vehicles were delivered in 1964 to both the Polish Army and Czechoslovak Army
and many are still in use today. Both Polish and Czech units are gradually replaced by newer vehicles. Czech units are scheduled to be replaced between 2007 and 2012.
 The OT-64's engine, transmission, suspension and axles were produced in Czechoslovakia
The OT-64's engine, transmission, suspension and axles were produced in Czechoslovakia
. The engine was produced by Tatra
and the semiautomatic transmission(shift now,transfer gear by pushing clutch later) by Praga
. The armored hull and weapons were produced in Poland
.
The OT-64 was the answer to the Soviet BTR-60
. Contrary to this the OT-64 used a diesel set in place of a petrol engine. That diminished the danger of fire and at the same time increased the range. The main advantage in relation to the Russian counterpart was the full-armored interior. The entrance is at the rear of the vehicle via twin doors. The OT-64 was air-transportable and amphibious
. For the amphibious
drive the vehicle used two propellers installed at the back. The OT-64 had an NBC protection facility and night-vision equipment. It also has central inflation for all wheels which can be controlled by driver during a drive.
Several variants were built. Some OT-64 were re-equipped for air defense or built as tank hunters. The latter used the AT-3 Sagger
missile as a weapon.






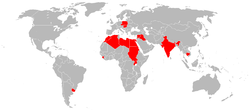 - 400 OT-64 SKOT and BTR-60
- 400 OT-64 SKOT and BTR-60
. - 40, however probably less are fully operational as only 140 of Cambodia's 266 APCs are fully operational. All the OT-64 APCs have apparently gone to the Phnom Penh reserve force and some are used by military police. - 28 OT-64 APCs in service as of 1 January 2008. They are scheduled to be replaced by new vehicles between 2007 and 2012. - 300 - On beginning of the 1990s, SKOT's were gradually withdrawn from the Polish Army, and consists of around 300-400, in particular in the versions R-2AM/AMT (for artillery units) and R-3M, engineer's, school. The SKOT is being replaced by the KTO Rosomak
. There were 110 SKOT APCs and SKOT based vehicles in service as of 2005. - OT-64 SKOT-based Command vehicles. - 90
Amphibious vehicle
An amphibious vehicle , is a vehicle or craft, that is a means of transport, viable on land as well as on water – just like an amphibian....
armored personnel carrier (8x8
Eight-wheel drive
Eight-wheel drive, 8WD, or 8x8 is an eight-wheeled vehicle with a drivetrain that allows all eight wheels to receive power from the engine simultaneously.Some severe/extreme duty semi tractors may have this configuration...
), developed jointly by Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
and Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992...
(ČSSR
Czechoslovak Socialist Republic
The Czechoslovak Socialist Republic was the official name of Czechoslovakia from 1960 until end of 1989 , a Soviet satellite state of the Eastern Bloc....
) well into the 1960s.
History
OT-64 was intended to replace the halftrack OT-810, which was nearly identical to the German SdKfz 251SdKfz 251
The Sd.Kfz. 251 half-track was an armored fighting vehicle designed and first built by Hanomag company during World War II. The largest and best armored of the wartime half-tracks, the Sd.Kfz. 251 was designed to transport the panzergrenadiers of the German mechanized infantry corps into battle....
from World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
. The first prototype
Prototype
A prototype is an early sample or model built to test a concept or process or to act as a thing to be replicated or learned from.The word prototype derives from the Greek πρωτότυπον , "primitive form", neutral of πρωτότυπος , "original, primitive", from πρῶτος , "first" and τύπος ,...
was built in 1959. In 1961 the first sample series were built and starting from October 1963 the vehicles were produced in Lublin
Lublin
Lublin is the ninth largest city in Poland. It is the capital of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 350,392 . Lublin is also the largest Polish city east of the Vistula river...
, Poland by Fabryka Samochodów Ciężarowych
Fabryka Samochodów Ciezarowych
FSC is a large automotive factory established in Poland while it was part of the Soviet bloc. It was founded in 1950 and the first vehicle left its assembly line on November 7, 1951...
. Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992...
supplied the driveline components, i.e. the engine, transmission and axles.
The first production vehicles were delivered in 1964 to both the Polish Army and Czechoslovak Army
Czechoslovak People's Army
The Czechoslovak People's Army was the army of the Czechoslovak State from 1954 until 1990. On March 14, 1990 the Army's name was changed to the Czechoslovak Army removing adjective "People's" from the name. Since 1955 it was a member force of the Warsaw Pact.- Ground Forces :Ground troops were...
and many are still in use today. Both Polish and Czech units are gradually replaced by newer vehicles. Czech units are scheduled to be replaced between 2007 and 2012.
Technology

Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992...
. The engine was produced by Tatra
Tatra (car)
Tatra is a vehicle manufacturer in Kopřivnice, Czech Republic. The company was founded in 1850 as Schustala & Company later renamed Nesselsdorfer Wagenbau-Fabriksgesellschaft, a wagon and carriage manufacturer, and in 1897 produced the first motor car in central Europe, the Präsident. In 1918, it...
and the semiautomatic transmission(shift now,transfer gear by pushing clutch later) by Praga
Praga Hostivar
Praga is a manufacturing company based in Prague. In 2006, it was purchased by International Truck Alliance.- History :Praga was founded in 1907 to build motor cars. as a venture between Frantisek Ringhoffer and the First Czech-Moravian Machine Factory. Ringhoffer only stayed for one year and in...
. The armored hull and weapons were produced in Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
.
The OT-64 was the answer to the Soviet BTR-60
BTR-60
The BTR-60 is the first vehicle in a series of Soviet eight-wheeled armoured personnel carriers. It was developed in the late 1950s as a replacement for the BTR-152 and was seen first time in public in 1961...
. Contrary to this the OT-64 used a diesel set in place of a petrol engine. That diminished the danger of fire and at the same time increased the range. The main advantage in relation to the Russian counterpart was the full-armored interior. The entrance is at the rear of the vehicle via twin doors. The OT-64 was air-transportable and amphibious
Amphibious vehicle
An amphibious vehicle , is a vehicle or craft, that is a means of transport, viable on land as well as on water – just like an amphibian....
. For the amphibious
Amphibious vehicle
An amphibious vehicle , is a vehicle or craft, that is a means of transport, viable on land as well as on water – just like an amphibian....
drive the vehicle used two propellers installed at the back. The OT-64 had an NBC protection facility and night-vision equipment. It also has central inflation for all wheels which can be controlled by driver during a drive.
Several variants were built. Some OT-64 were re-equipped for air defense or built as tank hunters. The latter used the AT-3 Sagger
AT-3 Sagger
The 9K11 Malyutka is a Manual Command to Line-of-Sight wire-guided anti-tank guided missile developed in the Soviet Union. It was the first man-portable anti-tank guided missile of the Soviet Union and is probably the most widely produced ATGM of all time—with Soviet production peaking at...
missile as a weapon.
Service history
OT-64 SKOT entered service with Polish and Czechoslovak armies in 1963.It was produced until early 1970s. It still is in service with Poland, Czech Republic and Slovakia. OT-64 SKOT was also exported to eleven different countries (Algeria, Cambodia, India, Iraq, Libya, Morocco, Pakistan, Sierra Leone, Sudan, Syria, Uganda and Uruguay). A total number of vehicles produced for the Polish Army, the Czechoslovak Army and for export is 4,500.Czechoslovakia


- OT-64 - Original version, used in the APC role. Early models were unarmed but later the vehicle was fitted with a pintle-mounted 7.62 mm light machine gun or 12.7 mm DShK 1938/46DShKThe DShK 1938 is a Soviet heavy machine gun firing the 12.7x108mm cartridge. The weapon was also used as a heavy infantry machine gun, in which case it was frequently deployed with a two-wheeled mounting and a single-sheet armour-plate shield...
heavy machine gun. They used to be known in the West as respectively OT-64A and OT-64B. Some 12.7 mm DShK 1938/46DShKThe DShK 1938 is a Soviet heavy machine gun firing the 12.7x108mm cartridge. The weapon was also used as a heavy infantry machine gun, in which case it was frequently deployed with a two-wheeled mounting and a single-sheet armour-plate shield...
heavy machine gun armed OT-64 APCs had shields around the heavy machine gun mount.- OT-64 fitted with a small turret from OT-65A. However this one is armed with twin machine guns and doesn't have the 82mm T-21 "TarasniceTarasnice-Specifications:-Notes and references:* Hogg, Ian , Jane's Infantry Weapons 1984-85, London: Jane's Publishing Company Ltd., 1984.-External links:* *...
" recoilless gun. - DTP-64 (dilna technicke pomoci) - Czech repair version with tow bars, welding equipment and a hand operated crane with a capacity of 1 tonne. There were two sub-versions, namely the DTP-64/M for mechanized infantry units and the DTP-64/T for tank units. Photos
- OT-64 ZDRAV or ZDR-64 (zdravotni): ambulance.Photos
- OT-64A - Improved version fitted with BPU-1 turret from Soviet BRDM-2BRDM-2The BRDM-2 is an amphibious armoured patrol car used by Russia and the former Soviet Union. It was also known under designations BTR-40PB, BTR-40P-2 and GAZ 41-08...
armoured scout car which is armed with a 14.5 mm KPVTKPV heavy machine gunThe KPV-14.5 heavy machine gun is a Soviet designed 14.5x114mm-caliber heavy machine gun, which first entered service as an infantry weapon in 1949. In the 1960s the infantry version was taken out of production because it was too big and heavy...
heavy machine gun and 7.62 mm PKT coaxial machine gun. In Western sources, this version is often called OT-64C. In the late 1990s, some vehicles had the turret replaced by a pintle-mounted machine gun for peace keeping operations.Photos The OT-64A is used as the basis for several command vehicles (velitelsko štábní obrněný transportér) fitted with multiple radio sets, a 1 kW generator and an antenna mast:- VSOT-64/R2 R102 - Unarmed signals and command variant.
- VSOT-64/R2 R105 - Unarmed signals and command variant.
- VSOT-64/R2 R108 - Unarmed signals and command variant.
- VSOT-64/R2M - Signals and command variant with OT-64A's turret.Photos
- VSOT-64/R3 - Unarmed signals and command variant.
- VSOT-64/R3MT - Unarmed signals and command variant.Photos
- VSOT-64/R4MT - Unarmed signals and command variant.
- VSOT-64/R4RT - Unarmed signals and command variant.
- OT-64A fitted with the ATGM mounts on the turret sides.
- OT-64A fitted with the new turret with higher elevation for armament. Similar to Polish SKOT-2AP.
- OT-93 - Export version of the OT-64A with the original turret replaced by the one from the OT-65BRDM-1The BRDM-1 was an amphibious armored scout car used by Russia and the former Soviet Union...
M or OT-62B. The armament consists of a single 7.62mm machine-gun.Photos
- Cobra - Infantry combat vehicle version with a new turret with 30mm gun 2A42. Did not enter production
- OT-64 fitted with a small turret from OT-65A. However this one is armed with twin machine guns and doesn't have the 82mm T-21 "Tarasnice
Poland



- SKOT-1 - Early, unarmed model, similar to the OT-64.
- SKOT-1A - SKOT-1 fitted with a superstructure in the front of the troop compartment. The superstructure a large, two piece hatch.
- SKOT R-3 - Unarmed command vehicle used by regiment and higher command. It is equipped with 4 radios, 1 radio receiver, 1 microwave radio relay and 1 radiotelephone. The vehicle is operated by seven man crew.
- SKOT R-3M - Unarmed signals and command variant for combat engineer units.
- SKOT R-3Z - SKOT R-3 with modernized radio equipment which it includes the second microwave radio relay.
- SKOT R-4 - Unarmed command vehicle used by division and army command. It is equipped with 4 radios, 3 radio receivers and 3 radiotelephones.
- SKOT-WPT (wóz pogotowia technicznego) - Technical support vehicle with a light crane.
- SKOT S-260 Art (artyleryjski) - Artillery tractor and transport vehicle for ammunition and mortar or anti-tank squads.
- SKOT S-260 Inż (inżynieryjny) - Fitted with racks for anti-tank mines and used to tow mechanical mine layers or mine-clearing systems.
- SKOT-2 - SKOT-1A with pintle MG mount around the hatch of the superstructure. Two types of machine guns were fitted there, 7.62 mm light machine gun (first SGMT and later PKT) or 12.7 mm DShK 1938/46DShKThe DShK 1938 is a Soviet heavy machine gun firing the 12.7x108mm cartridge. The weapon was also used as a heavy infantry machine gun, in which case it was frequently deployed with a two-wheeled mounting and a single-sheet armour-plate shield...
heavy machine gun. Sides of the machine gun mount are protected with armour plates.- SKOT-2A - Polish designator for the version with the BRDM-2BRDM-2The BRDM-2 is an amphibious armoured patrol car used by Russia and the former Soviet Union. It was also known under designations BTR-40PB, BTR-40P-2 and GAZ 41-08...
turret which was designed in late 1960s. The vehicle is fitted with conical turret armed with 14.5 mm KPV heavy machine gunKPV heavy machine gunThe KPV-14.5 heavy machine gun is a Soviet designed 14.5x114mm-caliber heavy machine gun, which first entered service as an infantry weapon in 1949. In the 1960s the infantry version was taken out of production because it was too big and heavy...
and 7.62 mm PKT coaxial light machine gun on the top of the vehicle. Number of soldiers transported in the troop compartment went down from 18 to 10. In Western sources, this version is often called OT-64C.- SKOT 2AM - A small number of Polish SKOT-2A APCs was fitted with 9M14 Malyutka (AT-3 Sagger) ATGM launchers on the turret sides. The launchers were protected with armour plate or wire mesh. In the West, they were known as OT-64C(1A).
- SKOT R-2 - Command vehicle used by battalion and regiment command. It is equipped with 4 radios: R-112, R-113 and 2 R-105. The vehicle is operated by seven man crew.
- SKOT R-2AM - Unarmed command and fire control variant for artillery units.
- SKOT R-2M - Signals and command variant with SKOT-2A's turret.
- SKOT R-6 - Unarmed signals and command variant.
- SKOT-2AP - Polish modification with a new anti-aircraft WAT turret armed with 14.5 mm heavy machine gun. The turret had higher elevation for its armament and therefore could be used to fire at air targets. The turret has the new CGS-90 sight. This vehicle was known in the West as OT-64C(2).
- SKOT-2A - Polish designator for the version with the BRDM-2
- SKOT R-3 - Unarmed command vehicle used by regiment and higher command. It is equipped with 4 radios, 1 radio receiver, 1 microwave radio relay and 1 radiotelephone. The vehicle is operated by seven man crew.
- KTO WR-02 "Ryś"KTO RysThe KTO Ryś is 8x8 multi-role military vehicle produced by , former WZM no. 5...
(KTO stands for Kołowy Transporter Opancerzony - Wheeled Armoured personnel Carrier) (Ryś - LynxLynxA lynx is any of the four Lynx genus species of medium-sized wildcats. The name "lynx" originated in Middle English via Latin from Greek word "λύγξ", derived from the Indo-European root "*leuk-", meaning "light, brightness", in reference to the luminescence of its reflective eyes...
) - Heavily upgraded version with IVECOIvecoIveco, an acronym for Industrial Vehicle Corporation, originally an alliance of European commercial vehicle manufacturers such as Fiat , Unic and Magirus. Iveco is now an Italian truck, bus, and diesel engine manufacturer, based in Turin...
Cursor 8 engine. Work is performed by the 5th Military Mechanical Institute in PoznańPoznanPoznań is a city on the Warta river in west-central Poland, with a population of 556,022 in June 2009. It is among the oldest cities in Poland, and was one of the most important centres in the early Polish state, whose first rulers were buried at Poznań's cathedral. It is sometimes claimed to be...
.- KTO WR-02 "Ryś-2"KTO RysThe KTO Ryś is 8x8 multi-role military vehicle produced by , former WZM no. 5...
(KTO stands for Kołowy Transporter Opancerzony - Wheeled Armoured personnel Carrier) (Ryś-2 - LynxLynxA lynx is any of the four Lynx genus species of medium-sized wildcats. The name "lynx" originated in Middle English via Latin from Greek word "λύγξ", derived from the Indo-European root "*leuk-", meaning "light, brightness", in reference to the luminescence of its reflective eyes...
-2) - The export version of KTO WR-02 "Ryś".
- KTO WR-02 "Ryś-2"
- SKOT-1A - SKOT-1 fitted with a superstructure in the front of the troop compartment. The superstructure a large, two piece hatch.
Military operators


BTR-60
The BTR-60 is the first vehicle in a series of Soviet eight-wheeled armoured personnel carriers. It was developed in the late 1950s as a replacement for the BTR-152 and was seen first time in public in 1961...
. - 40, however probably less are fully operational as only 140 of Cambodia's 266 APCs are fully operational. All the OT-64 APCs have apparently gone to the Phnom Penh reserve force and some are used by military police. - 28 OT-64 APCs in service as of 1 January 2008. They are scheduled to be replaced by new vehicles between 2007 and 2012. - 300 - On beginning of the 1990s, SKOT's were gradually withdrawn from the Polish Army, and consists of around 300-400, in particular in the versions R-2AM/AMT (for artillery units) and R-3M, engineer's, school. The SKOT is being replaced by the KTO Rosomak
KTO Rosomak
The KTO Rosomak is 8x8 multi-role military vehicle produced by...
. There were 110 SKOT APCs and SKOT based vehicles in service as of 2005. - OT-64 SKOT-based Command vehicles. - 90
Civilian Operators
- At least 2 SKOT APC's one in Czech Republic and one in Poland have been modified an are used as firefighting vehicles
- Many SKOT APCs in Poland and the Czech Republic were sold to private owners who make sure they are in working condition and regularly show them on military enthusiast's meetings. Some private Czech OT-64's have number platesVehicle registration plateA vehicle registration plate is a metal or plastic plate attached to a motor vehicle or trailer for official identification purposes. The registration identifier is a numeric or alphanumeric code that uniquely identifies the vehicle within the issuing region's database...
and can travel on public roads.
Literature
- Philip Terwhitt, “Tank”, New Emperor Publishing House, complaint ford, 2005, ISBN 3-7043-3197-X
External links
- Czech MoD official site
- English website for Russian Military Trucks
- www.globalsecurity.org: OT-64 (SKOT) (English)
- Panzermodelkit site
- SKOT (Polish)
- KTO Ryś (Polish)
- bharat-rakshak site
- OT-64 (Czech)

